Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: blogger
-

Pretérito Indefinido vs. Imperfecto – Usage and Contrast Between Two Types of Past Tense in Spanish
Mastering Spanish Past Tenses with Confidence
Struggling to decide between Pretérito Indefinido and Pretérito Imperfecto? You’re not alone! These two essential Spanish past tenses often confuse learners — but once you crack the code, your ability to speak and write about the past in Spanish will skyrocket.
In this practical guide, you’ll discover the clear differences between Pretérito Indefinido and Pretérito Imperfecto, along with simple usage rules, real-life examples, and helpful tips that will make choosing the right tense second nature.
Whether you’re preparing for a Spanish grammar exam, polishing your skills for travel, or just aiming for fluent Spanish communication, mastering these tenses is non-negotiable. By understanding when to use simple past (pretérito perfecto simple) versus habitual or descriptive past (pretérito imperfecto), you’ll add depth and precision to your Spanish storytelling.
🔥 What you’ll learn in this post:
- How to use Pretérito Indefinido vs. Pretérito Imperfecto
- Key grammar rules and timelines
- 20+ example sentences with English translations
- A practice quiz with answers to test yourself
So grab your notebook or open your favorite language app — it’s time to unlock one of the most powerful grammar tools in the Spanish language!

Understanding Pretérito Indefinido and Pretérito Imperfecto
Pretérito Indefinido (Simple Past) Usage:
Used to describe actions that are completed in the past with a definite beginning and end.
- Single events: “Ayer fui al cine.” (Yesterday, I went to the cinema.)
- Sequential actions: “Llegué a casa, cené y me acosté.” (I arrived home, had dinner, and went to bed.)
- Specific duration: “Viví en Madrid por tres años.” (I lived in Madrid for three years.)
Pretérito Imperfecto (Imperfect Past) Usage:
Used for habitual actions, descriptions, and ongoing past actions with no definite beginning or end.
- Habitual actions: “Cuando era niño, jugaba en el parque todos los días.” (When I was a child, I used to play in the park every day.)
- Descriptions: “La casa era grande y tenía un jardín bonito.” (The house was big and had a beautiful garden.)
- Simultaneous actions: “Mientras leía, escuchaba música.” (While I was reading, I was listening to music.)
2. Formation of Pretérito Indefinido and Pretérito Imperfecto
Regular Verbs Conjugation
Pretérito Indefinido:
Subject -AR Verbs (Hablar) -ER Verbs (Comer) -IR Verbs (Vivir) Yo hablé comí viví Tú hablaste comiste viviste Él/Ella/Usted habló comió vivió Nosotros/as hablamos comimos vivimos Vosotros/as hablasteis comisteis vivisteis Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes hablaron comieron vivieron Pretérito Imperfecto:
Subject -AR Verbs (Hablar) -ER Verbs (Comer) -IR Verbs (Vivir) Yo hablaba comía vivía Tú hablabas comías vivías Él/Ella/Usted hablaba comía vivía Nosotros/as hablábamos comíamos vivíamos Vosotros/as hablabais comíais vivíais Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes hablaban comían vivían
3. Common Irregular Verbs in Pretérito Indefinido & Imperfecto
Verb Pretérito Indefinido (Yo Form) Pretérito Imperfecto (Yo Form) Ser fui era Ir fui iba Ver vi veía Tener tuve tenía Hacer hice hacía Decir dije decía Poner puse ponía Estar estuve estaba Poder pude podía Querer quise quería
❌ Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Mixing up Pretérito Indefinido and Pretérito Imperfecto is one of the most frequent grammar mistakes among Spanish learners. Let’s look at the most common slip-ups — and how to fix them like a pro!
1. 📍 Using Pretérito Indefinido for Habitual Actions
Mistake: Cada verano fuimos a la playa.
Why it’s wrong: “Cada verano” (every summer) indicates a repeated, habitual action — not a one-time event.
Correct: Cada verano íbamos a la playa.
✅ Use Imperfecto for actions that happened regularly in the past.
2. ⌛ Using Pretérito Imperfecto for Completed Actions
Mistake: Ayer comía una pizza deliciosa.
Why it’s wrong: “Ayer” points to a specific, completed event.
Correct: Ayer comí una pizza deliciosa.
✅ Use Indefinido for actions with a defined start and end point.
3. 🧩 Forgetting Context Clues
Mistake: Choosing the tense randomly without thinking about the time frame.
How to fix it: Pay attention to time markers like:- Indefinido: ayer, el año pasado, una vez, en 2019
- Imperfecto: siempre, normalmente, cada día, cuando era niño
4. 💬 Mixing Both Tenses Incorrectly in the Same Sentence
Mistake: Cuando llegó, yo le abría la puerta.
Why it’s wrong: “Llegó” (arrived) is a completed action, and the ongoing action (opening the door) should also be in imperfect.
Correct: Cuando llegó, yo le abría la puerta.
✅ Use Indefinido for the interrupting action and Imperfecto for the ongoing one.
Pro Tip 💡
When in doubt, ask yourself:
- Is this a completed action? → Use Pretérito Indefinido
- Is this a habitual or ongoing action? → Use Pretérito Imperfecto
More Example Sentences
🕒 Pretérito Indefinido (Completed Past Actions):
- Ayer terminé mi tarea temprano.
Yesterday I finished my homework early. - El año pasado viajé a España.
Last year I traveled to Spain. - Compré un coche nuevo la semana pasada.
I bought a new car last week. - El concierto empezó a las ocho.
The concert started at eight. - Pedro ganó el premio en 2020.
Pedro won the prize in 2020. - Anoche cenamos en un restaurante elegante.
Last night we had dinner at a fancy restaurant. - Fui al médico el lunes.
I went to the doctor on Monday. - Ella escribió tres páginas en su diario.
She wrote three pages in her journal. - Ellos llegaron tarde a la reunión.
They arrived late to the meeting. - El examen terminó a las diez.
The exam ended at ten.
🔁 Pretérito Imperfecto (Ongoing or Habitual Past Actions):
- Cuando era pequeño, tenía un perro.
When I was little, I had a dog. - Siempre me gustaba leer antes de dormir.
I always liked to read before sleeping. - Mi abuela cocinaba todos los domingos.
My grandmother used to cook every Sunday. - En la escuela, escribíamos en cuadernos grandes.
At school, we used to write in big notebooks. - Cuando vivíamos en Barcelona, íbamos a la playa a menudo.
When we lived in Barcelona, we often went to the beach. - Los niños jugaban en el parque cada tarde.
The kids used to play in the park every afternoon. - Yo leía mucho cuando tenía tiempo libre.
I used to read a lot when I had free time. - Mi padre trabajaba en una oficina en el centro.
My father used to work in an office downtown. - Nosotros veíamos dibujos animados los sábados por la mañana.
We used to watch cartoons on Saturday mornings. - Antes, la gente escribía cartas en lugar de correos electrónicos.
In the past, people used to write letters instead of emails.
Things to Keep in Mind
- Gender & Plurality: Nouns and adjectives must agree in gender and number.
- Time Expressions: “Ayer” (yesterday) & “anoche” (last night) indicate Pretérito Indefinido, while “siempre” (always) & “antes” (before) suggest Pretérito Imperfecto.
- Mixed Usage: Some sentences may require both tenses: “Mientras estudiaba, sonó el teléfono.” (While I was studying, the phone rang.)
Exercise: Fill in the blanks
Complete the following sentences using the correct form of the verb in brackets—either Pretérito Indefinido or Pretérito Imperfecto.
- Cuando era niño, siempre __________ con mis amigos. (jugar)
- Ayer __________ una película muy interesante. (ver)
- Mi abuela __________ cuentos antes de dormir. (contar)
- La semana pasada __________ a la montaña. (ir)
- De pequeños, nosotros __________ mucho chocolate. (comer)
- El año pasado mi hermana __________ una guitarra. (comprar)
- Cuando vivía en México, __________ todos los días al trabajo en bici. (ir)
- El sábado pasado __________ una fiesta en casa de Laura. (haber)
- Antes, mis padres __________ en el campo. (vivir)
- Yo __________ muy feliz cuando estaba en la universidad. (ser)
- ¿Tú __________ en Madrid en 2019? (estar)
- Los niños __________ dibujos animados cada mañana. (ver)
- Mi primo __________ su pasaporte en el hotel. (olvidar)
- En el colegio, nosotros siempre __________ en grupo. (trabajar)
- Ayer por la tarde, ellos __________ a las cartas. (jugar)
- Mi madre __________ la cena cuando llegué. (preparar)
- Cuando era joven, Juan __________ muy tímido. (ser)
- ¿Qué __________ tú cuando sonó el teléfono? (hacer)
- Anoche, Marta __________ hasta tarde. (estudiar)
- Cuando llovía, nosotros no __________ al parque. (salir)
✅ Answers
Cuando era niño, siempre jugaba con mis amigos.
When I was a child, I always played with my friends.Ayer vi una película muy interesante.
Yesterday I watched a very interesting movie.Mi abuela contaba cuentos antes de dormir.
My grandmother used to tell stories before sleeping.La semana pasada fui a la montaña.
Last week I went to the mountains.De pequeños, nosotros comíamos mucho chocolate.
As kids, we used to eat a lot of chocolate.El año pasado mi hermana compró una guitarra.
Last year my sister bought a guitar.Cuando vivía en México, iba todos los días al trabajo en bici.
When I lived in Mexico, I used to go to work by bike every day.El sábado pasado hubo una fiesta en casa de Laura.
Last Saturday there was a party at Laura’s house.Antes, mis padres vivían en el campo.
Before, my parents used to live in the countryside.Yo era muy feliz cuando estaba en la universidad.
I was very happy when I was in college.¿Tú estuviste en Madrid en 2019?
Were you in Madrid in 2019?Los niños veían dibujos animados cada mañana.
The children used to watch cartoons every morning.Mi primo olvidó su pasaporte en el hotel.
My cousin forgot his passport at the hotel.En el colegio, nosotros siempre trabajábamos en grupo.
In school, we always worked in groups.Ayer por la tarde, ellos jugaron a las cartas.
Yesterday afternoon, they played cards.Mi madre preparaba la cena cuando llegué.
My mom was preparing dinner when I arrived.Cuando era joven, Juan era muy tímido.
When he was young, Juan was very shy.¿Qué hacías tú cuando sonó el teléfono?
What were you doing when the phone rang?Anoche, Marta estudió hasta tarde.
Last night, Marta studied until late.Cuando llovía, nosotros no salíamos al parque.
When it rained, we didn’t go out to the park.
✅ Conclusion: Mastering Spanish Past Tenses
Understanding the difference between Pretérito Indefinido and Pretérito Imperfecto is essential for speaking and writing accurately in Spanish. While the Indefinido is perfect for expressing completed actions at specific moments, the Imperfecto helps describe ongoing or habitual actions from the past. By practicing regularly and recognizing context clues, you’ll gain confidence in choosing the right past tense every time.
Ready to take your Spanish to the next level?
✅ Bookmark this guide for future reference.
✅ Share it with fellow Spanish learners!
✅ For more tips, example sentences, and grammar hacks, subscribe to our newsletter and follow MY Language Classes on YouTube and Instagram!✅Join our WhatsApp group
¿Tienes dudas? Drop your questions in the comments below — ¡estaré encantado de ayudarte!
- 100 Spanish Example Sentences
- 100 Spanish Fill-in-the-Blanks Exercises
- 100 Spanish Vocabulary Lists
- Spanish – Advanced
- Spanish – Beginner
- Spanish – Intermediate
-

Mastering the Past Participle in English: A Simple Guide with Examples and Rules
Have you ever heard someone say “I have eaten,” “She has gone,” or “They were invited” and wondered why they used those words? Welcome to the world of the past participle — one of the most essential, powerful, and frequently used parts of English grammar.
Whether you’re a beginner or brushing up on your skills, understanding the past participle in English is key to forming perfect tenses, passive voice, and more. This guide will make it super easy for you to learn how to use past participles naturally in your speaking and writing. With clear rules, real-life examples, and interactive exercises, you’ll quickly feel more confident in your English grammar.
In this blog post, we’ll cover:
- ✅ What the past participle is (with easy definitions)
- ✅ When and how to use it correctly
- ✅ The most common past participle verbs used every day
- ✅ Grammar rules, tips, examples, and common mistakes
- ✅ An easy fill-in-the-blank quiz to test your knowledge
If you’re ready to speak and write English more accurately, let’s dive into this important grammar point step by step!
What Is the Past Participle? Explanation and Overview
The past participle is one of the most important forms of a verb in English. It is often used to form perfect tenses, the passive voice, and adjectives. But don’t worry — this might sound difficult, but it’s actually simple once you understand how it works.
🔤 What is a Past Participle?
A past participle is the third form of a verb. Most English verbs have three main forms:
- Base form (do, eat, play)
- Past simple (did, ate, played)
- Past participle (done, eaten, played)
Let’s look at a few common examples:
Base Verb Past Simple Past Participle go went gone write wrote written break broke broken see saw seen help helped helped Some past participles are regular (just add -ed), while others are irregular and change completely. We’ll explore that in more detail later.
