Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: Japanese grammar guide
-

Using 〜とおり in Japanese | My Language Classes
Understanding「〜とおり」 in Japanese
If you’re learning Japanese, you’ve probably come across the phrase 「〜とおり」 at some point. This grammar pattern is incredibly useful for expressing actions, instructions, and events happening “as expected,” “just as,” or “in the same way” as something else. Whether you’re following a recipe, describing an event, or giving precise instructions, 「〜とおり」 helps you communicate with accuracy and clarity.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn:
✅ The true meaning of 「〜とおり」 and why it’s so powerful
✅ How to use 「〜とおり」 correctly in everyday conversations
✅ Common mistakes learners make (and how to avoid them!)
✅ Real-life example sentences with Romaji, and English translationsBy the end of this lesson, you’ll not only understand 「〜とおり」 perfectly, but you’ll also be able to use it naturally, just like a native speaker.
Let’s dive in!
Common Expressions Using 「〜とおり」
Now that you understand the basics of 「〜とおり」, let’s explore 10 useful expressions where this grammar pattern naturally appears. These phrases are commonly used in daily conversations, instructions, and even formal speech.
1. 思ったとおり (Omotta tōri) – Just as I thought
📌 Example:
🔹 思ったとおり、テストは難しかった。
🔹 Omotta tōri, tesuto wa muzukashikatta.
🔹 (Just as I thought, the test was difficult.)2. 予想どおり (Yosō dōri) – As expected
📌 Example:
🔹 予想どおり、雨が降り始めた。
🔹 Yosō dōri, ame ga furi hajimeta.
🔹 (As expected, it started to rain.)3. 指示どおり (Shiji dōri) – According to instructions
📌 Example:
🔹 先生の指示どおりに、宿題をしました。
🔹 Sensei no shiji dōri ni, shukudai o shimashita.
🔹 (I did my homework according to the teacher’s instructions.)4. 予定どおり (Yotei dōri) – As planned
📌 Example:
🔹 旅行は予定どおりに進んでいます。
🔹 Ryokō wa yotei dōri ni susundeimasu.
🔹 (The trip is going as planned.)5. ルールどおり (Rūru dōri) – According to the rules
📌 Example:
🔹 試合はルールどおりに行われました。
🔹 Shiai wa rūru dōri ni okonawaremashita.
🔹 (The match was conducted according to the rules.)6. 予報どおり (Yohō dōri) – Just like the forecast said
📌 Example:
🔹 天気は予報どおりに晴れた。
🔹 Tenki wa yohō dōri ni hareta.
🔹 (The weather cleared up just like the forecast said.)7. 計画どおり (Keikaku dōri) – As per the plan
📌 Example:
🔹 プロジェクトは計画どおりに進んでいます。
🔹 Purojekuto wa keikaku dōri ni susundeimasu.
🔹 (The project is progressing as per the plan.)8. 約束どおり (Yakusoku dōri) – As promised
📌 Example:
🔹 約束どおり、明日会いましょう。
🔹 Yakusoku dōri, ashita aimashō.
🔹 (Let’s meet tomorrow as promised.)9. 本のとおり (Hon no tōri) – Just like the book says
📌 Example:
🔹 この料理は本のとおりに作りました。
🔹 Kono ryōri wa hon no tōri ni tsukurimashita.
🔹 (I made this dish just like the book says.)10. マニュアルのとおり (Manyuaru no tōri) – Following the manual
📌 Example:
🔹 マニュアルのとおりに設定してください。
🔹 Manyuaru no tōri ni settei shite kudasai.
🔹 (Please set it up according to the manual.)These 10 practical expressions will help you use 「〜とおり」 in real-life situations with confidence. Try practicing them in conversations and writing to make them feel natural!
Usage of 「〜とおり」
The grammar point 「〜とおり」 is highly versatile and used in various real-life situations. Below are the key scenarios where this expression is commonly applied:
1. Expressing “Just as Expected”
You can use 「〜とおり」 to show that something happened exactly as you predicted or expected.
✅ Example:
🔹 思ったとおり、試験は難しかった。
🔹 Omotta tōri, shiken wa muzukashikatta.
🔹 (Just as I thought, the exam was difficult.)
2. Following Instructions or Orders
When you need to indicate that something was done according to given instructions, rules, or commands, 「〜とおり」 is the perfect phrase to use.
✅ Example:
🔹 先生の指示どおりに宿題をやりました。
🔹 Sensei no shiji dōri ni shukudai o yarimashita.
🔹 (I did my homework according to the teacher’s instructions.)
3. Describing Plans and Predictions
If something happens as planned or as forecasted, 「〜とおり」 helps to express that the outcome matched the expectation.
✅ Example:
🔹 旅行は予定どおりに進んでいます。
🔹 Ryokō wa yotei dōri ni susundeimasu.
🔹 (The trip is going as planned.)✅ Example:
🔹 天気は予報どおりに晴れた。
🔹 Tenki wa yohō dōri ni hareta.
🔹 (The weather cleared up just like the forecast said.)
4. Performing Actions in the Same Manner
You can use 「〜とおり」 when instructing someone to follow a manual, book, or any set of instructions exactly as given.
✅ Example:
🔹 マニュアルのとおりに設定してください。
🔹 Manyuaru no tōri ni settei shite kudasai.
🔹 (Please set it up according to the manual.)✅ Example:
🔹 本のとおりに料理を作りました。
🔹 Hon no tōri ni ryōri o tsukurimashita.
🔹 (I made the dish exactly as written in the book.)
5. Describing Rules and Regulations
When something follows a set of rules, laws, or official guidelines, 「〜とおり」 can be used to describe adherence to them.
✅ Example:
🔹 試合はルールどおりに行われました。
🔹 Shiai wa rūru dōri ni okonawaremashita.
🔹 (The match was conducted according to the rules.)
6. Keeping Promises
When you want to emphasize that something was done as promised, you can use 「〜とおり」 to confirm that the commitment was fulfilled.
✅ Example:
🔹 約束どおりにお金を返しました。
🔹 Yakusoku dōri ni okane o kaeshimashita.
🔹 (I returned the money as promised.)
7. Explaining Results Matching Expectations
When an outcome perfectly matches an expectation or prediction, 「〜とおり」 expresses that sense of alignment.
✅ Example:
🔹 予想どおり、彼が試合に勝った。
🔹 Yosō dōri, kare ga shiai ni katta.
🔹 (As expected, he won the match.)
8. Giving Step-by-Step Instructions
If you need to explain how to do something in a step-by-step manner, you can use 「〜とおり」 to ensure that actions are followed precisely.
✅ Example:
🔹 私の言うとおりにしてください。
🔹 Watashi no iu tōri ni shite kudasai.
🔹 (Please do exactly as I say.)These are the most common situations where 「〜とおり」 is used in Japanese. This grammar point is essential for daily communication, making instructions clear, and expressing expectations accurately.
Conjugation of 「〜とおり」 with Verb
The grammar point 「〜とおり」 can be used with verbs in different forms. Below is a complete breakdown of how to use it with:
- Dictionary Form (Plain Form) → (Verb as is)
- Past Form (Ta-form) → (Verb in た-form)
- Stem Form (Masu-stem for ます verbs) → (Verb without ます)
1. Conjugation of 「〜とおり」 with Different Verb Groups
Verb Group Dictionary Form (Plain Form) + とおり Past Form (Ta-form) + とおり Stem Form (Masu-stem) + とおり Group 1 (う-Verbs) 読むとおり (Yomu tōri) → (As one reads…) 読んだとおり (Yonda tōri) → (As one read…) 読みとおり (Yomi tōri) → (As one is reading…) Group 2 (る-Verbs) 見るとおり (Miru tōri) → (As one sees…) 見たとおり (Mita tōri) → (As one saw…) 見とおり (Mi tōri) → (As one is seeing…) Group 3 (Irregular Verbs) する通り (Suru tōri) → (As one does…) 来るとおり (Kuru tōri) → (As one comes…) したとおり (Shita tōri) → (As one did…) 来たとおり (Kita tōri) → (As one came…) しとおり (Shi tōri) → (As one is doing…) 来とおり (Ki tōri) → (As one is coming…)
2. Example Sentences for Each Verb Group in Different Forms
📌 Group 1 (う-Verbs) Example: 「書く」 (kaku – to write)
✅ Dictionary Form:
🔹 先生が書くとおりにメモしてください。
🔹 Sensei ga kaku tōri ni memo shite kudasai.
🔹 (Please take notes exactly as the teacher writes.)✅ Past Form (Ta-form):
🔹 先生が書いたとおりに答えを書いてください。
🔹 Sensei ga kaita tōri ni kotae o kaite kudasai.
🔹 (Please write the answer exactly as the teacher wrote.)✅ Stem Form (Masu-stem):
🔹 先生の書きとおりに書けば大丈夫です。
🔹 Sensei no kaki tōri ni kakeba daijōbu desu.
🔹 (If you write as the teacher is writing, you’ll be fine.)
📌 Group 2 (る-Verbs) Example: 「食べる」 (taberu – to eat)
✅ Dictionary Form:
🔹 レシピに書いてあるとおりに食べると美味しいです。
🔹 Reshipi ni kaite aru tōri ni taberu to oishii desu.
🔹 (It’s delicious if you eat it as written in the recipe.)✅ Past Form (Ta-form):
🔹 レシピのとおりに食べたら、美味しかった。
🔹 Reshipi no tōri ni tabetara, oishikatta.