🎯 Why Is the Past Participle Important?
You need the past participle to:
- Use perfect tenses:
- “I have finished my homework.”
- “She had left before I arrived.”
- Use the passive voice:
- “The cake was baked by my mom.”
- “The letters were sent yesterday.”
- Describe something as an adjective:
- “I feel tired.”
- “The broken window needs fixing.”
🧠 Quick Facts About Past Participles
- Used with helping verbs like has, have, had, was, were, is, am, are, be, been, being
- Can be regular (worked, walked, helped) or irregular (gone, done, seen)
- Very common in English — especially in everyday conversation and writing
Everyday Sentences Using the Past Participle – 10 Common Examples
To really understand how the past participle works, it helps to see it in action. These examples are short, simple, and used in real everyday English. We’ll highlight the past participle in each sentence so you can spot it easily.
🔟 Real-Life Past Participle Examples
- I have eaten breakfast already.
→ Used in the present perfect tense. - She has gone to the store.
→ “Gone” is the past participle of “go.” - They were invited to the wedding.
→ Passive voice using the past participle “invited.” - He had written five pages before lunch.
→ Used in the past perfect tense. - The window was broken by the storm.
→ Passive voice again, showing the result of an action. - We have seen that movie before.
→ Common structure in everyday conversations. - I have finished my homework.
→ “Finished” is a regular verb in the past participle form. - The work has been completed.
→ Shows something is done and over. - She has driven for three hours today.
→ “Driven” is the past participle of “drive.” - He has forgotten his keys again!
→ Perfect tense with an irregular verb.
These examples are just a small sample of how often we use past participles in daily life. You probably hear or say sentences like these every day without even realizing it!
When to Use the Past Participle – All the Key Situations
The past participle is not just a grammar form — it’s a tool we use in many different situations. It helps us talk about things that happened, things that are done, or things that have been affected in some way. Understanding when to use the past participle will make your English sound more natural and fluent.
Here are the main situations where the past participle is used:
✅ 1. Perfect Tenses
Past participles are always used in perfect tense structures, such as:
- Present Perfect
→ “She has eaten lunch.”
(Action completed recently) - Past Perfect
→ “He had finished before the meeting started.”
(An action completed before another past event) - Future Perfect
→ “They will have arrived by 6 PM.”
(An action that will be completed before a point in the future)
✅ 2. Passive Voice
We use the past participle to form passive sentences. In passive voice, the action is done to the subject, not by the subject.
- “The letter was written by Sarah.”
- “The cookies were baked this morning.”
- “The house has been cleaned.”
✅ 3. Adjectives
Some past participles are used as adjectives to describe people, feelings, or things.
- “I feel tired today.”
- “She looked confused by the question.”
- “The broken phone didn’t work.”
📝 Note: In these cases, the past participle acts like an adjective, not a verb.
✅ 4. Passive Infinitives
We also use the past participle in passive infinitives (to be + past participle).
- “This book is easy to read.”
- “The homework needs to be finished.”
✅ 5. Perfect Infinitives
Perfect infinitives (to have + past participle) are also built using the past participle.
- “He seems to have forgotten the meeting.”
- “I’m happy to have met you.”
✅ 6. Reported Speech or Past Descriptions
Sometimes past participles are used to describe something indirectly.
- “The stolen car was found yesterday.”
- “We stayed in a rented room.”
✅ 7. After Certain Verbs
Certain verbs require the past participle in their structure.
- “She got married last year.”
- “He was arrested by the police.”
How to Conjugate Verbs in the Past Participle – Conjugation Rules
Knowing how to form the past participle of a verb is one of the most important parts of learning English grammar. Luckily, the rules are simple for regular verbs — and with a little practice, you’ll remember even the irregular ones.
In this section, we’ll break down the conjugation rules for both regular and irregular verbs so you can use past participles correctly every time.
✅ 1. Regular Verbs – Add -ed
For most regular verbs, you simply add -ed to the base form of the verb.
Base Verb Past Participle work worked play played clean cleaned cook cooked jump jumped 🔹 Examples:
- “I have worked all day.”
- “She has played the piano for years.”
📌 Spelling Rules for Regular Verbs
- Verbs ending in -e: Just add -d
→ “love” → loved - Verbs ending in a consonant + y: Change y to i and add -ed
→ “study” → studied - One-syllable verbs ending in CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant): Double the final consonant and add -ed
→ “stop” → stopped
→ “plan” → planned
❗ 2. Irregular Verbs – Memorize These Forms
Irregular verbs do not follow a set rule. Their past participle forms must be memorized, but with frequent use, they’ll become natural.
Here’s a list of common irregular verbs and their past participles:
Base Verb Past Participle go gone eat eaten see seen write written break broken take taken come come drink drunk give given know known 🔹 Examples:
- “He has gone to the gym.”
- “They have taken the test.”
🎯 Pro Tip: Use Verb Charts
Make your own list of verbs with three columns:
- Base form
- Simple past
- Past participle
Keep practicing until it becomes second nature!
100 Irregular Verbs with Past Participle Forms – Learn These for Better English
Learning the past participle forms of irregular verbs is one of the most important steps to becoming confident in English. Unlike regular verbs, irregular verbs do not follow a set pattern. That’s why it’s helpful to study them in a list format and memorize them through use in sentences.
In the table below, you’ll find 100 of the most commonly used irregular verbs in English. These are essential for daily conversation, writing, reading, and especially for perfect tenses and passive voice.
🔤 Table: 100 Most Common Irregular Verbs in English
No. Base Verb Past Simple Past Participle 1 be was/were been 2 become became become 3 begin began begun 4 break broke broken 5 bring brought brought 6 build built built 7 buy bought bought 8 catch caught caught 9 choose chose chosen 10 come came come 11 cost cost cost 12 cut cut cut 13 do did done 14 draw drew drawn 15 drink drank drunk 16 drive drove driven 17 eat ate eaten 18 fall fell fallen 19 feel felt felt 20 fight fought fought 21 find found found 22 fly flew flown 23 forget forgot forgotten 24 forgive forgave forgiven 25 freeze froze frozen 26 get got gotten/got 27 give gave given 28 go went gone 29 grow grew grown 30 have had had 31 hear heard heard 32 hide hid hidden 33 hit hit hit 34 hold held held 35 keep kept kept 36 know knew known 37 lay laid laid 38 lead led led 39 leave left left 40 lend lent lent 41 let let let 42 lie (recline) lay lain 43 lose lost lost 44 make made made 45 mean meant meant 46 meet met met 47 pay paid paid 48 put put put 49 read read read 50 ride rode ridden 51 ring rang rung 52 rise rose risen 53 run ran run 54 say said said 55 see saw seen 56 sell sold sold 57 send sent sent 58 set set set 59 shake shook shaken 60 shine shone shone 61 shoot shot shot 62 show showed shown 63 shut shut shut 64 sing sang sung 65 sink sank sunk 66 sit sat sat 67 sleep slept slept 68 speak spoke spoken 69 spend spent spent 70 stand stood stood 71 steal stole stolen 72 stick stuck stuck 73 swim swam swum 74 take took taken 75 teach taught taught 76 tear tore torn 77 tell told told 78 think thought thought 79 throw threw thrown 80 understand understood understood 81 wake woke woken 82 wear wore worn 83 win won won 84 write wrote written 85 become became become 86 bet bet bet 87 bite bit bitten 88 bleed bled bled 89 blow blew blown 90 burn burnt/burned burnt/burned 91 deal dealt dealt 92 dig dug dug 93 dream dreamt/dreamed dreamt/dreamed 94 feed fed fed 95 flee fled fled 96 forgive forgave forgiven 97 hang hung hung 98 leap leapt/leaped leapt/leaped 99 prove proved proven 100 sweep swept swept 🧠 Tip for Learners:
Start by mastering the top 30 verbs. These are used in most everyday conversations. Gradually work your way through the list and practice them in sentences.
📘 Past Participle Grammar Rules You Need to Know
Mastering the past participle is essential for using perfect tenses, passive voice, and adjectives correctly in English. Here are the most important grammar rules to understand and remember:
✅ 1. Past Participle Is Used in Perfect Tenses
The past participle always follows a form of the auxiliary verb “have” when forming the present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect tenses.
Structure:
- Present Perfect: have/has + past participle
- Past Perfect: had + past participle
- Future Perfect: will have + past participle
Examples:
- I have eaten breakfast. (Present Perfect)
- She had gone to school before the rain started. (Past Perfect)
- They will have finished the project by tomorrow. (Future Perfect)
✅ 2. Past Participle Is Used in Passive Voice
In the passive voice, the past participle is used after a form of “to be” to show that something is done to the subject.
Structure:
to be + past participleExamples:
- The window was broken by the ball.
- These cakes are baked fresh every day.
- The project has been completed.
✅ 3. Past Participles Can Function as Adjectives
Some past participles are commonly used as adjectives to describe nouns.
Examples:
- I am interested in science.
- The broken vase was expensive.
- She felt tired after work.
✅ 4. Regular vs Irregular Verbs
- Regular verbs form their past participles by adding -ed (e.g., walk → walked → walked).
- Irregular verbs do not follow a fixed pattern (e.g., go → went → gone).
Always check the past participle form when using irregular verbs, as mistakes are common.
✅ 5. Don’t Confuse Simple Past with Past Participle
This is a common mistake among learners. Many irregular verbs have different past simple and past participle forms.
Examples:
- Simple past: I wrote a letter.
- Past participle: I have written a letter.
✅ 6. Perfect Tense Time Expressions Often Follow the Past Participle
When using past participles in perfect tenses, they often appear with words like:
- already, yet, just, ever, never, recently, so far, since, for
Examples:
- Have you ever eaten sushi?
- She has just arrived.
- They haven’t finished the work yet.
✅ 7. Modal Verbs + Have + Past Participle
Use past participles after modal verbs like could, would, should, might, must to talk about past possibilities or obligations.
Structure:
modal + have + past participleExamples:
- You should have called me.
- They might have forgotten the meeting.
- He must have left already.
🎯 Pro Tip:
To avoid confusion, always ask yourself:
Is this action complete or does it describe a result?
If yes, you’re probably looking for a past participle, not just a past tense verb.
💡 Important Tips for Using the Past Participle Correctly
The past participle is a powerful part of English grammar, but it can also be a little tricky. These important tips will help you avoid confusion and use it confidently in everyday speech and writing.
✅ 1. Always Pair Past Participles with the Right Helping Verb
Past participles don’t usually stand alone. They often follow “have,” “has,” “had,” or “been” to form perfect tenses or passive voice.
Correct:
- She has gone to school.
- The cake was baked this morning.
Incorrect:
- She gone to school. ❌
- The cake baked this morning. ❌
✅ 2. Don’t Mix Up Past Simple and Past Participle for Irregular Verbs
Some irregular verbs have different forms for the past simple and past participle. Mixing them up is a common mistake.
Base Verb Past Simple Past Participle speak spoke spoken break broke broken take took taken ❌ Incorrect: I have spoke to her.
✅ Correct: I have spoken to her.
✅ 3. Use Past Participles for Actions That Are Complete
Perfect tenses are used for actions that are already completed or have a result in the present.
- I have eaten lunch. (I’m not hungry now.)
- He had left before I arrived. (The action was completed in the past.)
✅ 4. Watch Out for Regular Verbs That Look Like Past Participles
Some regular past tense verbs look the same as the past participle. But remember: it’s only a past participle when it’s part of a perfect tense, passive voice, or used as an adjective.
- I walked home. (Past tense)
- I have walked home. (Present perfect)
- The walked path was quiet. (Adjective)
✅ 5. Some Past Participles Are Used As Adjectives—Not Verbs!
Be careful with participles that describe feelings or conditions. These are past participles used as adjectives.
- I feel bored.
- She looked tired.
- The door was locked.
They describe states and are not part of a verb tense here.
✅ 6. Learn Irregular Verbs in Groups
To remember irregular past participles more easily, group them by patterns:
- Same form for all three: cut – cut – cut, put – put – put
- Same past simple and past participle: buy – bought – bought, teach – taught – taught
- All three different: begin – began – begun, go – went – gone
✅ 7. Practice Using Past Participles in Context
Don’t just memorize verb forms—use them in real sentences! This helps you learn naturally and build confidence.
Try saying:
- I’ve eaten breakfast today.
- She has written a story.
- They’ve taken the bus.
✅ 8. Use Time Words with Perfect Tenses
When using perfect tenses with past participles, time expressions add clarity and context.
Use words like:
- Already, yet, just, ever, never, before, since, for, recently, so far
✅ 9. Check Verb Lists Often
Even advanced learners forget irregular past participles! Keep a list nearby or bookmark a chart for quick reference. It saves time and helps avoid mistakes.
✅ 10. Listen to Native Speakers
Watch movies, shows, or YouTube videos in English. Notice how speakers use have + past participle and try copying their sentence patterns. Listening helps your brain absorb natural usage without memorizing too hard!
With these tips in mind, you’re well on your way to mastering one of English grammar’s most powerful tools.
⚠️ Common Mistakes with the Past Participle and How to Fix Them
Even experienced learners—and sometimes native speakers—make mistakes with the past participle. Knowing these common errors and how to correct them will boost your confidence and help you speak and write more accurately.
❌ Mistake 1: Using the Past Simple Instead of Past Participle
Many learners confuse the past simple form with the past participle, especially with irregular verbs.
- Incorrect: I have wrote a letter.
- Correct: I have written a letter.
How to fix: Learn the difference between past simple and past participle for irregular verbs. Remember, after have/has/had, always use the past participle.
❌ Mistake 2: Forgetting the Auxiliary Verb “Have” or “Been”
The past participle cannot stand alone when forming perfect tenses or passive voice. Missing have, has, had, or been leads to incorrect sentences.
- Incorrect: She gone to the store.
- Correct: She has gone to the store.
- Incorrect: The book read by many people.
- Correct: The book was read by many people.
How to fix: Always check if your sentence has the necessary helper verb before the past participle.
❌ Mistake 3: Using Past Participle with Wrong Tense
Sometimes learners use past participles in simple past tense sentences, which require the past simple form instead.
- Incorrect: Yesterday, I have eaten pizza.
- Correct: Yesterday, I ate pizza.
How to fix: Use past simple for completed actions at a specific past time (yesterday, last week, etc.). Use present perfect (have + past participle) for actions with relevance to the present.
❌ Mistake 4: Confusing Passive Voice with Active Voice
Passive voice uses to be + past participle, but learners sometimes use the past participle incorrectly with active voice verbs.
- Incorrect: She was wrote the report.
- Correct: She wrote the report. (active)
- Correct: The report was written by her. (passive)
How to fix: Identify whether the subject is doing the action (active) or receiving it (passive).
❌ Mistake 5: Using Past Participles as Adjectives Incorrectly
Past participles can be adjectives, but they must describe a state or condition related to the noun.
- Incorrect: I am excited to the park.
- Correct: I am excited to go to the park.
How to fix: Use past participles as adjectives to describe feelings or conditions, and make sure the sentence is grammatically complete.
❌ Mistake 6: Mispronunciation or Misuse of Irregular Past Participles
Some irregular past participles are tricky to pronounce or remember (e.g., spoken, written, gone).
How to fix: Practice pronunciation and use them regularly in sentences. Listening and repeating helps build muscle memory.
❌ Mistake 7: Overusing the Past Participle in Simple Contexts
Sometimes learners try to use perfect tenses when simple past is enough.
- Incorrect: I have went to the store yesterday.
- Correct: I went to the store yesterday.
How to fix: Understand the time reference in your sentence and use the appropriate tense.
🔧 Quick Fix Checklist:
- Check if the verb after have/has/had is a past participle (not past simple).
- Always include auxiliary verbs for perfect tenses and passive voice.
- Use simple past for completed past actions at definite times.
- Confirm whether the sentence needs active or passive voice.
- Use past participles as adjectives only to describe states or conditions.
Fixing these mistakes will make your English sound clearer and more natural. Practice makes perfect!
✨ 20 Past Participle Example Sentences for Better Understanding
Seeing the past participle used in real sentences is one of the best ways to understand how it works. Here are 20 clear, useful examples that cover perfect tenses, passive voice, and adjectives.
Present Perfect Tense (have/has + past participle)
- I have visited many countries this year.
- She has finished her homework already.
- They have never seen such a beautiful sunset.
- We have eaten lunch, so we’re not hungry.
- He has written three books so far.
Past Perfect Tense (had + past participle)
- By the time I arrived, she had left the party.
- They had completed the project before the deadline.
- He had never traveled abroad before last year.
- We had just started dinner when the phone rang.
- The team had won five matches in a row.
Passive Voice (to be + past participle)
- The letter was sent yesterday.
- The house is being cleaned right now.
- The movies were watched by millions of people.
- The cake has been baked perfectly.
- The reports will be reviewed tomorrow.
Past Participles as Adjectives
- She looks excited about the trip.
- The broken window needs to be fixed.
- I was tired after a long day at work.
- The stolen car was found by the police.
- This is a well-written article.
These examples show how versatile the past participle is in English. Whether you are talking about completed actions, describing something, or forming passive sentences, it plays a crucial role.
📝 Past Participle Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Try to fill in the blanks with the correct past participle form of the verbs in parentheses. This exercise will help you practice using past participles in different sentence structures.
- She has ________ (write) a beautiful poem.
- The window was ________ (break) during the storm.
- They have ________ (finish) their homework already.
- The cake was ________ (bake) to perfection.
- He has never ________ (see) such a large crowd before.
- The letter has been ________ (send) to the wrong address.
- I had ________ (lose) my keys before I found them again.
- The movie was ________ (direct) by a famous filmmaker.
- We have ________ (travel) to many countries in Europe.
- The report has been ________ (review) by the manager.
- She had ________ (break) her phone last week.
- The books ________ (arrive) yesterday.
- They have ________ (choose) the best candidate for the job.
- The door was ________ (lock) before we left.
- He has ________ (teach) English for over ten years.
- The project was ________ (complete) ahead of schedule.
- I have never ________ (hear) that song before.
- The picture was ________ (take) by a professional photographer.
- We had ________ (forget) to call you earlier.
- The tickets have been ________ (book) for the concert.
✔️ Check Your Answers for the Past Participle Exercise
- She has written a beautiful poem.
- The window was broken during the storm.
- They have finished their homework already.
- The cake was baked to perfection.
- He has never seen such a large crowd before.
- The letter has been sent to the wrong address.
- I had lost my keys before I found them again.
- The movie was directed by a famous filmmaker.
- We have traveled to many countries in Europe.
- The report has been reviewed by the manager.
- She had broken her phone last week.
- The books were arrived yesterday.
- They have chosen the best candidate for the job.
- The door was locked before we left.
- He has taught English for over ten years.
- The project was completed ahead of schedule.
- I have never heard that song before.
- The picture was taken by a professional photographer.
- We had forgotten to call you earlier.
- The tickets have been booked for the concert.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Past Participle
1. What is a past participle in English?
The past participle is a verb form used with auxiliary verbs to form perfect tenses and passive voice. It often ends in -ed for regular verbs (e.g., walked, played) but can be irregular (e.g., gone, written).
2. How do I form the past participle for regular verbs?
For most regular verbs, simply add -ed to the base verb:
- walk → walked
- jump → jumped
- clean → cleaned
3. Are all past participles formed by adding -ed?
No, many verbs are irregular and have unique past participle forms that you need to memorize, such as:
- go → gone
- write → written
- break → broken
4. Can past participles be used as adjectives?
Yes! Past participles often describe nouns, showing a state or condition:
- a broken window
- a finished project
- an excited child
5. How do I use the past participle in perfect tenses?
Combine the auxiliary verbs have/has/had with the past participle:
- I have eaten.
- She had left before I arrived.
6. Can all verbs be used in passive voice with past participles?
Most transitive verbs (verbs that take an object) can be used in passive voice:
- The letter was sent.
- The cake was baked.
Intransitive verbs (no object), like “arrive,” cannot be passive.
7. How do I know if a verb is regular or irregular?
Regular verbs follow the simple -ed rule; irregular verbs have unique past participle forms. You can check in a dictionary or a verb list.
8. Is the past participle the same as the past tense?
Not always. For regular verbs, yes (walked is both past tense and past participle), but for irregular verbs, the past participle may differ:
- Past tense: I went to the store.
- Past participle: I have gone to the store.
9. Can past participles be used without auxiliary verbs?
Yes, as adjectives or in perfect participle phrases:
- The broken vase lay on the floor.
- Having finished the work, she rested.
10. How can I improve my use of past participles?
Practice using them in sentences, learn irregular verb lists, and read English texts carefully. Exercises like fill-in-the-blanks also help!
📌 Key Takeaways: Past Participle Summary and Important Points
- The past participle is a special verb form used mainly in perfect tenses and passive voice.
- For regular verbs, form the past participle by adding -ed (e.g., walked, cleaned).
- Many irregular verbs have unique past participle forms that must be memorized (e.g., gone, written, broken).
- The past participle is often used with auxiliary verbs have, has, or had to form perfect tenses.
- It is combined with forms of to be (is, was, were) to create the passive voice.
- Past participles can act as adjectives to describe states or conditions (e.g., broken window, excited child).
- Not all verbs can be used in passive voice—only those that take an object (transitive verbs).
- The past participle is not always the same as the simple past tense, especially for irregular verbs.
- Regular practice with examples, exercises, and reading helps master past participles.
- Watch out for common mistakes such as confusing past tense and past participle or using intransitive verbs in passive constructions.
🎯 Conclusion: Mastering the Past Participle for Confident English
Understanding the past participle is essential for speaking and writing clear, correct English. Whether you’re forming perfect tenses like the present perfect or crafting sentences in the passive voice, mastering past participles will boost your grammar skills and help you communicate with confidence.
Remember, while regular verbs are easy to master with the simple -ed ending, irregular verbs require practice and memorization. Use the tips, examples, and exercises in this guide to sharpen your skills every day. Soon, using the past participle will feel natural and effortless!
Keep practicing, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes—they are stepping stones to mastery. For more helpful lessons, practical tips, and engaging exercises, visit My Language Classes Blog.
Follow us on Instagram for quick daily language tips, and subscribe to our YouTube channel My Language Classes for detailed video lessons that make learning English fun and easy!
Your journey to fluent, confident English starts now. Let’s keep learning together!
Keep learning, keep growing — you’ve got this!👇
A Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future)
Mastering the Simple Present Tense: A Complete Guide
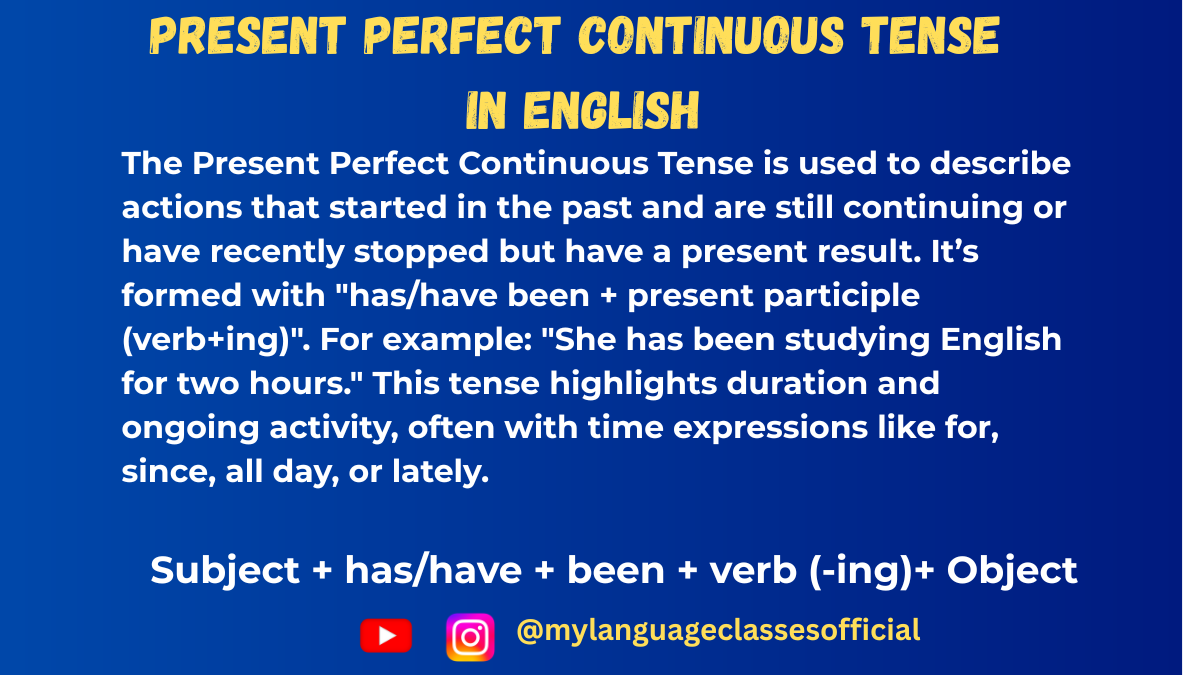
The Present Perfect Tense in English
Present Continuous Tense In English: A Complete Guide
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English
Articles in English: A, An, and The
Understanding Material Nouns in English: Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Definite Article in English: The
-

Future Perfect Tense in English: Complete Guide with Easy Rules, Examples, and Exercises
Have you ever wondered how to talk about something that will be finished before a certain time in the future? Maybe you’ve said things like, “I will have finished my homework by dinner” or “They will have arrived before we leave.” If so, you’ve already used the Future Perfect Tense in English!