🔹 (It was delicious when I ate it as per the recipe.)✅ Stem Form (Masu-stem):
🔹 レシピの食べとおりに作れば大丈夫です。
🔹 Reshipi no tabe tōri ni tsukureba daijōbu desu.
🔹 (If you cook it as you are eating, it will be fine.)
📌 Group 3 (Irregular Verbs) Example: 「する」 (suru – to do) & 「来る」 (kuru – to come)
✅ Dictionary Form:
🔹 彼がする通りにやってください。
🔹 Kare ga suru tōri ni yatte kudasai.
🔹 (Please do it just as he does.)✅ Past Form (Ta-form):
🔹 彼がしたとおりにやれば成功します。
🔹 Kare ga shita tōri ni yareba seikō shimasu.
🔹 (If you do it as he did, you will succeed.)✅ Stem Form (Masu-stem):
🔹 彼のしとおりに練習すれば上手になります。
🔹 Kare no shi tōri ni renshū sureba jōzu ni narimasu.
🔹 (If you practice as he is doing, you will improve.)
📌 Example with 「来る」 (Kuru – to come)
✅ Dictionary Form:
🔹 先生が来るとおりに準備してください。
🔹 Sensei ga kuru tōri ni junbi shite kudasai.
🔹 (Prepare as the teacher comes.)✅ Past Form (Ta-form):
🔹 先生が来たとおりに、試験が始まります。
🔹 Sensei ga kita tōri ni, shiken ga hajimarimasu.
🔹 (As the teacher arrived, the exam started.)✅ Stem Form (Masu-stem):
🔹 先生の来とおりに行動してください。
🔹 Sensei no ki tōri ni kōdō shite kudasai.
🔹 (Act as the teacher is coming.)By mastering the different verb conjugations with 「〜とおり」, you can express actions that are done exactly as expected, predicted, or instructed. Whether you are following a manual, repeating someone’s actions, or verifying if something happened as anticipated, this grammar pattern is essential for clear and natural Japanese communication!
Conjugation of 「〜とおり」 with Nouns and Adjectives
In addition to verbs, 「〜とおり」 can also be used with nouns and adjectives to express “as expected,” “just like,” or “exactly as.” Below is a detailed breakdown of how to use 「〜とおり」 with:
- Nouns
- い-Adjectives
- な-Adjectives
1. Conjugation of 「〜とおり」 with Nouns
📌 Rule for Nouns:
For nouns, 「の」 is added before 「とおり」 to link the two words.
🔹 Noun + の + とおり → (As per [Noun], Just like [Noun])Noun Example Sentence Romaji English Translation 予想 (yosou) – Expectation 予想のとおり、試験は難しかった。 Yosou no tōri, shiken wa muzukashikatta. As expected, the exam was difficult. 説明 (setsumei) – Explanation 先生の説明のとおりにやってください。 Sensei no setsumei no tōri ni yatte kudasai. Please do it exactly as explained by the teacher. 計画 (keikaku) – Plan 計画のとおりに進めます。 Keikaku no tōri ni susumemasu. We will proceed according to the plan. 指示 (shiji) – Instructions 指示のとおりに行動してください。 Shiji no tōri ni kōdō shite kudasai. Please act as per the instructions. 地図 (chizu) – Map 地図のとおりに行けば、迷いません。 Chizu no tōri ni ikeba, mayoimasen. If you follow the map, you won’t get lost.
2. Conjugation of 「〜とおり」 with い-Adjectives
📌 Rule for い-Adjectives:
Since い-adjectives cannot directly attach to 「とおり」, they are converted into their noun form by adding 「こと」 before 「とおり」.
🔹 い-Adjective + こと + とおり → (As [Adjective] as expected)い-Adjective Example Sentence Romaji English Translation 簡単 (kantan) – Simple 思ったこととおり、問題は簡単だった。 Omotta koto tōri, mondai wa kantan datta. As I thought, the problem was simple. 難しい (muzukashii) – Difficult 聞いたこととおり、その試験は難しい。 Kiita koto tōri, sono shiken wa muzukashii. As I heard, that exam is difficult. 楽しい (tanoshii) – Fun 予想したこととおり、旅行はとても楽しかった。 Yosou shita koto tōri, ryokō wa totemo tanoshikatta. As I expected, the trip was really fun. 正しい (tadashii) – Correct あなたの言ったこととおり、それは正しかった。 Anata no itta koto tōri, sore wa tadashikatta. As you said, that was correct. 高い (takai) – Expensive 店員が言ったこととおり、その時計は高かった。 Ten’in ga itta koto tōri, sono tokei wa takakatta. As the clerk said, that watch was expensive.
3. Conjugation of 「〜とおり」 with な-Adjectives
📌 Rule for な-Adjectives:
Since な-adjectives function like nouns, they follow the same rule as nouns and use 「の」 before 「とおり」.
🔹 な-Adjective + な + の + とおり → (As [Adjective] as expected)な-Adjective Example Sentence Romaji English Translation 静か (shizuka) – Quiet 彼の部屋は聞いたのとおり、静かだった。 Kare no heya wa kiita no tōri, shizuka datta. As I heard, his room was quiet. 有名 (yuumei) – Famous 彼女は写真のとおり、有名な人です。 Kanojo wa shashin no tōri, yūmei na hito desu. As in the photo, she is a famous person. 便利 (benri) – Convenient このアプリは説明のとおり、便利ですね。 Kono apuri wa setsumei no tōri, benri desu ne. As described, this app is convenient. 元気 (genki) – Energetic あなたの言ったのとおり、彼は元気だった。 Anata no itta no tōri, kare wa genki datta. As you said, he was energetic. 親切 (shinsetsu) – Kind その人は紹介のとおり、とても親切だった。 Sono hito wa shōkai no tōri, totemo shinsetsu datta. As introduced, that person was very kind. By learning how to use 「〜とおり」 with nouns, い-adjectives, and な-adjectives, you can express confirmation, expectations, and precise descriptions in various situations.
Got it! Here’s the Grammar Rules section with the “How to Use 「〜とおり」 with Different Word Types” part removed.
Grammar Rules of 「〜とおり」
The 「〜とおり」 grammar structure is used to express that something happens exactly as expected, planned, instructed, or perceived. Below are all the essential grammar rules related to 「〜とおり」, along with clear explanations and examples.
1️⃣ Basic Sentence Structure
「〜とおり」 is commonly used in the following pattern:
🔹 [Action/Noun] + とおり (に) + [Main Clause]
(Do something exactly as [Action/Noun] describes.)Examples:
✅ 予想のとおり、試験は難しかった。
(Yosou no tōri, shiken wa muzukashikatta.)
➡️ As expected, the exam was difficult.✅ 先生が言ったとおりに、宿題をしました。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni, shukudai o shimashita.)
➡️ I did my homework exactly as the teacher said.
2️⃣ 「〜とおり」 vs. 「〜のとおり」
The choice between 「〜とおり」 and 「〜のとおり」 depends on the word before it.
Word Before 「とおり」 Grammar Rule Verbs Use dictionary form (plain form) or past form (た-form) before 「とおり」. Nouns Attach 「の」 before 「とおり」. Examples:
✅ 計画のとおりに進めます。
(Keikaku no tōri ni susumemasu.)
➡️ We will proceed according to the plan. (Noun + のとおり)✅ 聞いたとおりにやってください。
(Kiita tōri ni yatte kudasai.)
➡️ Please do it as you heard. (Verb in past form + とおり)
3️⃣ Optional Use of 「に」 after 「とおり」
Sometimes, 「に」 is added after 「とおり」, depending on the sentence structure.
Form Example Sentence Romaji Translation Without に 予想のとおり、彼は合格した。 Yosou no tōri, kare wa goukaku shita. As expected, he passed. With に 先生が言ったとおりにやりました。 Sensei ga itta tōri ni yarimashita. I did it exactly as the teacher said. ✅ 「に」 is optional if the meaning is still clear without it.
✅ 「に」 is required when followed by a verb, such as やる (do), 行く (go), 書く (write), 話す (speak).
4️⃣ 「〜とおり」 vs. Similar Expressions
Grammar Point Meaning Example Sentence Translation 〜とおり “As expected / As instructed” 先生が言ったとおりにやってください。 Do it as the teacher said. 〜ように “So that / In order to” 風邪を引かないように、マスクをしてください。 Wear a mask so that you don’t catch a cold. 〜まま “As is / Leave as is” 電気をつけたまま寝てしまった。 I fell asleep with the lights on. ✅ 「〜とおり」 focuses on following instructions, plans, or expectations.
✅ 「〜ように」 focuses on purpose or results.
✅ 「〜まま」 describes unchanged states.
Things to Keep in Mind When Using 「〜とおり」
Understanding 「〜とおり」 is straightforward, but there are a few tricky points and exceptions to be aware of. Below are some important rules, nuances, and mistakes to avoid when using this grammar structure.
1️⃣ Be Careful with 「に」 After 「とおり」
- The particle 「に」 is sometimes added after 「とおり」, but not always.
- 「に」 is required when a verb follows 「とおり」.
- 「に」 is optional when there is no verb immediately after 「とおり」.
Examples:
✅ 先生が言ったとおりにやってください。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni yatte kudasai.)
➡️ Do it exactly as the teacher said. (Verb follows → に is necessary)✅ 予想のとおり、彼は合格した。
(Yosou no tōri, kare wa goukaku shita.)
➡️ As expected, he passed. (No verb immediately after → に is not used)
2️⃣ 「〜とおり」 Changes to 「〜どおり」 in Some Cases
- When attached to certain nouns, 「とおり」 becomes 「どおり」 instead.
- This happens mainly with common set expressions.
Examples:
✅ 予定どおりに試験が終わった。
(Yotei dōri ni shiken ga owatta.)
➡️ The exam ended as scheduled. (Instead of 予定のとおり, we use 予定どおり.)✅ 指示どおりに動いてください。
(Shiji dōri ni ugoite kudasai.)
➡️ Move according to the instructions.🔹 Common nouns that use 「どおり」 instead of 「とおり」:
- 予定どおり (As scheduled)
- 指示どおり (As instructed)
- 思ったどおり (As I thought)
- 希望どおり (As hoped)
💡 Tip: If a noun directly follows 「とおり」, check if it has a common どおり form!
3️⃣ Difference Between 「〜とおり」 and 「〜まま」
🔹 「〜とおり」 → Focuses on following instructions or expectations.
🔹 「〜まま」 → Focuses on keeping something unchanged.Examples:
✅ 先生が言ったとおりにやりました。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni yarimashita.)
➡️ I did it exactly as the teacher said. (Followed the instructions)✅ 電気をつけたまま寝てしまった。
(Denki o tsuketa mama nete shimatta.)
➡️ I fell asleep with the lights on. (State remained unchanged)💡 Tip: If you’re following a plan or instructions, use 「とおり」.
If you’re keeping a condition unchanged, use 「まま」 instead.
4️⃣ Be Careful with Negative Forms
- When using 「〜とおり」 in negative sentences, be careful with meaning.
- If the first clause is negative, the second clause also follows the negative meaning.
Examples:
✅ 思ったとおり、彼は来なかった。
(Omotta tōri, kare wa konakatta.)
➡️ Just as I thought, he didn’t come.✅ 聞いたとおりにしなかったので、失敗しました。
(Kiita tōri ni shinakatta node, shippai shimashita.)
➡️ I failed because I didn’t do it as I was told.💡 Tip: If using 「〜とおり」 in a negative sentence, make sure the meaning is logical!
5️⃣ Difference Between 「〜ように」 and 「〜とおり」
Grammar Meaning Example Translation 〜とおり As expected / instructed 先生が言ったとおりに書いてください。 Write as the teacher said. 〜ように So that / In order to 風邪を引かないようにマスクをしてください。 Wear a mask so that you don’t catch a cold. 💡 Tip: If you’re talking about following instructions → Use 「〜とおり」.
If you’re talking about purpose or goals → Use 「〜ように」 instead.
6️⃣ Watch Out for Particle Changes When Using 「〜のとおり」
- When a noun comes before 「〜とおり」, use 「の」.
- When a verb comes before 「〜とおり」, do not use 「の」.
Examples:
✅ 先生の指示のとおりにやってください。
(Sensei no shiji no tōri ni yatte kudasai.)
➡️ Do it according to the teacher’s instructions. (Noun → Use の)✅ 先生が言ったとおりにやってください。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni yatte kudasai.)
➡️ Do it exactly as the teacher said. (Verb → No の)💡 Tip: If the phrase before 「とおり」 is a noun, always use 「の」!
7️⃣ 「〜とおりにする」 vs. 「〜とおりになる」
- 「〜とおりにする」 → You actively do something as planned.
- 「〜とおりになる」 → Something naturally happens as expected.
Examples:
✅ 先生が言ったとおりにしました。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni shimashita.)
➡️ I did exactly as the teacher said. (You actively followed instructions)✅ 予想のとおりになった。
(Yosou no tōri ni natta.)
➡️ It turned out just as expected. (Happened naturally)💡 Tip: If you’re taking action, use 「する」.
If something happens naturally, use 「なる」.
Example Sentences
Here are some example sentences using 「〜とおり」to help you understand its real-life usage.
Following Instructions or Expectations
- 先生が言ったとおりに宿題をしました。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni shukudai o shimashita.)
➡️ I did my homework exactly as the teacher said. - レシピのとおりに料理を作りました。
(Reshipi no tōri ni ryōri o tsukurimashita.)
➡️ I cooked according to the recipe. - 説明書のとおりにパソコンを設定しました。
(Setsumeisho no tōri ni pasokon o settei shimashita.)
➡️ I set up the computer according to the manual. - 先生の指示のとおりに動いてください。
(Sensei no shiji no tōri ni ugoite kudasai.)
➡️ Please move according to the teacher’s instructions. - 私が言ったとおりにやれば、大丈夫です。
(Watashi ga itta tōri ni yareba, daijōbu desu.)
➡️ If you do it as I said, it will be fine.
Describing Things That Happened as Expected
- 予想のとおり、試験は難しかった。
(Yosou no tōri, shiken wa muzukashikatta.)
➡️ As expected, the exam was difficult. - 思ったとおりの結果でした。
(Omotta tōri no kekka deshita.)
➡️ The result was just as I thought. - 天気予報のとおりに雨が降りました。
(Tenki yohō no tōri ni ame ga furimashita.)
➡️ It rained just as the weather forecast predicted. - 彼は私が考えたとおりの人でした。
(Kare wa watashi ga kangaeta tōri no hito deshita.)
➡️ He was exactly the kind of person I thought he would be. - 噂のとおり、そのレストランの料理は美味しかった。
(Uwasa no tōri, sono resutoran no ryōri wa oishikatta.)
➡️ As the rumors said, the food at that restaurant was delicious.
Following Movements, Plans, or Changes
- 地図のとおりに進んでください。
(Chizu no tōri ni susunde kudasai.)
➡️ Please follow the map to proceed. - スケジュールのとおりに会議を進めます。
(Sukejūru no tōri ni kaigi o susumemasu.)
➡️ We will proceed with the meeting according to the schedule. - 計画どおりに仕事が進んでいます。
(Keikaku dōri ni shigoto ga susunde imasu.)
➡️ The work is progressing as planned. - マニュアルのとおりにソフトをインストールしてください。
(Manyuaru no tōri ni sofuto o insutōru shite kudasai.)
➡️ Please install the software according to the manual. - 道のとおりに歩けば、駅に着きます。
(Michi no tōri ni arukeba, eki ni tsukimasu.)
➡️ If you walk along the road, you will reach the station.
Expressing Personal Thoughts and Opinions
- あなたが言ったとおり、日本の夏はとても暑いですね。
(Anata ga itta tōri, Nihon no natsu wa totemo atsui desu ne.)
➡️ As you said, summers in Japan are very hot. - 映画は期待したとおりに面白かったです。
(Eiga wa kitai shita tōri ni omoshirokatta desu.)
➡️ The movie was as interesting as I expected. - 彼の話は聞いたとおりに正しかった。
(Kare no hanashi wa kiita tōri ni tadashikatta.)
➡️ His story was correct just as I had heard. - 彼女の料理は評判のとおりに美味しかった。
(Kanojo no ryōri wa hyōban no tōri ni oishikatta.)
➡️ Her cooking was as delicious as the reviews said. - 私が想像したとおりの素晴らしい景色でした。
(Watashi ga sōzō shita tōri no subarashii keshiki deshita.)
➡️ It was a magnificent view, just as I had imagined.
These example sentences cover different contexts where 「〜とおり」 is used. Let me know in comment if you want more examples! 😊
Exercise: Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentences using 「〜とおり」 appropriately. The verb, noun, or adjective that needs to be conjugated is given in parentheses (bold).
- 先生が ______ に答えてください。(言う)
- ______ に料理を作りました。(レシピ)
- ______ にパソコンを設定しました。(説明書)
- 試験は ______ 、難しかった。(予想する)
- 雨が ______ に降りました。(天気予報)
- ______ に進んでください。(地図)
- 先生の指示の ______ に動いてください。(とおり)
- 彼女の料理は ______ に美味しかった。(評判)
- 彼は私が ______ の人でした。(考える)
- あなたが ______ 、彼は本当に親切な人ですね。(言う)
- ______ に仕事が進んでいます。(計画)
- ______ に歩けば、駅に着きます。(道)
- 私が ______ の結果でした。(思う)
- 私が ______ の素晴らしい景色でした。(想像する)
- 彼の話は ______ に正しかった。(聞く)
- ______ にソフトをインストールしてください。(マニュアル)
- ______ に会議を進めます。(スケジュール)
- 先生が ______ にやれば、大丈夫です。(言う)
- 映画は ______ に面白かったです。(期待する)
- ______ 、そのレストランの料理は美味しかった。(噂)
Answers
Here are the correct answers along with Romaji and English translations.
- 先生が 言ったとおり に答えてください。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni kotaete kudasai.)
➡️ Please answer as the teacher said. - レシピのとおり に料理を作りました。
(Reshipi no tōri ni ryōri o tsukurimashita.)
➡️ I cooked according to the recipe. - 説明書のとおり にパソコンを設定しました。
(Setsumeisho no tōri ni pasokon o settei shimashita.)
➡️ I set up the computer according to the manual. - 試験は 予想したとおり 、難しかった。
(Shiken wa yosou shita tōri, muzukashikatta.)
➡️ The exam was as difficult as predicted. - 雨が 天気予報のとおり に降りました。
(Ame ga tenki yohō no tōri ni furimashita.)
➡️ It rained just as the weather forecast predicted. - 地図のとおり に進んでください。
(Chizu no tōri ni susunde kudasai.)
➡️ Please follow the map to proceed. - 先生の指示の とおり に動いてください。
(Sensei no shiji no tōri ni ugoite kudasai.)
➡️ Please move according to the teacher’s instructions. - 彼女の料理は 評判のとおり に美味しかった。
(Kanojo no ryōri wa hyōban no tōri ni oishikatta.)