The Future Perfect Tense may sound complicated, but it’s actually quite simple once you understand how it works. This powerful tense helps you describe actions that will be completed before another time or action in the future. It’s often used in daily conversation, storytelling, and formal writing. Whether you’re preparing for an English exam, improving your spoken English, or just curious about how English works, this guide will help you master the Future Perfect Tense with ease.
In this friendly and easy-to-follow post, you’ll learn:
- What the Future Perfect Tense is
- When and how to use it
- Common grammar rules and mistakes
- Real-life examples
- Practice exercises to test your skills
So, let’s dive in and unlock the future—one sentence at a time!
📘 What Is the Future Perfect Tense? Explanation and Overview
The Future Perfect Tense is a verb tense used to describe an action that will be completed before a specific time in the future. It tells us what will have happened by a certain point.
🔍 Simple Definition:
The Future Perfect Tense shows that something will be finished before another time or action in the future.
🧠 Structure of the Future Perfect Tense:
Subject + will have + past participle (V3 of the verb)
✅ Examples:
- I will have eaten dinner by 8 PM.
- She will have finished her homework before school starts.
- They will have arrived at the airport by noon.
These examples help us imagine an action that is done before something else in the future happens.
🗣️ Why Is the Future Perfect Tense Important?
The Future Perfect Tense is important because:
- It gives clarity about when an action will be completed.
- It helps us organize future plans clearly.
- It is useful in writing, speaking, exams, and everyday life.
🔑 Key Phrases Often Used with Future Perfect Tense:
Here are some common time expressions that often go with the Future Perfect Tense:
- By tomorrow
- By next week
- By the time…
- Before she arrives
- In two hours
- By the end of the day
🔁 These time phrases help us understand when the action will be completed.
📢 Real-World Use:
Whether you’re saying:
- “I will have completed the project by Friday.”
- “He will have learned English before the trip.”
…you are showing something will already be done when something else happens in the future.
🗓️ Everyday Sentences Using the Future Perfect Tense: 10 Common Examples
To truly understand how the Future Perfect Tense works, it helps to see it in real-life, everyday examples. These sentences show how native speakers use this tense to talk about things that will be completed before a certain future time.
Each example below includes a clear subject, the “will have + past participle” structure, and a time reference.
🔟 Common Future Perfect Tense Sentences:
- I will have finished my homework by 7 PM.
- She will have cooked dinner before we get home.
- They will have arrived at the hotel by midnight.
- We will have completed the project before the deadline.
- He will have left the office by the time you arrive.
- You will have learned a lot of new words by the end of this week.
- My parents will have reached home before the storm starts.
- The kids will have gone to bed by 9 o’clock.
- I will have saved enough money to buy a new laptop by next month.
- She will have visited five countries by the end of the year.
💡 Notice:
- Each sentence talks about an action completed in the future before a specific moment.
- These are all real, practical, and natural-sounding.
- Perfect for both casual conversation and formal writing.
🕒 When to Use the Future Perfect Tense: All the Key Situations
Knowing when to use the Future Perfect Tense can help you express yourself more clearly and sound more fluent in English. This tense is especially useful when you’re talking about what will be done or completed before something else happens in the future.
Here are the main situations where the Future Perfect Tense is the right choice:
✅ 1. To Show Completion Before a Specific Future Time
Use this tense when you want to show that something will be finished before a certain time or date in the future.
- By 10 AM, I will have written the report.
- They will have graduated by June.
✅ 2. To Indicate Completion Before Another Future Action
This is when one action will be completed before another action starts in the future.
- He will have left before you arrive.
- We will have eaten dinner before the movie begins.
✅ 3. To Talk About Achievements by a Future Time
Use it to describe something that will be achieved or completed by a future point.
- I will have saved enough to buy a car by December.
- She will have read 50 books by the end of this year.
✅ 4. In Predictions or Expectations About the Future
This tense is used when you want to predict that something will be finished at a certain time in the future.
- The builders will have finished the house by next month.
- The plane will have landed by the time we reach the airport.
✅ 5. In Passive Voice Statements (Advanced Use)
The Future Perfect can also be used in the passive voice, especially in formal English.
- The work will have been completed by Friday.
- All the documents will have been signed before the deadline.
✅ 6. In Conditional Sentences (if necessary)
Sometimes it appears in conditional sentences where you imagine future events.
- If he keeps practicing, he will have mastered English by the end of the year.
🔑 Summary of When to Use Future Perfect:
Situation Example Completion before future time I will have slept by midnight. Completion before another action She will have gone before I arrive. Future achievements They will have saved $1,000 by May. Predictions The sun will have set before we finish. Passive voice use The room will have been cleaned. Conditionals He will have learned enough if he studies daily.
🧩 How to Conjugate Verbs in the Future Perfect Tense: Conjugation Rules
Understanding how to form and conjugate verbs in the Future Perfect Tense is key to using it correctly in speaking and writing. The good news is, it follows a simple and regular pattern.
🔧 Basic Structure:
Subject + will have + past participle (V3)
- The verb “will have” stays the same for all subjects.
- The main verb is always in the past participle form (also called V3).
📘 Conjugation Chart for Regular Verbs
Subject Future Perfect Form I will have worked You will have worked He/She/It will have worked We will have worked They will have worked ✅ Example:
- By this evening, I will have cleaned the kitchen.
- They will have played three matches by tomorrow.
📕 Conjugation Chart for Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs don’t follow a fixed pattern, so their past participle forms are different. But the structure “will have + past participle” still stays the same.
Verb Base Past Participle (V3) Example go gone She will have gone to bed. do done You will have done your task. eat eaten We will have eaten lunch. see seen I will have seen that movie. write written He will have written the letter.
🔄 Negative Form
To make a negative sentence, simply add “not” after will.
📝 Structure:
Subject + will not have + past participleExamples:
- I will not have finished the book by then.
- She won’t have arrived before the meeting starts.
❓ Question Form
To ask a question, start with “Will”, then the subject, then “have”, followed by the past participle.
📝 Structure:
Will + subject + have + past participle?Examples:
- Will he have completed his work by Friday?
- Will they have reached the station in time?
📌 Tip: Remember the V3 Form
If you’re unsure about the past participle of a verb, check a list of irregular verbs or use a dictionary. Getting the verb form right is crucial for making correct Future Perfect sentences.
📚 Future Perfect Tense Grammar Rules You Need to Know
The Future Perfect Tense follows a set of clear grammar rules that help us express future actions that will be completed before another time or event. Once you learn these simple rules, you’ll feel confident using this tense in speaking and writing.
✅ Rule 1: Use “Will Have” for All Subjects
No matter the subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), the form stays the same:
Subject + will have + past participle (V3)
Examples:
- I will have visited the museum.
- They will have left by 6 PM.
- She will have graduated by next year.
✅ Rule 2: Always Use the Past Participle (V3) of the Verb
The main verb in the Future Perfect Tense is always in its past participle form.
Examples:
- Work → worked: He will have worked all day.
- Go → gone: She will have gone to the store.
- Write → written: I will have written the essay.
✅ Rule 3: Use Time Expressions to Show the Future Moment
The Future Perfect is linked to a time in the future. Use time phrases to give your sentence meaning and clarity.
Common expressions:
- By tomorrow
- Before he comes
- By 6 PM
- In two weeks
- By the end of the year
Examples:
- She will have left by the time we arrive.
- I will have cleaned the room by 5 o’clock.
✅ Rule 4: Negative Form — Use “Will Not Have” or “Won’t Have”
To make the Future Perfect negative, insert “not” after “will.”
Examples:
- I will not have eaten before the party.
- He won’t have studied for the test.
✅ Rule 5: Question Form — Start with “Will”
To ask a question in the Future Perfect, follow this word order:
Will + subject + have + past participle + (rest of the sentence)?
Examples:
- Will you have completed the report by noon?
- Will she have arrived before the show starts?
✅ Rule 6: Passive Voice in Future Perfect (Advanced)
Sometimes, the Future Perfect is used in the passive voice.
📝 Structure:
Subject + will have been + past participleExamples:
- The cake will have been baked by 3 PM.
- The emails will have been sent before the meeting.
✅ Rule 7: Use for Predictions, Expectations, and Goals
You can use the Future Perfect to talk about:
- Things you expect to finish
- Goals you plan to reach
- Events that will be done before something else
Examples:
- He will have finished college by 2026.
- They will have reached their goal soon.
🔁 Quick Recap Table
Type Rule Example Positive Will have + V3 I will have left by noon. Negative Will not have + V3 She will not have eaten. Question Will + subject + have + V3 Will you have studied? Passive Will have been + V3 The work will have been done.
💡 Important Tips for Using the Future Perfect Tense Correctly
The Future Perfect Tense is not used as often as other tenses in everyday conversation, which is why learners sometimes feel unsure about it. But with the right tips and habits, you can use it naturally and confidently. Below are some smart and easy tips to help you master this tense.
✅ 1. Always Include a Time Reference
The Future Perfect Tense must include a time reference—either stated clearly or understood from context. This helps show when the action will be completed.
🔸 Good:
- I will have finished the book by tomorrow.
❌ Not clear:
- I will have finished the book. (When?)
✅ 2. Know the Past Participle (V3) Form of the Verb
Make sure you know the past participle of the verb you’re using. For regular verbs, it’s easy. But for irregular ones, you need to memorize them.
Examples:
- do → done, go → gone, take → taken, see → seen
📝 Practice:
Make flashcards of common irregular past participles and review them often.
✅ 3. Use Future Perfect for Clear Deadlines or Goals
This tense is perfect when you want to set goals, track deadlines, or show what will be done at a certain point.
Examples:
- We will have completed the website by next Monday.
- She will have saved enough to buy a car by July.
✅ 4. Don’t Use Future Time Words with Past Tenses
Sometimes learners mix the Future Perfect with Past Tenses and future time phrases. Don’t say:
❌ Wrong: I finished the work by next week.
✅ Correct: I will have finished the work by next week.
✅ 5. Use It to Sound Professional and Clear
The Future Perfect is commonly used in:
- Business settings
- Academic writing
- Future planning
- Goal setting
It sounds organized, professional, and precise. Use it when talking about what will be accomplished.
✅ 6. Don’t Confuse It with Future Simple or Future Continuous
It’s easy to confuse these three future tenses. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Tense Use Example Future Simple Action in the future I will eat at 8 PM. Future Continuous Action in progress in the future I will be eating at 8 PM. Future Perfect Action finished before a future time I will have eaten by 8 PM.
✅ 7. Practice With Time Expressions
Get used to using the following phrases with the Future Perfect:
- By the time
- Before
- In two hours
- By the end of the day
- By next week
- Within a month
🧠 Pro Tip:
When in doubt, ask yourself:
“Will this action be done before a future time or event?”
If yes, then the Future Perfect Tense is probably the right choice.
❌ Common Mistakes with the Future Perfect Tense and How to Fix Them
Even experienced learners sometimes make mistakes when using the Future Perfect Tense. The good news is, most of these errors are easy to fix once you recognize them. Let’s look at some of the most common ones and learn how to correct them.
❌ Mistake 1: Using the Wrong Verb Form
Error:
She will have go to the store.
Why it’s wrong:
The main verb must be in the past participle (V3) form.✅ Correct:
She will have gone to the store.
❌ Mistake 2: Forgetting the Time Expression
Error:
They will have finished.
Why it’s wrong:
Without a time reference, the sentence feels incomplete and confusing.✅ Correct:
They will have finished by 8 PM.
✅ Better:
They will have finished the meeting before you arrive.
❌ Mistake 3: Using “Will Have” with Past Time
Error:
I will have eaten by yesterday.
Why it’s wrong:
The Future Perfect Tense is used for future actions, not past.✅ Correct:
I had eaten by yesterday. (Past Perfect)
✅ Or:
I will have eaten by tomorrow. (Future Perfect)
❌ Mistake 4: Confusing Future Perfect with Future Simple
Error:
She will arrive by 5 PM.
Why it’s confusing:
This is in Future Simple, and while correct, it doesn’t show completion before a certain time.✅ Future Perfect:
She will have arrived by 5 PM.
(This means: She’ll already be there when the clock hits 5.)
❌ Mistake 5: Overusing Future Perfect in Casual Speech
Error:
I will have finished my coffee now.
Why it’s wrong:
In casual or real-time situations, use Present Perfect or Simple Past.✅ Correct:
I have finished my coffee.
✅ Or:
I just finished my coffee.
❌ Mistake 6: Incorrect Question Form
Error:
Will have you finished the book?
Why it’s wrong:
The correct word order must be followed.✅ Correct:
Will you have finished the book?
❌ Mistake 7: Using Future Perfect Without Understanding Its Meaning
Error:
He will have playing the guitar by next year.
Why it’s wrong:
“Playing” is the present participle, not the past participle.✅ Correct:
He will have played the guitar by next year.
🛠 Quick Fix Checklist
Before using the Future Perfect Tense, ask yourself:
- ✔️ Does it describe something completed before a point in the future?
- ✔️ Did I use “will have + V3” correctly?
- ✔️ Did I include a clear future time reference?
- ✔️ Is the verb in the correct past participle form?
- ✔️ Did I follow the correct sentence structure?
If your answer is “yes” to all, then you’re doing it right!
✨ 20 Future Perfect Tense Example Sentences for Better Understanding
Seeing plenty of clear examples is one of the best ways to master the Future Perfect Tense. Below are 20 carefully chosen sentences that show how to use this tense naturally in different situations. Notice the use of “will have + past participle” and time expressions.
- By next week, I will have finished reading this book.
- She will have completed her project before the deadline.
- They will have traveled to five countries by the end of the year.
- We will have moved into our new house by June.
- He will have learned how to swim by the summer vacation.
- By tomorrow morning, you will have received the package.
- The train will have left the station by the time we arrive.
- I will have saved enough money to buy a car next month.
- She will have finished cooking dinner by 7 PM.
- They will have fixed the car before the weekend.
- By the time you get here, I will have cleaned the entire house.
- We will have watched all the episodes by the time the new season starts.
- He will have passed the exam if he studies hard.
- The team will have won the championship by this time next year.
- I will have written five articles by the end of this week.
- She will have arrived at the airport before the flight takes off.
- By next month, they will have opened their new restaurant.
- We will have finished the meeting before lunch.
- He will have repaired the computer by tomorrow afternoon.
- I will have visited all my relatives by the time the holidays end.
These examples cover everyday, professional, and travel contexts, giving you a solid idea of when and how to use the Future Perfect Tense.
📝 Future Perfect Tense Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Now it’s your turn to practice! Fill in the blanks using the Future Perfect Tense. Remember to use “will have” + past participle and include the correct verb form.
- By 8 PM, she __________ (finish) her homework.
- They __________ (arrive) before the movie starts.
- I __________ (complete) the report by tomorrow.
- We __________ (move) to a new city by next year.
- He __________ (save) enough money by the end of the month.
- By next summer, she __________ (learn) to drive.
- The train __________ (leave) the station by 5 PM.
- You __________ (read) all the books on the list by December.
- They __________ (build) the new bridge by next spring.
- I __________ (finish) cooking dinner before you get home.
- By the time you call, I __________ (send) the email.
- We __________ (visit) five countries by the end of the trip.
- She __________ (write) three novels by 2025.
- The students __________ (take) the exam before noon.
- He __________ (fix) the car by tomorrow afternoon.
- By next week, I __________ (practice) piano for 100 hours.
- They __________ (open) the new shop by Christmas.
- I __________ (clean) the house before the guests arrive.
- We __________ (finish) the project by Friday.
- She __________ (arrive) at the airport before the flight leaves.
✅ Check Your Answers for the Future Perfect Tense Exercise
- By 8 PM, she will have finished her homework.
- They will have arrived before the movie starts.
- I will have completed the report by tomorrow.
- We will have moved to a new city by next year.
- He will have saved enough money by the end of the month.
- By next summer, she will have learned to drive.
- The train will have left the station by 5 PM.
- You will have read all the books on the list by December.
- They will have built the new bridge by next spring.
- I will have finished cooking dinner before you get home.
- By the time you call, I will have sent the email.
- We will have visited five countries by the end of the trip.
- She will have written three novels by 2025.
- The students will have taken the exam before noon.
- He will have fixed the car by tomorrow afternoon.
- By next week, I will have practiced piano for 100 hours.
- They will have opened the new shop by Christmas.
- I will have cleaned the house before the guests arrive.
- We will have finished the project by Friday.
- She will have arrived at the airport before the flight leaves.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Future Perfect Tense
Here are some common questions learners ask about the Future Perfect Tense, answered clearly and simply.
1. What is the Future Perfect Tense used for?
The Future Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future. For example:
- By next year, I will have graduated from college.
2. How do you form the Future Perfect Tense?
Use “will have” + past participle (V3) of the verb.
Example:- She will have finished her work by 6 PM.
3. Can we use contractions in the Future Perfect?
Yes! Contractions like “I’ll have,” “she’ll have,” “they’ll have” are common in spoken and informal English.
Example:- I’ll have completed the project by tomorrow.
4. Is the Future Perfect Tense common in daily conversation?
Not very common in casual talk, but often used in formal speech, writing, and planning to describe future completions.
5. What are some common time expressions with the Future Perfect?
- By the time
- Before
- By next week/month/year
- By then
- Within a few days
6. Can we use the Future Perfect with modal verbs?
Usually, the Future Perfect uses will have, but modal verbs like might have or could have express possibility in the past or future perfect context.
Example:- She might have finished by now.
- They could have left before we arrived.
7. How is the Future Perfect different from the Present Perfect?
- Future Perfect: Action completed before a future time.
- Present Perfect: Action completed before now (the present).
Example: - Future Perfect: I will have eaten by 7 PM.
- Present Perfect: I have eaten already.
8. Can the Future Perfect describe an action that is still ongoing?
No. The Future Perfect describes an action that will be finished by a certain time. For ongoing actions, use the Future Continuous Tense.
Example:- Future Perfect: By 5 PM, she will have left.
- Future Continuous: At 5 PM, she will be leaving.
📌 Key Takeaways: Future Perfect Tense Summary and Important Points
Let’s quickly review the most important things you need to remember about the Future Perfect Tense. These key points will help you use this tense correctly and confidently.
- The Future Perfect Tense expresses actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future.
- It is formed using “will have” + past participle (V3) of the verb.
- Common time expressions used with this tense include: by then, by the time, before, by next week/month/year.
- Use it to show the completion of future actions, plans, or events.
- The past participle must be correct—regular verbs add “-ed,” irregular verbs have unique forms (e.g., gone, done, written).
- It’s different from the Present Perfect (which relates to the past and present) and Future Continuous (which talks about ongoing future actions).
- Don’t forget to include a clear time reference to make the meaning clear.
- Common mistakes include wrong verb forms, missing time expressions, and confusing with other tenses.
- This tense is often used in formal writing, plans, predictions, and future deadlines.
- You can use contractions like I’ll have, she’ll have for informal speech.
- Remember to practice with sentences and exercises to build your confidence and fluency.
🚀 Conclusion: Master the Future Perfect Tense and Speak with Confidence!
Understanding the Future Perfect Tense opens up a whole new level of clarity when talking about future plans, deadlines, and events. This powerful tense helps you express what will have been completed by a certain time, making your English sound precise and professional. Whether you’re planning your career goals, telling stories about the future, or discussing schedules, the Future Perfect Tense is your go-to tool for clear communication.
Remember, mastering this tense takes practice, but with the right examples, exercises, and tips shared in this guide, you are well on your way to using it naturally and confidently.
Ready to take your English to the next level?
👉 Visit My language Classes for more in-depth grammar guides, language tips, and free resources.
👉 Follow us on Instagram for daily language learning inspiration and mini-lessons.
👉 Subscribe to our YouTube channel My Language Classes for easy-to-follow videos that make learning English fun and effective.Keep practicing, stay curious, and soon you’ll find yourself speaking and writing like a true English expert!
Keep learning, keep growing — you’ve got this!👇
A Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future)
Mastering the Simple Present Tense: A Complete Guide
The Present Perfect Tense in English
Present Continuous Tense In English: A Complete Guide
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English
Articles in English: A, An, and The
Understanding Material Nouns in English: Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Definite Article in English: The
-

Adverbs of Manner in Spanish: Learn How to Use “-mente” Like a Native
When learning Spanish, one of the keys to sounding natural and fluent is mastering adverbs of manner—those handy little words that describe how an action is performed. Just like in English (e.g., quickly, gently, carefully), Spanish has its own set of adverbs that can bring clarity, precision, and flair to your sentences.
In this post, we’ll break down how to form and use adverbs of manner in Spanish, highlight some tricky exceptions, and help you avoid common learner mistakes. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to polish your Spanish expression, this guide will give you the tools to speak and write more naturally.
Let’s dive in and explore the how behind every action—en español.

🧩 What Are Adverbs of Manner in Spanish?
If you’re learning Spanish grammar, one key topic to understand is adverbs of manner. These are words that tell us how an action is performed, and they’re essential for speaking and writing Spanish more fluently.
✅ Definition:
Adverbs of manner in Spanish (adverbios de modo) describe how something happens—in other words, they explain the manner in which an action takes place.
For example:
- Ella canta dulcemente.
(She sings sweetly.) - Él escribe cuidadosamente.
(He writes carefully.)
In both sentences, the adverb gives us more detail about how the action is being done. This is a big part of building more natural, expressive sentences in Spanish.
🎯 Why Are Adverbs of Manner Important?
Understanding how to use Spanish adverbs of manner helps learners create more specific and natural sentences. It’s one of the key grammar skills needed to speak Spanish fluently and with confidence.
Whether you’re a beginner trying to learn basic Spanish grammar or an intermediate learner looking to improve your writing, this topic is essential. You’ll often come across these adverbs in conversations, books, and media—so the more familiar you are with them, the better!
📚 Difference Between Adverbs of Manner and Other Spanish Adverbs
Spanish adverbs come in many forms—not just adverbs of manner. To really learn Spanish adverbs effectively, it helps to compare the different types.
Type of Adverb Question Answered Example English Translation Adverb of Manner ¿Cómo? Habla suavemente She speaks softly Adverb of Time ¿Cuándo? Llegó temprano He arrived early Adverb of Place ¿Dónde? Está aquí She is here Adverb of Quantity ¿Cuánto? Estudia mucho He studies a lot Adverb of Cause ¿Por qué? No vino porque llovía He didn’t come because it was raining So, while adverbs of manner in Spanish grammar describe the way an action is done, other adverbs focus on time, place, quantity, or reason.
How to Form Adverbs of Manner in Spanish
Once you understand what adverbs of manner in Spanish are, the next step is learning how to form them. Luckily, Spanish grammar rules for this are quite regular — especially compared to English!
✅ Basic Rule: Add “-mente” to the Feminine Form of the Adjective
To form most Spanish adverbs of manner, simply take the feminine singular form of an adjective and add -mente, which is the Spanish equivalent of the English “-ly” (as in slowly, quickly, happily).
📌 Examples:
- rápido → rápidamente (quick → quickly)
- fácil → fácilmente (easy → easily)
- claro → claramente (clear → clearly)
- correcto → correctamente (correct → correctly)
So if you’re wondering how to use adverbs of manner in Spanish, this is your go-to rule!
⚠️ Spelling & Accent Notes
When the original adjective has an accent, it usually keeps it after adding -mente.
- fácil → fácilmente
- cómodo → cómodamente
This follows standard Spanish spelling and pronunciation rules, so the stress stays natural.
❗ Irregular & Common Exceptions
Not all adverbs follow the -mente rule. Some common Spanish adverbs of manner are formed irregularly or don’t use -mente at all. These are important to memorize:
📌 Examples:
- bien (well)
- mal (badly)
- despacio (slowly)
- así (like this / in this way)
These often appear in everyday conversations and are frequently used by native Spanish speakers.
⚠️ Adjectives Used as Adverbs
Some adjectives can function as adverbs without changing form. These are often used after verbs.
Examples:
- Corre rápido. (Run fast.)
- Habla claro. (Speak clearly.)
- Camina despacio. (Walk slowly.)
💡 Quick Tip for Learners
If two adverbs with -mente appear together, Spanish often only adds -mente to the last one.
🗣️ Example:
Habló clara y cuidadosamente.
(She spoke clearly and carefully.)This keeps the sentence natural and fluid — a great trick to sound more fluent!
List of Common Adverbs of Manner and Example
Spanish English Meaning Example Sentence Bien Well Ella canta bien. (She sings well.) Mal Badly, poorly Hiciste el trabajo mal. (You did the job badly.) Rápido / Rápidamente Fast, quickly Terminaron la tarea rápido. (They finished the homework fast.) Despacio Slowly Habla despacio, por favor. (Speak slowly, please.) Suavemente Gently Tocó la puerta suavemente. (He knocked on the door gently.) Claramente Clearly Explicó el problema claramente. (She explained the problem clearly.) Cuidadosamente Carefully Maneja cuidadosamente. (Drive carefully.) Fácilmente Easily Puedo resolver esto fácilmente. (I can solve this easily.) Fuertemente Strongly El viento soplaba fuertemente. (The wind was blowing strongly.) Alegremente Happily Bailaron alegremente en la fiesta. (They danced happily at the party.)
Things to Keep in Mind When Using Adverbs of Manner
1. Placement of Adverbs
- In Spanish, adverbs of manner generally go after the verb they modify:
- Ella canta bien. (She sings well.)
- If modifying an adjective or another adverb, they come before it:
- Está muy feliz. (She is very happy.)
2. Agreement of Adverbs
- Unlike adjectives, adverbs do not change for gender or number:
- Ellos trabajan rápidamente. (They work quickly.)
- Ella habla rápidamente. (She speaks quickly.)