➡️ Her cooking was as delicious as the reviews said. - 彼は私が 考えたとおり の人でした。
(Kare wa watashi ga kangaeta tōri no hito deshita.)
➡️ He was exactly the kind of person I thought he would be. - あなたが 言ったとおり 、彼は本当に親切な人ですね。
(Anata ga itta tōri, kare wa hontō ni shinsetsu na hito desu ne.)
➡️ As you said, he is really a kind person. - 計画どおり に仕事が進んでいます。
(Keikaku dōri ni shigoto ga susunde imasu.)
➡️ The work is progressing as planned. - 道のとおり に歩けば、駅に着きます。
(Michi no tōri ni arukeba, eki ni tsukimasu.)
➡️ If you walk along the road, you will reach the station. - 私が 思ったとおり の結果でした。
(Watashi ga omotta tōri no kekka deshita.)
➡️ The result was just as I thought. - 私が 想像したとおり の素晴らしい景色でした。
(Watashi ga sōzō shita tōri no subarashii keshiki deshita.)
➡️ It was a magnificent view, just as I had imagined. - 彼の話は 聞いたとおり に正しかった。
(Kare no hanashi wa kiita tōri ni tadashikatta.)
➡️ His story was correct just as I had heard. - マニュアルのとおり にソフトをインストールしてください。
(Manyuaru no tōri ni sofuto o insutōru shite kudasai.)
➡️ Please install the software according to the manual. - スケジュールのとおり に会議を進めます。
(Sukejūru no tōri ni kaigi o susumemasu.)
➡️ We will proceed with the meeting according to the schedule. - 先生が 言ったとおり にやれば、大丈夫です。
(Sensei ga itta tōri ni yareba, daijōbu desu.)
➡️ If you do it as the teacher said, it will be fine. - 映画は 期待したとおり に面白かったです。
(Eiga wa kitai shita tōri ni omoshirokatta desu.)
➡️ The movie was as interesting as I expected. - 噂どおり 、そのレストランの料理は美味しかった。
(Uwasa dōri, sono resutoran no ryōri wa oishikatta.)
➡️ As the rumors said, the food at that restaurant was delicious.
This exercise helps reinforce 「〜とおり」 usage with different types of words.
Summary of 「〜とおり」
Here’s a quick recap of the key points covered in this blog:
- Meaning & Usage:
- 「〜とおり」 is used to express “as, just as, according to” in Japanese.
- It conveys that something happens exactly as expected, planned, or instructed.
- Common Sentence Structures:
- Verb (Dictionary/Past form) + とおり → As (someone) does/did
- Noun + のとおり → According to (noun)
- Noun + どおり → As (noun) states/shows
- Adjective (な/い) + とおり → Just as (adjective) describes
- Situations Where 「〜とおり」 is Used:
- Following instructions (マニュアルのとおりに設定する – Set it up as per the manual.)
- Predictions coming true (予想したとおり、試験は難しかった – As expected, the test was difficult.)
- Following someone’s words (先生が言ったとおりにする – Do as the teacher said.)
- Describing something as imagined (想像したとおりの景色 – A view just as imagined.)
- Key Considerations:
- 「〜とおり」 can be used with verbs, nouns, and adjectives, but the structure changes slightly.
- Noun + のとおり and Noun + どおり are interchangeable in many cases, but どおり is more commonly used with set phrases.
- Verb + とおり requires proper conjugation, especially for past and dictionary forms.
- Be mindful of the context – it should indicate similarity, accuracy, or following a reference.
- By mastering 「〜とおり」, you can express instructions, expectations, and confirmations naturally in Japanese. Keep practicing, and soon, using this grammar pattern will feel effortless!
Mastering 「〜とおり」 is essential for expressing actions, expectations, and results accurately in Japanese. Whether you’re following instructions, describing events as predicted, or comparing reality with expectations, this grammar structure allows you to communicate with clarity and precision.
By understanding its different forms—when used with verbs, nouns, and adjectives—you can naturally incorporate it into daily conversations and written Japanese. The more you practice, the easier it becomes to use 「〜とおり」 effortlessly, just like native speakers do.
So, keep practicing with real-life examples, listen to how native speakers use it, and don’t hesitate to try it in your own sentences. With time and effort, you’ll be able to use 「〜とおり」 just as fluently as you imagined! 🚀🔥
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊
-
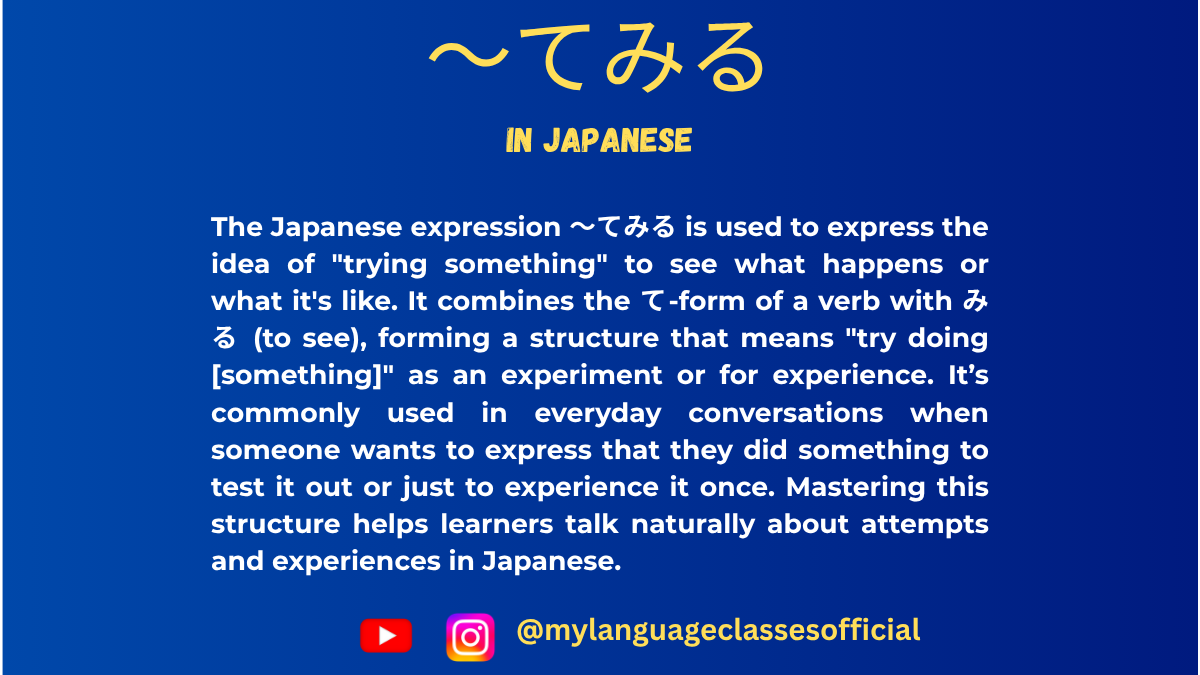
Using 〜てみる in Japanese | My Language Classes
Mastering 〜てみる in Japanese
If you’re learning Japanese, you’ve likely come across the phrase 〜てみる (te miru). This little-known but essential grammar point is a game-changer for expressing curiosity, experimentation, or trying something new.
In this extensive guide, we’ll reveal everything you need to know about 〜てみる, including its meaning, usage, and mind-blowing examples that will take your Japanese to the next level. Don’t miss out on this must-know Japanese grammar point—here’s why it’s so important!
What is 〜てみる in Japanese?
〜てみる is a Japanese grammar structure that combines the te-form of a verb with the auxiliary verb みる (miru), which means “to see” or “to try.” Together, 〜てみる translates to “try to do something” or “give something a try.” It’s used when you want to express the idea of experimenting with an action or attempting something for the first time.
For example:
- 食べてみる (tabete miru) – Try to eat / Give eating a try.
- 読んでみる (yonde miru) – Try to read / Give reading a try.
This structure is incredibly versatile and can be used in both casual and formal contexts. Whether you’re trying new food, testing a new skill, or experimenting with a hobby, 〜てみる is your go-to expression.
How to Use 〜てみる: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Conjugate the Verb into its Te-Form
To use 〜てみる, you first need to conjugate the verb into its te-form. Here’s a quick refresher on how to do that:
- Group 1 (U-verbs): Change the final -u sound to -te or -de (e.g., 書く → 書いて, 飲む → 飲んで).
- Group 2 (Ru-verbs): Replace る with て (e.g., 食べる → 食べて).
- Irregular Verbs: する → して, 来る → 来て (きて).
Step 2: Add みる
Once you have the te-form, simply add みる to the end of the verb. For example:
- 見る (miru) → 見てみる (mite miru) – Try to watch.
- 作る (tsukuru) → 作ってみる (tsukutte miru) – Try to make.
Step 3: Adjust for Politeness
In casual conversations, 〜てみる is perfectly fine. However, in formal situations, you can use 〜てみます (te mimasu) to sound more polite. For example:
- 食べてみます (tabete mimasu) – I will try to eat.
When to Use 〜てみる
1. Trying Something New
〜てみる is often used when you’re trying something for the first time. It conveys a sense of curiosity or experimentation.
- Example: この料理を食べてみたいです。
Romaji: Kono ryouri o tabete mitai desu.
Translation: I want to try this dish.
2. Testing an Idea or Hypothesis
You can also use 〜てみる to test an idea or see how something works.
- Example: この方法を試してみましょう。
Romaji: Kono houhou o tameshite mimashou.