3. Difference Between Adjective and Adverb Usage
- Incorrect: Ella es bien en matemáticas. ❌
- Correct: Ella es buena en matemáticas. ✅
- “Bien” is an adverb, while “buena” is an adjective.
- Incorrect: Él corre rápidamente en la carrera. ❌
- Correct: Él corre rápido en la carrera. ✅
- Some adjectives can function as adverbs without “-mente.”
Expressions with Adverbs of Manner in Daily Life
Here are some commonly used expressions with adverbs of manner:
Expression Meaning “Más vale tarde que nunca.” Better late than never. “Habla claro.” Speak clearly. “Hazlo bien o no lo hagas.” Do it well or don’t do it. “Trabaja duro.” Work hard. “Pídelo amablemente.” Ask for it politely. “Siempre actúa con prudencia.” Always act wisely. “No conduzcas tan rápido.” Don’t drive so fast.
⚠️ 3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even advanced learners of Spanish make errors with adverbs of manner. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
❌ 1. Using the adjective instead of the adverb
- Incorrect: Él habla claro.
- Correct: Él habla claramente.
(Adverbs describe how someone does something — not adjectives.)
❌ 2. Forgetting the feminine form before adding -mente
- Incorrect: rápido → rápidomente
- Correct: rápido → rápidamente
Always use the feminine singular form of the adjective.
❌ 3. Translating directly from English
English: She runs fast.
Learners often try: Ella corre rápida.
Correct: Ella corre rápidamente / Ella corre rápido (when used informally)
🔍 4. Tricky Points and Special Cases
Some cases don’t follow the usual -mente pattern. These are exceptions and commonly used alternatives:
✅ Informal and Irregular Adverbs:
- bien (well)
- mal (badly)
- despacio (slowly)
- así (like this/that)
✅ Double Adverbs:
When using two -mente adverbs, only the last one keeps the suffix:
- Ella habló clara y cuidadosamente.
✅ Sentence Placement:
Adverbs of manner usually follow the verb:
- Canta suavemente.
But they can also go at the end: - Habló rápidamente.
📝 Example Sentences with Translation
- Ella habla claramente. — She speaks clearly.
- Juan corre rápidamente. — Juan runs quickly.
- Ellos trabajan cuidadosamente. — They work carefully.
- Ella escribe lentamente. — She writes slowly.
- Él responde educadamente. — He responds politely.
- María canta dulcemente. — María sings sweetly.
- El bebé duerme tranquilamente. — The baby sleeps peacefully.
- El estudiante respondió correctamente. — The student answered correctly.
- Cocinamos fácilmente con esta receta. — We cook easily with this recipe.
- Hablan amablemente con los clientes. — They speak kindly with the customers.
- El perro camina silenciosamente. — The dog walks silently.
- Marta resolvió el problema inteligentemente. — Marta solved the problem cleverly.
- Él contestó mal. — He answered badly.
- Bailaron alegremente. — They danced happily.
- Reaccionó violentamente. — He reacted violently.
- Cocinó rápido. — He cooked fast.
- Lo hizo bien. — He did it well.
- Llegaron puntualmente. — They arrived punctually.
- El niño contestó tímidamente. — The boy answered shyly.
- Nos miraron extrañamente. — They looked at us strangely.
🧠 Exercise: Fill in the Blanks
Fill in each blank with the correct Spanish adverb of manner:
- Ella canta ___ (sweet).
- Él corre ___ (fast).
- María escribe ___ (slow).
- Respondió ___ (politely).
- Trabajan ___ (careful).
- Marta resolvió el examen ___ (intelligent).
- Juan llegó ___ (punctual).
- Ellos hablaron ___ (friendly).
- Lo hizo ___ (well).
- El perro entró ___ (silent).
- El niño respondió ___ (shy).
- Ella cocinó ___ (easy).
- Gritó ___ (angry).
- Me miraron ___ (strange).
- Él actuó ___ (honest).
- Completó la tarea ___ (correct).
- El bebé duerme ___ (peaceful).
- Manejó ___ (dangerous).
- Él bailó ___ (happy).
- Lo resolvió ___ (simple).
✅ Answers
- Ella canta dulcemente.
- Él corre rápidamente.
- María escribe lentamente.
- Respondió educadamente.
- Trabajan cuidadosamente.
- Marta resolvió el examen inteligentemente.
- Juan llegó puntualmente.
- Ellos hablaron amablemente.
- Lo hizo bien.
- El perro entró silenciosamente.
- El niño respondió tímidamente.
- Ella cocinó fácilmente.
- Gritó violentamente.
- Me miraron extrañamente.
- Él actuó honestamente.
- Completó la tarea correctamente.
- El bebé duerme tranquilamente.
- Manejó peligrosamente.
- Él bailó alegremente.
- Lo resolvió simplemente.
📌 Summary: Key Points About Adverbs of Manner in Spanish
- Adverbs of manner (adverbios de modo) describe how an action is done.
- Most are formed by adding -mente to the feminine singular form of an adjective.
- Irregular and informal adverbs include: bien, mal, despacio, así.
- Adverbs typically come after the verb but can be placed at the end of the sentence.
- Avoid using adjectives instead of adverbs.
- Double adverbs only need -mente on the second one.
- Practice with real sentences and fill-in-the-blank activities helps internalize usage.
🏁 Conclusion: Mastering Spanish Adverbs of Manner
Learning how to use adverbs of manner in Spanish is a major step toward building richer, more expressive sentences. Whether you’re speaking or writing, these words help you describe actions with clarity and confidence. From understanding basic grammar rules to practicing real-life examples, you’ve now got a strong foundation for mastering adverbios de modo.
👉 Ready to go further?
Explore our section on Spanish grammar👉And if you found this guide helpful, don’t forget to subscribe to My language Classes, leave a comment, or share it with fellow learners!
👉Subscribe to My YouTube channel
👉Join our WhatsApp group for real time updates and discussion.
👉Follow on Instagarm
Check out our related post on Types of Adverbs in Spanish 👇👇
Adverbs of Time in Spanish: A Complete Guide
- Ella canta dulcemente.
-

Simple Future Tense in English: How to Use ‘Will’ and ‘Going to’ Like a Native Speaker
Do you want to speak confidently about future plans, dreams, or predictions in English? Whether you’re learning English as a second language or just brushing up your grammar skills, mastering the Simple Future Tense in English is a must. This powerful tense helps you talk about things that haven’t happened yet—but will soon. From planning a trip to making a promise, the simple future tense is your best friend for speaking like a native.
If you’ve ever wondered:
- “How do I say what I will do tomorrow?”
- “What’s the difference between ‘will’ and ‘going to’?”
- “How do native speakers talk about the future?”
—then you’re in the right place.
In this blog, you’ll learn everything you need to know about the Simple Future Tense, with plenty of easy examples, fun practice, and grammar tips that stick. Whether you’re using English in school, work, or travel, this guide will help you use the future tense naturally and clearly.
Let’s start with the basics.
📚 What Is the Simple Future Tense? Explanation and Overview
The Simple Future Tense is one of the most commonly used tenses in English. It’s how we talk about things that will happen after now. If you want to make predictions, promises, plans, or decisions, the simple future tense is the tool you need.
🔑 Definition
The Simple Future Tense describes an action that has not yet happened but will happen later. You can form this tense using two main structures:
- will + base verb
- be going to + base verb
Both forms are correct, but they are used in slightly different ways, which we’ll explain later in this blog.
🗣️ Keywords That Often Appear with the Simple Future Tense
When you see or hear these words, it’s usually a good sign that the sentence is in the future tense:
- Tomorrow
- Later
- Next (week, year, month, etc.)
- Soon
- In a few minutes/hours/days
- In the future
- Someday
- Tonight
🧠 Why Is It Important?
Understanding the simple future tense helps you:
- Talk about your plans: “I will visit my grandma next weekend.”
- Make promises: “I’ll help you with your homework.”
- Give warnings or predictions: “It’s going to rain later.”
- Respond to someone quickly: “Okay, I’ll call him now.”
No matter your age or level, if you want to sound fluent and clear in English, you need to know how to use the simple future tense.
🛠️ Basic Structures
Type Formula Example With “will” Subject + will + base verb She will cook dinner tonight. With “going to” Subject + be + going to + base verb They are going to travel next week. Let’s now look at how the simple future tense is used in everyday English sentences.
🗨️ Everyday Sentences Using the Simple Future Tense: 10 Common Examples
The best way to understand any grammar tense is to see it in action. Below are 10 simple future tense examples you can use in everyday English conversations. These examples use both “will” and “going to” forms, so you can get a feel for how both work naturally.
✨ Real-Life Examples Using “Will”:
- I will call you after dinner.
- She will finish her homework tonight.
- We will go to the beach next weekend.
- He will help you carry your bags.
- They will not come to the party. (Negative form)
🌟 Real-Life Examples Using “Going to”:
- I am going to watch a movie tonight.
- She is going to bake a cake for his birthday.
- We are going to meet at 5 PM.
- He is not going to join the football team. (Negative form)
- They are going to travel to Japan next year.
📝 Quick Notes:
- “Will” is often used for decisions made at the moment, promises, or predictions.
- “Going to” is often used when you’ve already decided to do something or see signs that something will happen soon.
As you read these sentences, imagine yourself using them in real situations—at home, school, or while chatting with friends.
🕒 When to Use the Simple Future Tense: All the Key Situations
The Simple Future Tense is more than just talking about “what’s next.” It’s used in many real-life situations where we express future plans, intentions, predictions, or quick decisions. Let’s break down all the key times when you should use the simple future tense.
🔮 1. To Make Predictions
We use the simple future tense when we think something will happen in the future, even if we’re not 100% sure.
- It will rain tomorrow.
- I think she will win the competition.
- People will live on Mars someday.
📅 2. To Talk About Future Plans or Intentions
When you already have a plan or decision, especially using “going to”, this is the form to use.
- I am going to visit my cousin next week.
- She’s going to start a new job in July.
- They are going to build a new house.
🎯 3. To Make Decisions at the Moment of Speaking
Use “will” when you decide to do something right now, often as a response to a situation.
- I’m tired. I will take a nap.
- You dropped your pen—I’ll get it.
- It’s cold. I’ll close the window.
🗣️ 4. To Make Promises or Offers
The word “will” is often used when you’re offering help or making a promise.
- I will help you with your project.
- Don’t worry—I’ll be there on time.
- We’ll never forget your kindness.
⚠️ 5. To Warn or Threaten (Lightly)
It can also be used to talk about something that may go wrong—or to give a gentle warning.
- You’ll get hurt if you’re not careful.
- If you lie again, I’ll be very angry.
- He’ll miss the bus if he doesn’t hurry.
🧪 6. To Talk About Scientific or General Truths in the Future
Even facts and logical outcomes can use the simple future tense.
- Water will boil at 100 degrees Celsius.
- The sun will rise at 6:30 AM tomorrow.
- Ice will melt in warm temperatures.
Knowing these situations will help you choose the right future form confidently. Whether you’re planning something or making a fast decision, the simple future tense is your go-to tool.
🛠️ How to Conjugate Verbs in the Simple Future Tense: Conjugation Rules
Using the Simple Future Tense becomes easy once you know how to form it correctly. In English, this tense doesn’t require changing the main verb into a different form—instead, you simply add “will” or “going to” in front of the base form of the verb.
Let’s learn how to conjugate verbs in both forms:
👉 “Will” + base verb
👉 “Be going to” + base verb
🔹 1. Using “Will” – The Quick and Simple Way
Structure:
Subject + will + base verbSubject Example I I will read a book. You You will enjoy the movie. He/She/It He will eat lunch at noon. We We will travel tomorrow. They They will play soccer. 🔄 Negative Form:
Subject + will not (won’t) + base verb- She will not (won’t) come to class.
- I won’t forget your birthday.
❓ Question Form:
Will + subject + base verb?- Will you come to the party?
- Will they finish the project?
🔹 2. Using “Going to” – The Planned Future
Structure:
Subject + be (am/is/are) + going to + base verbSubject Example I I am going to study English. You You are going to love this song. He/She/It She is going to cook dinner. We We are going to visit Grandma. They They are going to watch a movie. 🔄 Negative Form:
Subject + be + not + going to + base verb- I am not going to eat fast food.
- He isn’t going to stay late.
❓ Question Form:
Be + subject + going to + base verb?- Are you going to study tonight?
- Is she going to take the test?
📌 Helpful Tips:
- The main verb stays in base form (do, go, eat, etc.) no matter the subject.
- Use “will” when the future is uncertain or decided at the moment.
- Use “going to” when the action is already planned or certain.
📏 Simple Future Tense Grammar Rules You Need to Know
Understanding the grammar rules of the simple future tense helps you build correct, natural-sounding sentences. Whether you’re using “will” or “going to,” these rules will guide you step by step.
✅ Rule 1: Use the Base Form of the Verb
No matter which subject you use, the main verb always stays in its base form (no -s, -ed, or -ing).
- Correct: She will go to school.
- ❌ Wrong: She will goes to school.