Translation: Let’s try this method.
3. Encouraging Someone to Try Something
〜てみる is great for encouraging others to give something a try.
- Example: このゲームをやってみて!
Romaji: Kono geemu o yatte mite!
Translation: Try playing this game!
Nuances of 〜てみる vs. Other “Try” Expressions
〜てみる vs. 〜ようとする
While 〜てみる means “to try something to see how it is,” 〜ようとする means “to attempt to do something.”
- Example:
- 食べてみる (tabete miru) – Try eating (to see how it tastes).
- 食べようとする (tabeyou to suru) – Attempt to eat (but might not succeed).
〜てみる vs. 〜てみせる
〜てみせる means “to try something to show someone else.”
- Example:
- やってみる (yatte miru) – Try doing something.
- やってみせる (yatte miseru) – Try doing something to show someone.
Negative and Past Tense Forms of 〜てみる
Negative Form: 〜てみない
Use 〜てみない to say “not try” or 〜てみなかった to say “didn’t try.”
- Example:
- 食べてみない (tabete minai) – I won’t try eating.
- 食べてみなかった (tabete minakatta) – I didn’t try eating.
Past Tense: 〜てみた
Use 〜てみた to say “tried.”
- Example:
- 食べてみた (tabete mita) – I tried eating.
Casual vs. Polite Forms
Casual: 〜てみる
- Example: やってみる (yatte miru) – I’ll try doing it.
Polite: 〜てみます
- Example: やってみます (yatte mimasu) – I will try doing it.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake 1: Confusing 〜てみる with 〜ておく
- Incorrect: 食べておく (tabete oku) – Eat in advance.
- Correct: 食べてみる (tabete miru) – Try eating.
Mistake 2: Using 〜てみる for Future Intentions
- Incorrect: 明日、食べてみる (ashita, tabete miru) – Tomorrow, I’ll try eating.
- Correct: 明日、食べてみたい (ashita, tabete mitai) – Tomorrow, I want to try eating.
Advanced Usage in Compound Sentences
With Conditionals (〜たら)
- Example: 食べてみたら、美味しかった (tabete mitara, oishikatta) – When I tried eating it, it was delicious.
With Conjunctions (〜ので、〜けど)
- Example: やってみたけど、難しかった (yatte mita kedo, muzukashikatta) – I tried doing it, but it was hard.
Cultural Context
In Japanese culture, 〜てみる is often used when trying new foods, activities, or experiences.
- Example: 日本の温泉に入ってみたい (Nihon no onsen ni haitte mitai) – I want to try entering a Japanese hot spring.
Example Sentences: 〜てみる in Action
Here are ten jaw-dropping example sentences that showcase the versatility of 〜てみる. Each sentence includes romaji and English translation to help you master this grammar point.
- この本を読んでみました。
Romaji: Kono hon o yonde mimashita.
Translation: I tried reading this book. - 新しいレストランに行ってみたい。
Romaji: Atarashii resutoran ni itte mitai.
Translation: I want to try going to the new restaurant. - このシャツを着てみてもいいですか?
Romaji: Kono shatsu o kite mite mo ii desu ka?
Translation: Can I try on this shirt? - 日本語で話してみてください。
Romaji: Nihongo de hanashite mite kudasai.
Translation: Please try speaking in Japanese. - この薬を飲んでみたら、元気になりました。
Romaji: Kono kusuri o nonde mitara, genki ni narimashita.
Translation: After trying this medicine, I felt better. - 彼のアドバイスを聞いてみました。
Romaji: Kare no adobaisu o kiite mimashita.
Translation: I tried listening to his advice. - このアプリを使ってみたら、便利でした。
Romaji: Kono apuri o tsukatte mitara, benri deshita.
Translation: When I tried using this app, it was convenient. - この映画を見てみたいと思っています。
Romaji: Kono eiga o mite mitai to omotte imasu.
Translation: I’m thinking of trying to watch this movie. - この方法を試してみたら、成功しました。
Romaji: Kono houhou o tameshite mitara, seikou shimashita.
Translation: When I tried this method, it worked. - このゲームをやってみたら、面白かったです。
Romaji: Kono geemu o yatte mitara, omoshirokatta desu.
Translation: When I tried playing this game, it was fun.
Fill in the Blanks: Test Your Knowledge
Now that you’ve learned about 〜てみる, it’s time to test your skills! Fill in the blanks with the correct form of 〜てみる.
- このケーキを__。 (食べる)
- あの映画を__。 (見る)
- 新しいカフェに__。 (行く)
- このシャツを__。 (着る)
- 日本語で__。 (話す)
- この方法を__。 (試す)
- 彼のアドバイスを__。 (聞く)
- このアプリを__。 (使う)
- この本を__。 (読む)
- このゲームを__。 (やる)
Answers to Fill in the Blanks
- 食べてみる
- 見てみる
- 行ってみる
- 着てみる
- 話してみる
- 試してみる
- 聞いてみる
- 使ってみる
- 読んでみる
- やってみる
Why 〜てみる is a Must-Know Grammar Point
Mastering 〜てみる is essential for anyone looking to achieve fluency in Japanese. It’s a versatile and practical grammar point that allows you to express curiosity, experimentation, and encouragement. By incorporating 〜てみる into your daily conversations, you’ll sound more natural and confident in Japanese.
Final Thoughts
The 〜てみる structure is a proven way to elevate your Japanese skills. Whether you’re trying new foods, testing out hobbies, or encouraging others, this grammar point is a must-know for every Japanese learner. Don’t make the mistake of overlooking it—start using 〜てみる today and watch your Japanese reach legendary levels!
Before it’s too late, practice the examples and fill-in-the-blank exercises in this guide. Guaranteed, you’ll see a breakthrough in your language mastery.
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊
-
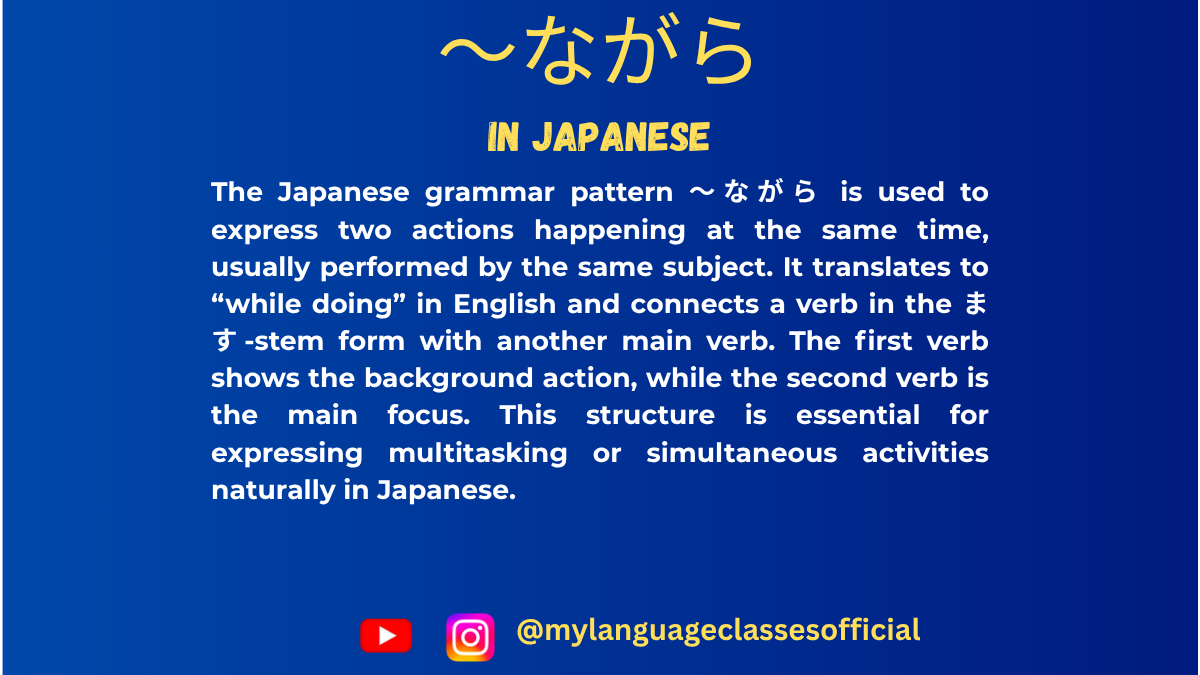
Using 〜ながら Form in Japanese | My Language Classes
〜ながら Form in Japanese
The 〜ながら (nagara) form is an essential Japanese grammar structure used to describe two actions happening simultaneously. It is widely used in both casual and formal conversations to indicate multitasking or actions occurring at the same time.
In this blog, we will explore the formation of 〜ながら for all three verb groups, its various usages, and a comprehensive list of verbs with example sentences. Additionally, we will provide a section with more example sentences, fill-in-the-blank exercises, key points to remember, and a conclusion.
Formation of 〜ながら for Different Verb Groups
Japanese verbs are categorized into three groups: Group 1 (Godan verbs), Group 2 (Ichidan verbs), and Group 3 (Irregular verbs). Each group follows a specific rule for forming 〜ながら.
1. Group 1 (Godan Verbs)
For Godan verbs, take the ます-stem of the verb and add ながら.
- Example Formation
- 話す (hanasu – to speak) → 話しながら (hanashinagara – while speaking)
- 書く (kaku – to write) → 書きながら (kakinagara – while writing)
2. Group 2 (Ichidan Verbs)
For Ichidan verbs, remove る from the dictionary form and add ながら.
- Example Formation
- 食べる (taberu – to eat) → 食べながら (tabenagara – while eating)
- 見る (miru – to see) → 見ながら (minagara – while watching)
3. Group 3 (Irregular Verbs)
There are only two irregular verbs in Japanese: する and くる.
- Example Formation
- する (suru – to do) → しながら (shiinagara – while doing)
- くる (kuru – to come) → きながら (kinagara – while coming)
Situations Where 〜ながら Form is Used
- Describing Two Simultaneous Actions
- 音楽を聞きながら勉強する (Ongaku o kikinagara benkyou suru) – Study while listening to music.
- Multitasking in Daily Life
- テレビを見ながらご飯を食べる (Terebi o minagara gohan o taberu) – Eat while watching TV.
- Speaking While Performing Another Action
- 笑いながら話す (Warainagara hanasu) – Talk while laughing.
- Contrasting Two Simultaneous Actions
- 悲しみながら笑う (Kanashiminagara warau) – Laugh while feeling sad.
- Working or Performing a Task While Doing Something Else
- 仕事をしながらコーヒーを飲む (Shigoto o shinagara koohii o nomu) – Drink coffee while working.
Verb List with 〜ながら Form and Example Sentences
Verb (Dictionary Form) 〜ながら Form Example Sentence (Japanese) Romaji English Translation 話す (hanasu) 話しながら (hanashinagara) 彼は笑いながら話しました。 Kare wa warainagara hanashimashita. He spoke while laughing. 書く (kaku) 書きながら (kakinagara) 先生は黒板に書きながら説明した。 Sensei wa kokuban ni kakinagara setsumei shita. The teacher explained while writing on the board. 読む (yomu) 読みながら (yominagara) 彼女は本を読みながら寝てしまった。 Kanojo wa hon o yominagara nete shimatta. She fell asleep while reading a book. 見る (miru) 見ながら (minagara) 子供たちはアニメを見ながら笑った。 Kodomotachi wa anime o minagara waratta. The children laughed while watching anime. 歩く (aruku) 歩きながら (arukinagara) 彼は音楽を聞きながら歩いた。 Kare wa ongaku o kikinagara aruita. He walked while listening to music. 食べる (taberu) 食べながら (tabenagara) 彼女はテレビを見ながら食べる。 Kanojo wa terebi o minagara taberu. She eats while watching TV. 泳ぐ (oyogu) 泳ぎながら (oyoginagara) 彼は海で泳ぎながら歌った。 Kare wa umi de oyoginagara utatta. He sang while swimming in the sea.
More Example Sentences
- 音楽を聞きながら勉強する。
Ongaku o kikinagara benkyou suru.
Study while listening to music. - コーヒーを飲みながらニュースを見る。
Koohii o nominagara nyuusu o miru.
Watch the news while drinking coffee. - 料理をしながらラジオを聞く。
Ryouri o shinagara rajio o kiku.
Listen to the radio while cooking. - 車を運転しながら歌う。
Kuruma o unten shinagara utau.
Sing while driving. - 宿題をしながら電話をする。
Shukudai o shinagara denwa o suru.
Talk on the phone while doing homework.
Fill in the Blanks Questions
- 本を______ながら、リラックスします。(読む)
- 音楽を______ながら、運転する。(聞く)
- 仕事を______ながら、テレビを見る。(する)
- ご飯を______ながら、友達と話す。(食べる)
- 日本語を______ながら、メモを取る。(勉強する)
Answers
- 読みながら (yominagara)
- 聞きながら (kikinagara)
- しながら (shiinagara)
- 食べながら (tabenagara)
- 勉強しながら (benkyou shinagara)
Things to Keep in Mind
- The subject of both actions must be the same.
- The ながら clause comes before the main action.
- ながら is used only for actions, not states.
Conclusion
The 〜ながら form is an important grammar structure in Japanese that allows smooth expression of simultaneous actions. By practicing with various verbs and sentences, you will become more fluent in using it naturally in conversations.
Keep practicing and incorporating 〜ながら into your daily Japanese studies!
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊
- Example Formation
-

Everything You Need to Know About PARA in Spanish
When learning Spanish, one of the trickiest aspects is understanding the difference between “por” and “para.” While both can translate to “for” in English, they serve different purposes in Spanish. This article will focus on “para”—its uses, common expressions, and grammatical rules.
Uses of PARA in Spanish
“Para” is generally used to indicate purpose, destination, deadlines, recipients, and opinions. Below is a detailed explanation of its main uses:
Usage Explanation Example Sentence Purpose (In order to) Used to indicate the reason for doing something. Often translates to “in order to” in English. Estudio español para hablar con fluidez. (I study Spanish in order to speak fluently.) Recipient (For someone) Used when something is intended for a person or entity. Este regalo es para ti. (This gift is for you.) Destination (Towards a place) Indicates movement towards a destination. Salimos para Madrid mañana. (We are leaving for Madrid tomorrow.) Deadline (By, For a time limit) Used to indicate a deadline for an action. La tarea es para mañana. (The homework is for tomorrow.) Employment (To work for someone) Indicates employment or who you work for. Trabajo para una empresa grande. (I work for a big company.) Comparison (Considering that) Used when making a comparison or contrast. Para un niño de 5 años, él es muy alto. (For a five-year-old, he is very tall.) Opinion (According to someone) Used to express personal opinions. Para mí, este restaurante es el mejor. (For me, this restaurant is the best.) Use (For a specific use) Used when indicating the purpose of an object. Necesito un cepillo para el pelo. (I need a brush for my hair.)
Common Expressions with PARA
Below is a list of commonly used phrases and idioms with para in daily Spanish:
Expression Meaning Example Sentence Estar para + infinitive To be about to do something Estoy para salir. (I am about to leave.) Para siempre Forever Te amaré para siempre. (I will love you forever.) Para nada Not at all No me gusta el café para nada. (I don’t like coffee at all.) Para variar Just for a change Hoy vamos a la playa para variar. (Today we are going to the beach just for a change.) No es para tanto It’s not a big deal No llores, no es para tanto. (Don’t cry, it’s not a big deal.) Para colmo To top it all off Perdimos el tren y, para colmo, empezó a llover. (We missed the train, and to top it all off, it started raining.) Para que (+ subjunctive) So that Estudia mucho para que pases el examen. (Study hard so that you pass the exam.) Ser tal para cual To be two of a kind Juan y Ana son tal para cual. (Juan and Ana are two of a kind.)
Important Grammar Rules When Using PARA
1. Articles with PARA
- When using para before a noun, it may require a definite or indefinite article (el, la, los, las, un, una, unos, unas).
- Example: Este libro es para el profesor. (This book is for the teacher.)
2. Singular vs. Plural Forms
- “Para” itself does not change with gender or number, but the words following it do.
- Example: Las flores son para las madres. (The flowers are for the mothers.)
3. Using PARA with Pronouns
- Personal pronouns with “para”: para mí, para ti, para él/ella, para nosotros, para ellos.
- Example: Este mensaje es para ti. (This message is for you.)
4. PARA vs. POR
Since “por” and “para” both mean “for” in English, beginners often confuse them. Here’s a simple trick:
- Use PARA when there’s a destination or purpose. (Voy para Madrid.)
- Use POR when there’s a cause or reason. (Voy por el trabajo.)
Things to Keep in Mind When Using PARA
- If you are expressing a purpose (“in order to”), always use the infinitive verb form after “para.”
✅ Vine para aprender español. (I came to learn Spanish.)
❌ Vine para aprendo español. (Incorrect) - “Para” is not used when talking about duration—use “por” instead.
✅ Estudié por dos horas. (I studied for two hours.)
❌ Estudié para dos horas. (Incorrect) - In spoken Spanish, native speakers often use “para” with shortened forms like “pa’” in informal speech.
Example: Voy pa’ la casa. (I’m going home.) (Casual speech)
Final Thoughts
Understanding para is crucial for mastering Spanish. By learning its different uses and practicing with common expressions, you’ll improve both comprehension and fluency. Try to use para in your daily conversations, and pay attention to how native speakers use it!
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have.
Happy learning! 😊
-

Understanding 〜がする in Japanese | My Language Classes
Understanding the Usage of 〜がする in Japanese
The expression 〜がする is a common grammatical structure in Japanese used to describe perceptions and sensations related to the five senses, as well as intuitive feelings. It is often translated as “to smell,” “to taste,” “to feel,” or “to sound like.” This phrase allows the speaker to express their sensory or emotional experience in a natural way.
Basic Structure of 〜がする
The pattern generally follows this structure:
[Noun] + がする
Here, [Noun] represents something perceived through the senses (such as smell, taste, sound, or feeling). The verb する indicates that the sensation exists.
Situations Where 〜がする is Used
Below are the different contexts where 〜がする is commonly used:
1. Smell (Odor-related Perception)
Used when describing a smell that one perceives.
- 変なにおいがする。 (Henna nioi ga suru.) – “There is a strange smell.”
- 花の香りがする。 (Hana no kaori ga suru.) – “I smell the fragrance of flowers.”
- ガスのにおいがする。 (Gasu no nioi ga suru.) – “It smells like gas.”
2. Taste (Flavor-related Perception)
Used when describing the taste of something.
- 変な味がする。 (Henna aji ga suru.) – “It has a strange taste.”
- この水は鉄の味がする。 (Kono mizu wa tetsu no aji ga suru.) – “This water tastes like iron.”
- 甘い味がする。 (Amai aji ga suru.) – “It tastes sweet.”