✅ Rule 2: Use “Will” for Quick Decisions, Offers, and Promises
“Will” is best used when:
- You decide something on the spot
- You make an offer
- You make a promise
Examples:
- I will call you later. (promise)
- Don’t worry, I will help you. (offer)
- It’s hot. I will open the window. (quick decision)
✅ Rule 3: Use “Be Going to” for Plans and Intentions
When something is already planned or clearly going to happen, use “going to.”
Examples:
- I am going to visit my aunt tomorrow. (already planned)
- Look at those dark clouds! It is going to rain. (clear sign)
✅ Rule 4: Form Negatives with “Will Not” or “Be Not Going To”
- She won’t join us for dinner.
- We aren’t going to travel this summer.
✅ Rule 5: Ask Questions by Inverting the Verb
With “will”, place it before the subject:
- Will he come to the meeting?
With “going to”, move the be verb before the subject:
- Are you going to study tonight?
✅ Rule 6: Do Not Use “Will” After “If” in Conditional Sentences
In first conditional sentences, use present simple after “if”, and will in the main clause.
- Correct: If it rains, I will stay home.
- ❌ Wrong: If it will rain, I will stay home.
✅ Rule 7: Do Not Confuse Future with Present Continuous
Sometimes, we use the present continuous for planned future events. But it’s only for very definite arrangements.
- Present Continuous (planned): I am meeting my friend at 5.
- Going to (intended plan): I am going to meet my friend at 5.
- Will (decision now): I will meet my friend at 5.
These grammar rules form the solid foundation you need to use the simple future tense accurately and confidently.
💡 Important Tips for Using the Simple Future Tense Correctly
Mastering the Simple Future Tense is not just about knowing the rules—it’s also about using it smoothly in daily conversation. These helpful tips will make your sentences sound more natural, confident, and correct.
🌟 Tip 1: “Will” vs. “Going to”—Understand the Difference
Will
- Use it when you decide something at the moment.
- Great for promises, offers, predictions without proof.
Going to
- Use it when you have a plan or intention.
- Also good for predictions with evidence.
Examples:
- I think it will snow tonight. (Prediction)
- Look at the sky! It is going to snow. (Prediction with evidence)
🧠 Tip 2: Avoid Mixing Future Forms in One Sentence
Stick to one future form per idea. Don’t mix “will” and “going to” unless you clearly need both.
✅ Correct: I am going to visit grandma, and I will buy her flowers.
❌ Wrong: I will going to visit grandma.
🧾 Tip 3: Use “Will” for Polite Requests and Promises
- Will you help me with this bag? (polite request)
- I will always support you. (promise)
This is common in everyday polite conversation and formal writing.
📢 Tip 4: Don’t Forget the Be Verb with “Going to”
It’s easy to forget the helping verb (am/is/are) when using “going to.”
❌ Wrong: I going to study.
✅ Correct: I am going to study.Always use:
- I am,
- You/We/They are,
- He/She/It is
⛔ Tip 5: Don’t Add -ing or -ed After “Will” or “Going to”
Use only the base form of the verb after “will” or “going to.”
❌ Wrong: She will going to the store.
✅ Correct: She will go to the store.
✅ Correct: She is going to go to the store.
⏳ Tip 6: Use Time Expressions with the Future Tense
These words help make your future sentence more clear:
- Tomorrow
- Next week/month/year
- Soon
- In a few minutes/hours/days
- Later
- Tonight
Example:
We will leave in five minutes.
She is going to start her new job next week.
📅 Tip 7: Know When to Use the Present Continuous Instead
If the plan is firm and arranged, you might hear the present continuous used instead of “going to.”
- I am meeting the teacher at 3 PM. (Very fixed plan)
- I am going to meet the teacher. (General intention)
Both are correct, but present continuous shows more certainty.
📌 Summary of Key Tips:
- Know when to use “will” vs. “going to”
- Use the base verb form
- Include “am/is/are” with “going to”
- Use time markers to show when something will happen
- Don’t mix future tenses in the same clause
With these tips, your English will sound more natural and fluent when talking about future events!
🚫 Common Mistakes with the Simple Future Tense and How to Fix Them
Making mistakes is part of learning, but knowing the common errors with the simple future tense will help you avoid confusion and sound more natural in English. Here are some frequent mistakes learners make and how to correct them.
❌ Mistake 1: Using the Wrong Verb Form After “Will” or “Going to”
Wrong: She will goes to school.
Correct: She will go to school.Fix: Always use the base form of the verb after “will” or “going to.” No -s, -ed, or -ing endings.
❌ Mistake 2: Forgetting the Helping Verb in “Going to” Forms
Wrong: I going to call you later.
Correct: I am going to call you later.Fix: Always include the correct form of be (am/is/are) before “going to.”
❌ Mistake 3: Mixing “Will” and “Going to” Incorrectly in One Sentence
Wrong: I will going to visit my friend tomorrow.
Correct: I will visit my friend tomorrow.
Or: I am going to visit my friend tomorrow.Fix: Use either “will” or “going to,” not both together.
❌ Mistake 4: Using “Will” After “If” in Conditional Sentences
Wrong: If it will rain, I will stay home.
Correct: If it rains, I will stay home.Fix: Use present simple after “if” in first conditional sentences, not “will.”
❌ Mistake 5: Using Present Continuous Without a Clear Future Plan
Wrong: I am meeting the doctor (when it’s not scheduled yet).
Correct: I am going to meet the doctor. (if planned)
Or: I will meet the doctor. (decision made now)Fix: Use present continuous only for fixed plans or arrangements.
❌ Mistake 6: Double Negatives
Wrong: I won’t not go to the party.
Correct: I won’t go to the party.Fix: Avoid using two negatives in one sentence when talking about the future.
❌ Mistake 7: Omitting Time Expressions That Clarify the Future
Wrong: I will travel.
Better: I will travel next week.Fix: Adding time expressions makes your meaning clearer and sounds more natural.
❓ Quick Tip: Always read your sentences aloud. If something sounds awkward or confusing, it might be a grammar mistake!
By learning these common mistakes and fixing them, your future tense sentences will become clearer and more confident.
✨ 20 Simple Future Tense Example Sentences for Better Understanding
Seeing plenty of examples helps you get comfortable using the Simple Future Tense naturally. Below are 20 sentences using “will” and “going to” that show different ways to talk about the future.
Using “Will” for Predictions, Promises, and Decisions
- I will call you as soon as I arrive.
- She will finish her homework before dinner.
- Don’t worry, I will help you with your project.
- They will probably come to the party later.
- We will see what happens tomorrow.
- I will always support you no matter what.
- It will rain this evening according to the weather report.
- He will not (won’t) agree to that plan.
- Will you join us for lunch tomorrow?
- I will try my best to learn English quickly.
Using “Be Going to” for Plans and Intentions
- I am going to visit my grandparents next weekend.
- She is going to start a new job next month.
- They are going to buy a new car soon.
- We are going to watch a movie tonight.
- He is going to travel to Spain this summer.
- I am not going to eat junk food anymore.
- Are you going to attend the meeting tomorrow?
- The sky is dark; it is going to rain soon.
- She isn’t going to come to the party because she’s sick.
- We are going to have a picnic if the weather stays nice.
Quick Recap:
- Use “will” for sudden decisions, promises, offers, and general predictions.
- Use “going to” for plans, intentions, and predictions with evidence.
These examples cover many everyday situations, helping you confidently talk about the future with the correct tense.
📝 Simple Future Tense Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Try to complete the following 20 sentences using the correct form of the simple future tense—either “will” + base verb or “be going to” + base verb. Think carefully about whether the sentence shows a plan, intention, prediction, or sudden decision.
- I __________ (call) you when I arrive.
- She __________ (not/attend) the meeting tomorrow.
- They __________ (travel) to Japan next year.
- Look at those clouds! It __________ (rain) soon.
- We __________ (help) you with your homework.
- He __________ (buy) a new laptop next week.
- I think she __________ (like) the gift.
- You __________ (feel) better after some rest.
- I __________ (not/go) to the party tonight.
- __________ you __________ (come) with us to the movie?
- She __________ (start) her new job on Monday.
- I __________ (try) my best to pass the exam.
- They __________ (not/finish) the project by Friday.
- We __________ (have) a picnic if the weather is nice.
- He __________ (call) his parents later today.
- I __________ (visit) my grandparents next weekend.
- You __________ (be) surprised by the news.
- They __________ (not/come) to the event this time.
- I __________ (help) you as soon as I can.
- She __________ (meet) us at the restaurant at 7 PM.
✔️ Check Your Answers for the Simple Future Tense Exercise
- I will call you when I arrive.
- She is not (isn’t) going to attend the meeting tomorrow.
- They are going to travel to Japan next year.
- Look at those clouds! It is going to rain soon.
- We will help you with your homework.
- He is going to buy a new laptop next week.
- I think she will like the gift.
- You will feel better after some rest.
- I am not going to go to the party tonight.
- Will you come with us to the movie?
- She is going to start her new job on Monday.
- I will try my best to pass the exam.
- They are not (aren’t) going to finish the project by Friday.
- We will have a picnic if the weather is nice.
- He will call his parents later today.
- I am going to visit my grandparents next weekend.
- You will be surprised by the news.
- They are not (aren’t) going to come to the event this time.
- I will help you as soon as I can.
- She is going to meet us at the restaurant at 7 PM.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Simple Future Tense
Here are some common questions learners ask about the Simple Future Tense, along with clear, simple answers to help you understand this grammar point better.
1. What is the Simple Future Tense?
The Simple Future Tense shows actions or events that will happen later than now. We use it to talk about plans, predictions, promises, and decisions made at the moment.
2. What is the difference between “will” and “going to”?
- Use “will” for sudden decisions, promises, or predictions without clear evidence.
- Use “going to” for plans or predictions based on present evidence.
3. Can I use “will” and “going to” in the same sentence?
Yes, but only if they refer to different ideas. For example:
“I am going to visit my friend, and I will bring her a gift.”
4. Is it correct to say “I will going to…” ?
No. After “will,” always use the base verb form, never “going to.” The correct form is: “I will go,” not “I will going to.”
5. How do I make negative sentences in the Simple Future?
Add “not” after “will” or after the correct form of “be” in “going to.”
Examples:- I will not (won’t) eat pizza tonight.
- She is not (isn’t) going to attend the party.
6. How do I ask questions in the Simple Future?
For “will,” start the question with “Will.”
Example: “Will you come to the meeting?”
For “going to,” use the correct form of “be” at the beginning:
“Are you going to travel next week?”
7. Can I use the present continuous to talk about the future?
Yes. Use the present continuous for fixed plans or arrangements. For example: “I am meeting my teacher tomorrow.” But for general plans or predictions, use “going to” or “will.”
8. What time expressions do I use with the Simple Future?
Common time words include: tomorrow, next week/month/year, soon, later, in a few days, tonight.
9. Can the Simple Future Tense be used for polite requests?
Yes! For example: “Will you help me?” sounds polite and friendly.
10. What’s the difference between “will” and the present simple for future events?
The present simple is used for scheduled or timetabled events (e.g., trains, classes):
“The train leaves at 6 PM.”
Use “will” to talk about predictions or decisions made now.
📌 Key Takeaways: Simple Future Tense Summary and Important Points
- The Simple Future Tense is used to talk about actions or events that will happen later.
- Use “will” + base verb for:
- Sudden decisions
- Promises and offers
- Predictions without strong evidence
- Use “be going to” + base verb for:
- Plans and intentions
- Predictions based on present signs or evidence
- The verb after “will” is always the base form (no -s, -ed, or -ing).
- After “going to,” use the correct form of “be” (am/is/are).
- For negatives, add “not” after “will” or the correct “be” verb.
- Form questions by placing “will” or the correct “be” form before the subject.
- Use time expressions like tomorrow, next week, soon, later to clarify the future time.
- Avoid mixing “will” and “going to” incorrectly in the same phrase.
- Be careful with conditionals: after “if,” use the present simple, not “will.”
- The present continuous can also talk about fixed future plans or arrangements.
Keep practicing these points, and your confidence with the Simple Future Tense will grow every day!
🎯 Conclusion: Mastering the Simple Future Tense in English
The Simple Future Tense is one of the most important tools you need to confidently talk about the future in English. Whether you’re making promises, sharing plans, or predicting what will happen, understanding when and how to use “will” and “going to” makes your English clear and natural.
Remember, practice makes perfect! Use the examples and tips in this post to try writing your own future tense sentences. Don’t be afraid to make mistakes—they are stepping stones to becoming fluent.
Take Your English Further!
For more easy-to-understand lessons on English grammar and other languages, visit my blog at mylanguageclassesblog.wordpress.com.
Follow us on Instagram for daily tips and fun language learning content.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel My Language Classes for videos that make learning simple and enjoyable.