3. Sound (Auditory Perception)
Used when describing a sound that one hears.
- ドアの開く音がする。 (Doa no hiraku oto ga suru.) – “I hear the sound of a door opening.”
- 雷の音がする。 (Kaminari no oto ga suru.) – “I hear the sound of thunder.”
- 人の話し声がする。 (Hito no hanashigoe ga suru.) – “I hear people’s voices.”
4. Feeling (Emotional or Intuitive Perception)
Used when describing a feeling, intuition, or an atmosphere.
- 嫌な感じがする。 (Iyana kanji ga suru.) – “I have a bad feeling.”
- 胸騒ぎがする。 (Munasawagi ga suru.) – “I have a premonition (of something bad).”
- ワクワクする感じがする。 (Wakuwaku suru kanji ga suru.) – “I have an exciting feeling.”
5. Physical Sensations (Pain or Bodily Feelings)
Used when describing physical sensations or discomfort.
- 頭が痛い感じがする。 (Atama ga itai kanji ga suru.) – “I feel like I have a headache.”
- 吐き気がする。 (Hakike ga suru.) – “I feel nauseous.”
- 寒気がする。 (Samuke ga suru.) – “I feel chills.”
6. Other Abstract Feelings and Situations
It can be used to describe abstract or indirect experiences.
- あの人は信用できない気がする。 (Ano hito wa shinyou dekinai ki ga suru.) – “I feel like that person is untrustworthy.”
- ここは何か違う感じがする。 (Koko wa nanika chigau kanji ga suru.) – “This place feels different.”
Key Points to Remember
- 〜がする is used to describe sensory experiences, including smell, taste, sound, and physical or emotional feelings.
- It is typically used with nouns related to perception, such as におい (smell), 味 (taste), 音 (sound), 気 (feeling), 感じ (sensation), 痛み (pain), etc.
- It can be used for both literal (real sensory perceptions) and abstract (intuition, atmosphere, emotions) experiences.
- The phrase makes statements subjective, meaning it expresses the speaker’s personal perception rather than an objective fact.
Conclusion
Understanding 〜がする is essential for expressing sensory perceptions naturally in Japanese. Whether you’re describing a delicious meal, a strange smell, an ominous feeling, or an unexpected noise, this structure is an invaluable tool in communication. Mastering its usage will enhance your ability to express experiences vividly and naturally in Japanese.
By practicing various sentence patterns using 〜がする, learners can deepen their understanding and fluency in Japanese conversation. Try using it in your daily observations to get more comfortable with its application!
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊
-

Understanding 〜ように in Japanese | My Language Classes
Using 〜ように in Japanese
The Japanese expression 「〜ように」 is an essential grammatical structure that serves various purposes, including expressing hopes, requests, instructions, comparisons, goals, and habitual actions. This guide will provide an in-depth look at the different uses of 「〜ように」, along with clear explanations and example sentences.
1. Expressing Hopes or Wishes
「〜ように」 is used to express a hope or wish for something to happen, similar to saying “I hope that…” in English.
Structure:
Verb (potential form / negative form) + ように
Examples:
- 試験に合格できますように。
(Shiken ni goukaku dekimasu you ni.)
→ “I hope I can pass the exam.” - 雨が降らないように。
(Ame ga furanai you ni.)
→ “I hope it doesn’t rain.”
2. Expressing Goals or Objectives
This usage is similar to saying “in order to” in English. It indicates a goal or purpose for an action.
Structure:
Verb (potential form / dictionary form) + ように
Examples:
- 日本語が話せるように、毎日勉強しています。
(Nihongo ga hanaseru you ni, mainichi benkyou shiteimasu.)
→ “I study every day in order to be able to speak Japanese.” - 風邪を引かないように、マフラーをします。
(Kaze wo hikanai you ni, mafuraa wo shimasu.)
→ “I wear a scarf so that I don’t catch a cold.”
3. Giving Instructions or Advice (Indirect Commands)
When making polite or indirect requests, suggestions, or advice, 「〜ように」 is often used.
Structure:
Verb (plain non-past form) + ように 言う / 注意する / 頼む / 伝える
Examples:
- 先生は学生に宿題を忘れないように言いました。
(Sensei wa gakusei ni shukudai wo wasurenai you ni iimashita.)
→ “The teacher told the students not to forget their homework.” - 医者に早く寝るように注意された。
(Isha ni hayaku neru you ni chuui sareta.)
→ “The doctor advised me to sleep early.” - 彼に遅刻しないように頼みました。
(Kare ni chikoku shinai you ni tanomimashita.)
→ “I asked him not to be late.”
4. Making Comparisons
When used with verbs like なる (to become), 「〜ように」 can indicate a comparison or similarity.
Structure:
Noun + のように / Verb (plain form) + ように
Examples:
- 彼は先生のように話します。
(Kare wa sensei no you ni hanashimasu.)
→ “He speaks like a teacher.” - この部屋はまるでホテルのように綺麗です。
(Kono heya wa marude hoteru no you ni kirei desu.)
→ “This room is as clean as a hotel.”
5. Indicating Habitual Actions or Natural Consequences
This structure shows that something naturally happens or occurs habitually.
Structure:
Verb (dictionary form / negative form) + ようになる
Examples:
- 毎日練習して、日本語が話せるようになった。
(Mainichi renshuu shite, nihongo ga hanaseru you ni natta.)
→ “After practicing every day, I became able to speak Japanese.” - 最近、早く起きるようになりました。
(Saikin, hayaku okiru you ni narimashita.)
→ “Recently, I have started waking up early.”
6. Expressing Something Indirectly
When introducing a previous statement or explanation, 「〜ように」 can mean “as mentioned before” or “as expected.”
Structure:
Verb (plain form) + ように
Examples:
- 前に話したように、このプロジェクトは重要です。
(Mae ni hanashita you ni, kono purojekuto wa juuyou desu.)
→ “As I mentioned before, this project is important.” - 先生が言ったように、復習することが大切です。
(Sensei ga itta you ni, fukushuu suru koto ga taisetsu desu.)
→ “As the teacher said, reviewing is important.”
7. Expressing a Desired Outcome in a Prayer or Wish
This structure is common in prayers and formal expressions.
Structure:
Verb (potential form / negative form) + ように
Examples:
- みんなが幸せになりますように。
(Minna ga shiawase ni narimasu you ni.)
→ “I hope everyone becomes happy.” - 悪いことが起こらないように。
(Warui koto ga okoranai you ni.)
→ “I hope nothing bad happens.”
Summary: Situations Where 「〜ように」 is Used
Usage Meaning Example Expressing Hopes or Wishes “I hope that…” 試験に合格できますように。 Expressing Goals “In order to…” 日本語が話せるように勉強しています。 Giving Instructions / Advice Indirect commands 先生は学生に宿題を忘れないように言いました。 Making Comparisons “Like…” 彼は先生のように話します。 Indicating Habitual Actions “To become able to…” 日本語が話せるようになった。 Introducing Statements “As mentioned…” 前に話したように、このプロジェクトは重要です。 Expressing Wishes in Prayer Formal wishes みんなが幸せになりますように。
Conclusion
「〜ように」 is a versatile and essential grammar structure in Japanese. Understanding its different uses can greatly enhance your ability to communicate hopes, goals, indirect commands, comparisons, and habitual changes. By mastering this structure, you will sound more natural and fluent in Japanese!
Would you like me to cover any other grammar points in detail? Let me know in the comments!
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊
- 試験に合格できますように。
-

Using 〜ほど〜ない in Japanese | My Language Classes
Understanding 〜ほど〜ない in Japanese
The Japanese grammar pattern 「〜ほど〜ない」 is commonly used for making comparisons and expressing degree or extent. It implies that something is “not as much as” something else. This phrase is often translated as “not as… as…” in English.
Basic Structure of 〜ほど〜ない
The structure of this grammar pattern is as follows:
Noun + ほど + Adjective (ない-form)
or
Verb (dictionary form) + ほど + Adjective (ない-form)
General Meaning
「A ほど B ない」 means that B is not as A.
- A is the standard of comparison.
- B is the thing being compared.
Examples:
- この町は東京ほど賑やかではない。
(Kono machi wa Tōkyō hodo nigiyaka de wa nai.)
→ This town is not as lively as Tokyo. - 彼は私ほど速く走れない。
(Kare wa watashi hodo hayaku hashirenai.)
→ He cannot run as fast as I do. - この問題は思ったほど難しくない。
(Kono mondai wa omotta hodo muzukashiku nai.)
→ This problem is not as difficult as I thought.
Situations Where 〜ほど〜ない is Used
1. Comparing Extent or Degree
- Used when two things are compared, but the second one (B) has less intensity than the first (A).
Example:
北海道の冬は東京の冬ほど寒くない。
(Hokkaidō no fuyu wa Tōkyō no fuyu hodo samuku nai.)
→ Hokkaido’s winter is not as cold as Tokyo’s winter.2. Expressing Subjective Opinions
- Often used to express personal opinions about differences in perception.
Example:
数学は国語ほど難しくないと思います。
(Sūgaku wa kokugo hodo muzukashiku nai to omoimasu.)
→ I think math is not as difficult as Japanese.3. Negative Comparison in Abilities or Characteristics
- Used when comparing someone’s ability or characteristics with another’s.
Example:
彼の英語は先生ほど上手ではない。
(Kare no eigo wa sensei hodo jōzu de wa nai.)
→ His English is not as good as the teacher’s.4. Comparing Expectations vs Reality
- Used when expectations were high, but the actual situation is not as expected.
Example:
この映画は評判ほど面白くない。
(Kono eiga wa hyōban hodo omoshiroku nai.)
→ This movie is not as interesting as its reputation suggests.5. Comparing Feelings and Emotions
- Used when talking about feelings that are not as strong as expected.
Example:
彼は私が思ったほど優しくない。
(Kare wa watashi ga omotta hodo yasashiku nai.)
→ He is not as kind as I thought.6. Comparing Physical Condition or Health
- Used to compare health conditions or physical states.
Example:
風邪は思ったほどひどくない。
(Kaze wa omotta hodo hidoku nai.)
→ The cold is not as bad as I thought.7. Comparing Amount or Frequency
- Used when comparing quantity or frequency of actions.
Example:
今日は昨日ほど忙しくない。
(Kyō wa kinō hodo isogashiku nai.)
→ Today is not as busy as yesterday.8. Comparing Importance or Necessity
- Used when comparing levels of importance or necessity.
Example:
宿題はテストほど大事ではない。
(Shukudai wa tesuto hodo daiji de wa nai.)
→ Homework is not as important as tests.9. Comparing Strength of Desire or Preference
- Used to compare desires, preferences, or interests.
Example:
私は映画を見るのが好きですが、本を読むほど好きではない。
(Watashi wa eiga o miru no ga suki desu ga, hon o yomu hodo suki de wa nai.)
→ I like watching movies, but not as much as reading books.
Key Points to Remember About 〜ほど〜ない
- It is used for making comparisons where the second element has less intensity.
- It is often used to express subjective opinions.
- It is used to compare expectations vs reality.
- It can be used in various contexts: ability, frequency, amount, physical conditions, and emotions.
- It follows a simple pattern: “A ほど B ない”, where A is the standard, and B is the thing being compared.
Conclusion
The 「〜ほど〜ない」 grammar pattern is an essential part of Japanese when making negative comparisons. Mastering it will help you express your opinions, compare things effectively, and sound more natural in conversations. Make sure to practice using this structure in daily life to reinforce your understanding!
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊
-

How to Use 〜てもらう | My Language Classes
The Japanese Grammar 〜てもらう
The Japanese grammar pattern 〜てもらう is an essential structure used to express receiving a favor from someone. It emphasizes that someone is doing something beneficial for the speaker or a third party. Understanding this grammar is crucial for natural and polite Japanese communication.
This post will explain 〜てもらう in various situations, provide example sentences, and list common contexts where it is used.
Structure of 〜てもらう
The pattern follows this structure:
Person A (receiver) + は/が + Person B (doer) + に + Verb in 〜て form + もらう
- A is the person who benefits from the action.
- B is the person performing the action for A.
- The verb is conjugated into the て-form and followed by もらう (to receive).
Example:
- 私は先生に日本語を教えてもらいました。
(I had my teacher teach me Japanese.)
Difference Between 〜てもらう and 〜てあげる
- 〜てもらう: Focuses on the receiver of the favor.
- 〜てあげる: Focuses on the giver of the favor.
Example:
- 私は先生に日本語を教えてもらいました。 (I received Japanese lessons from my teacher.)
- 私は先生に日本語を教えてあげました。 (I taught Japanese to my teacher.)
Various Situations Where 〜てもらう Is Used
1. Receiving Help
When someone helps you with a task or does something for your benefit.
Example:
- 私は彼氏に財実を送ってもらいました。
(I had my boyfriend send my wallet.)
2. Receiving Permission
Used when asking for permission to do something.
Example:
- 先生にはやく帰らせてもらいました。
(I got permission from my teacher to leave early.)
3. Receiving a Favor Indirectly
You receive a favor, but a third party performs the action.
Example:
- 母は先生にむすこの学校の事を説明してもらいました。
(My mother had the teacher explain about the school to her.)
4. Making Polite Requests
When requesting someone to do something politely.
Example:
- この文章を正しく直してもらえますか。
(Could you please correct this text for me?)
5. Receiving Information
When someone shares knowledge or guidance.
Example:
- 先生にいろいろな情報を教えてもらいました。
(I received a lot of information from my teacher.)
6. Asking for Medical Assistance
Used when getting treatment or medical help from someone.
Example:
- 医者に病治をしてもらいました。
(I got treated by the doctor.)
7. Receiving a Physical Object
Used when someone gives you something.
Example:
- 友人に好きな本を買ってもらいました。
(My friend bought me a book I like.)
8. Receiving Guidance or Instructions
Used when someone teaches you or gives instructions.
Example:
- 先生に作文の書き方を教えてもらいました。
(I had my teacher teach me how to write essays.)
Summary of Situations Where 〜てもらう Is Used
Here’s a quick reference list:
- Receiving help (task-related support)
- Receiving permission
- Receiving a favor indirectly
- Making polite requests
- Receiving information or knowledge
- Asking for medical assistance
- Receiving a physical object
- Receiving guidance or instructions
Conclusion
〜てもらう is a crucial grammar point in Japanese, allowing you to express receiving favors, help, or benefits from others. Mastering this structure enhances your ability to communicate politely and effectively in various situations. Practice using it in conversations to improve fluency and comprehension!
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊
-

Using 〜なら for hypothetical situations | My Language Classes
〜なら: Expressing “If” or “As for” in Japanese
In Japanese, 〜なら is a versatile grammar structure often used to express conditionality (“if”) or to provide contextual emphasis (“as for”). This blog post will explore its usage in various contexts and provide a comprehensive list of situations where 〜なら is applicable.
What is 〜なら?
The particle なら is derived from the verb 成る (なる), which means “to become.” In grammar, it functions as a conditional marker or a topic-related particle depending on the context. It is commonly attached to the plain form of verbs, nouns, or adjectives.
Usage of 〜なら
1. Conditional “If”
- Meaning: Expresses a hypothetical or conditional situation.
- Structure:
Clause A (plain form) + なら, Clause B
Clause B often represents the speaker’s judgment, advice, or consequence.
Examples:
- 日本に行くなら、富士山を見たほうがいいですよ。
(Nihon ni iku nara, Fujisan o mita hō ga ii desu yo.)
If you’re going to Japan, you should see Mt. Fuji. - 雨が降るなら、外出しないほうがいいです。
(Ame ga furu nara, gaishutsu shinai hō ga ii desu.)
If it rains, you shouldn’t go out.
2. Topic-Based “As for”
- Meaning: Indicates that a specific topic is being addressed in response to a preceding statement or question.
- Structure:
Noun + なら
Examples:
- 映画なら、コメディが一番好きです。
(Eiga nara, komedi ga ichiban suki desu.)
As for movies, I like comedies the best. - この本なら、もう読んだことがあります。
(Kono hon nara, mō yonda koto ga arimasu.)
As for this book, I’ve already read it.
3. Contrasting Ideas
- Meaning: Suggests a contrast between two different ideas or topics.
- Structure:
Noun/Adjective/Verb + なら
Examples:
- 英語なら話せますが、フランス語は話せません。
(Eigo nara hanasemasu ga, Furansugo wa hanasemasen.)
If it’s English, I can speak it, but I can’t speak French. - 安いなら買いますが、高いなら買いません。
(Yasui nara kaimasu ga, takai nara kaimasen.)
If it’s cheap, I’ll buy it, but if it’s expensive, I won’t.
4. Hypothetical Suggestions
- Meaning: Used when giving suggestions or advice based on hypothetical conditions.
- Structure:
Clause + なら
Examples:
- 東京に行くなら、スカイツリーを訪れるべきです。
(Tōkyō ni iku nara, Sukaitsurī o otozureru beki desu.)
If you’re visiting Tokyo, you should check out the Skytree. - 勉強するなら、早めに始めたほうがいいですよ。
(Benkyō suru nara, hayame ni hajimeta hō ga ii desu yo.)
If you’re going to study, it’s better to start early.
5. Clarifications or Conditions
- Meaning: Used when responding to a condition or clarifying information.
- Structure:
Noun + なら
Examples:
- 山田さんなら、もう帰りましたよ。
(Yamada-san nara, mō kaerimashita yo.)
If you’re talking about Yamada-san, he’s already gone home. - 駅なら、この道をまっすぐ行けば着きます。
(Eki nara, kono michi o massugu ikeba tsukimasu.)
If you mean the station, go straight down this road.
When to Use 〜なら?
Here is a quick checklist of situations where 〜なら is appropriate:
- Making a Hypothetical Conditional Statement:
“If you’re going to X, then Y.” - Responding to Questions or Comments with Context:
“As for X, Y applies.” - Contrasting Two Scenarios or Topics:
“If X is true, Y. But if not, Z.” - Providing Advice Based on Hypothetical Situations:
“If you’re considering X, then Y is a good idea.” - Clarifying or Confirming a Specific Topic:
“If you’re talking about X, then Y.”
Tips for Using 〜なら
- Be Contextual: 〜なら thrives on context. Make sure the listener understands the implied condition or topic.
- Be Specific: Use it to address clear contrasts or hypothetical situations, avoiding vague statements.
- Practice Intonation: When using 〜なら in spoken Japanese, emphasize the conditional tone to make your intent clear.
By mastering 〜なら, you’ll find yourself able to express conditions, offer advice, and clarify topics more effectively in Japanese. Practice by creating your own sentences in real-life scenarios!
If you enjoyed this lesson, be sure to check out more posts like this on my blog at My Language Classes. Don’t forget to subscribe my YouTube channel and follow me on Instagram for the latest language learning tips and lessons. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, or ask any questions you have about nouns.
Happy learning! 😊