Keep learning, keep growing — you’ve got this!👇
A Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future)
Mastering the Simple Present Tense: A Complete Guide
The Present Perfect Tense in English
Present Continuous Tense In English: A Complete Guide
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English
Articles in English: A, An, and The
Understanding Material Nouns in English: Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Definite Article in English: The
-

Title: Past Perfect Continuous Tense in English: Simple Guide with Examples, Rules, and Practice
Have you ever wondered how to talk about an action that started in the past and continued up until another point in the past? That’s where the past perfect continuous tense comes in. This powerful and useful verb tense helps you describe what had been happening before something else occurred. Whether you’re studying for an English test, trying to improve your writing, or just want to sound more fluent in English conversations, learning the past perfect continuous tense can take your language skills to the next level.
In this easy-to-follow guide, you’ll discover everything you need to understand and use the past perfect continuous tense in English. We’ll cover its meaning, how and when to use it, verb conjugation rules, and plenty of real-life examples. You’ll also get grammar tips, a fun exercise to test your skills, and a clear summary to review what you’ve learned.
By the end of this blog post, you’ll be able to:
- Use the past perfect continuous tense correctly in speaking and writing
- Recognize it in everyday English conversations
- Avoid common mistakes English learners often make
- Feel more confident with past tenses overall
Let’s dive in and explore the world of past perfect continuous tense—a must-know tool for every English language learner!
What Is the Past Perfect Continuous Tense? Explanation and Overview
The past perfect continuous tense (also called the past perfect progressive tense) is used to show that an action started in the past, continued for a period of time, and ended just before another action or time in the past. It focuses on the duration of the activity and helps us understand what was going on in the background.
🔍 Key Definition:
The past perfect continuous tense describes something that had been happening over a period of time before something else happened in the past.
🧠 Basic Structure:
Subject + had been + present participle (verb+ing)
Example:
She had been studying for hours before she finally took a break.Here, “had been studying” is the past perfect continuous tense. It tells us she started studying earlier, and it continued for some time until the moment she took a break.
🗂️ Why Is This Tense Important?
This tense helps you:
- Describe the background of a story or situation in the past.
- Show the reason for something that happened later.
- Emphasize the length or continuity of an activity.
🧾 More Examples:
- I had been working on the project when the power went out.
- They had been arguing before the teacher entered the room.
- He had been feeling sick for days before he went to the doctor.
🗣️ Common Questions Learners Ask:
- “Is this the same as the past continuous?” 👉 No. Past continuous is used for one-time actions in the past. Past perfect continuous is used to show that an action continued up to a point in the past.
- “Can I use it with all verbs?” 👉 Mostly yes, but some state verbs (like know, believe, love) are not usually used in continuous forms.
Everyday Sentences Using the Past Perfect Continuous Tense: 10 Common Examples
Now that you understand what the past perfect continuous tense means, let’s bring it to life with some simple and relatable examples. These sentences show how people use this tense in daily conversations, stories, and real-life situations. Each one helps you see how this grammar form gives us details about duration, background, or the reason for something in the past.
These examples are easy to understand, practical, and great for learners at all levels.
🗣️ 10 Common Past Perfect Continuous Sentences
- She had been cooking all afternoon before the guests arrived.
- I had been feeling tired because I hadn’t slept well for days.
- They had been playing outside when it suddenly started to rain.
- He had been working at that company for ten years before he quit.
- We had been watching the movie for an hour before the lights went out.
- You had been studying hard, so you deserved a break.
- The kids had been jumping on the bed until their mom told them to stop.
- It had been raining nonstop before the sun finally came out.
- My brother had been fixing his bike all morning.
- She had been waiting at the station when the train got delayed again.
💡 Why These Sentences Matter
Each of these examples:
- Shows an action that started earlier in the past
- Continued for some time
- Ended right before another past moment or event
Understanding these sentence patterns will help you use the past perfect continuous naturally when telling stories or explaining situations.
When to Use the Past Perfect Continuous Tense: All the Key Situations
Knowing when to use the past perfect continuous tense helps you speak and write more clearly about the past. This tense is not used randomly—there are specific situations where it fits best. Let’s break them down so you can recognize these situations easily and use the tense confidently.
🎯 Key Situations to Use the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Here are the main times when the past perfect continuous tense is used:
1. To Show Duration Before Something in the Past
This is the most common use. It shows how long something had been happening before another event in the past.
🔹 Example: I had been reading for two hours before dinner.
2. To Explain the Cause of a Past Event
Sometimes, we want to explain why something happened. This tense helps link cause and effect in the past.
🔹 Example: He was tired because he had been running.
3. To Describe Background Actions in a Story
It gives details about what was happening in the background before something else took place.
🔹 Example: The kids had been playing quietly before the thunderstorm started.
4. To Emphasize Repeated or Ongoing Past Behavior
You can use it to describe actions that kept going or were repeated over a period.
🔹 Example: She had been calling him every day for a week before he finally replied.
5. To Talk About Temporary Past Actions
This tense is also used for temporary activities that continued before a point in the past.
🔹 Example: We had been living in that town for a few months before we moved.
6. To Show a Change in Situation
It marks a change from one past condition to another by showing what had been happening beforehand.
🔹 Example: The roads were wet because it had been raining.
⚠️ Note:
We don’t use this tense when the action didn’t last or wasn’t continuous. For short or completed actions, we usually use the past perfect tense, not the continuous form.
How to Conjugate Verbs in the Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Conjugation Rules
Conjugating verbs in the past perfect continuous tense is easy once you learn the simple structure. This tense always follows the same basic pattern, no matter what the subject is. Once you understand the rule, you can use it with any action verb in English.
Let’s break it down step by step.
🔤 Basic Formula:
Subject + had been + present participle (verb + -ing)
✅ This rule is the same for all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
📘 Conjugation Examples with Different Subjects:
Subject Verb (Work) Example Sentence I had been working I had been working all morning. You had been working You had been working too hard. He had been working He had been working before the accident. She had been working She had been working on the project for hours. It had been working It had been working fine until yesterday. We had been working We had been working as a team. They had been working They had been working late every night.
🧩 Key Components Explained:
- “Had” – the past perfect helper verb
- “Been” – stays the same in every sentence
- Verb+ing – the present participle (e.g., playing, eating, running, studying)
❌ Negative Form:
To make it negative, add “not” after “had”.
Subject + had not been + verb-ing
Examples:
- I had not been sleeping well.
- She had not been practicing much before the test.
- They had not been following the rules.
📝 Tip: “Had not” can also be written as “hadn’t” in casual speech.
❓ Question Form:
To ask questions, place “Had” at the beginning of the sentence.
Had + subject + been + verb-ing?
Examples:
- Had he been working when you arrived?
- Had they been waiting long?
- Had you been feeling okay?
⏳ Common Verbs in This Tense:
- Studying
- Running
- Eating
- Living
- Driving
- Working
- Cleaning
- Waiting
- Practicing
- Crying
You can use these with the structure above to form hundreds of correct sentences.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense Grammar Rules You Need to Know
To use the past perfect continuous tense correctly in English, it’s important to follow a few basic grammar rules. These rules help make your sentences clear, accurate, and easy to understand. Let’s look at what you should always remember when using this tense.
📏 1. Use “Had Been” for All Subjects
Whether the subject is singular or plural, always use “had been”—it never changes.
✅ Correct:
- I had been studying.
- She had been reading.
- They had been sleeping.
❌ Incorrect:
- He has been running. (That’s present perfect continuous, not past perfect continuous.)
🧠 2. Always Use the Present Participle (Verb + ing)
After “had been,” the verb must be in the -ing form.
✅ Examples:
- I had been working.
- They had been playing.
- She had been cooking.
⚠️ 3. Use It for Ongoing or Repeated Past Actions
This tense describes something that was happening over time before another past event. Don’t use it for one-time, short, or completed actions.
✅ Correct:
- We had been walking for hours before we found help.
❌ Incorrect: - We had been arrived late. (Use simple past or past perfect here.)
⏰ 4. Show a Clear Link to a Second Past Action or Time
The past perfect continuous almost always connects two points in the past:
- What had been happening
- What happened after that
✅ Example:
- She had been crying before the phone rang.
📝 5. Avoid Using Stative Verbs in Continuous Form
Some verbs (called stative verbs) describe states, feelings, or thoughts, and usually don’t take -ing forms.
❌ Don’t say:
- I had been knowing him for years.
✅ Say: - I had known him for years.
Common stative verbs: know, believe, own, understand, need, want, love, hate
🙅♂️ 6. Don’t Use With Finished-Time Words
Avoid using this tense with time expressions that refer to exact, finished points in the past like yesterday, last year, or in 2010.
✅ Better options:
- Before she left, he had been calling her.
❌ Incorrect: - He had been calling her yesterday. (Use simple past or past perfect instead.)
These grammar rules will help you use the past perfect continuous tense correctly and naturally in both writing and speech.
Important Tips for Using the Past Perfect Continuous Tense Correctly
Using the past perfect continuous tense can feel tricky at first, but with the right tips, it becomes much easier. This section will help you avoid confusion and use this tense with confidence in your everyday English—whether you’re writing a story, talking about your day, or sharing an experience.
🧠 1. Use It to Emphasize Duration
The past perfect continuous is perfect when you want to highlight how long something had been happening before another event in the past.
✅ Example:
- I had been studying for five hours before dinner.
This adds detail and gives the listener more context.
⏳ 2. Think in Two Parts: Ongoing Action + Later Past Event
This tense always refers to two points in time:
- A longer action that started earlier in the past
- Another event that came after
Ask yourself:
👉 What had been happening?
👉 What happened after that?✅ Example:
- She had been crying before I arrived.
🔄 3. Keep It Consistent with Other Tenses
Make sure the main action is in past perfect continuous, and the later event is in simple past.
✅ Example:
- We had been walking for hours before we found shelter.
❌ Wrong:
- We had been walking for hours before we find shelter.
👂 4. Listen for Clues in the Conversation
Words like before, until, when, and because often signal that this tense might be needed.
✅ Examples:
- He was hungry because he had been working all day.
- She looked tired when I saw her. She had been traveling.
❗ 5. Don’t Overuse It
Not every past action needs the past perfect continuous. Use it when:
- The duration is important
- The cause or background matters
- There are two time points in the past
For quick, finished past actions, the simple past or past perfect is usually better.
🤔 6. Use Time Expressions Naturally
Common time expressions that work well with this tense:
- For (for two hours, for three days)
- Since (since morning, since Monday)
- All (all night, all week, all day)
- Before, until, by the time
✅ Example:
- I had been waiting since morning before the store opened.
💬 7. Practice Speaking and Writing With It
The best way to master this tense is by using it in your own sentences. Try to describe:
- Your past week
- An experience before something important
- A story with two time points
The more you use it, the more natural it will feel.
Common Mistakes with the Past Perfect Continuous Tense and How to Fix Them
Even advanced learners make mistakes with the past perfect continuous tense. But the good news is—these mistakes are easy to fix once you understand what causes them. Below are some of the most common errors and how to correct them.
❌ Mistake 1: Using “Has/Have Been” Instead of “Had Been”
This is the most frequent mix-up. Learners often confuse past perfect continuous with present perfect continuous.
❌ Wrong:
- I have been waiting for hours before she came.
✅ Correct:
- I had been waiting for hours before she came.
✅ Remember: “Had been” = Past, “Have/has been” = Present
❌ Mistake 2: Using the Wrong Verb Form After “Had Been”
After “had been,” we must always use the -ing form (present participle).
❌ Wrong:
- They had been work all night.
✅ Correct:
- They had been working all night.
❌ Mistake 3: Using Time Expressions Incorrectly
Some expressions (like yesterday, last year) don’t pair well with this tense because they refer to a specific time, not duration.
❌ Wrong:
- She had been practicing yesterday.
✅ Better:
- She had been practicing before the concert.
❌ Mistake 4: Using It for Short or Completed Actions
This tense is not meant for one-time, completed actions. Use simple past or past perfect in those cases.
❌ Wrong:
- He had been falling asleep when the phone rang.
✅ Correct:
- He fell asleep when the phone rang.
(If it was a one-time, quick action.)
❌ Mistake 5: Using “Been” with Stative Verbs
Stative verbs describe a state, not an action (e.g., know, love, believe). These are rarely used in continuous tenses.
❌ Wrong:
- I had been knowing her for a long time.
✅ Correct:
- I had known her for a long time.
❌ Mistake 6: Confusing the Order of Events
This tense is used to show an action that happened before something else in the past. Reversing this order confuses the meaning.
❌ Wrong:
- The game started before they had been arriving.
✅ Correct:
- The game started before they had arrived. (Use past perfect here, not continuous.)
- They had been arriving slowly throughout the afternoon. (This works only if you’re showing an ongoing process.)
✅ Pro Tip: Use Context Clues
To avoid these errors:
- Think: Did the action last over time?
- Ask: Did it happen before another event?
- Use: “Had been + verb-ing” only when both answers are yes.
With these mistakes in mind, you’re now better prepared to use the past perfect continuous tense accurately.
20 Past Perfect Continuous Tense Example Sentences for Better Understanding
The best way to understand and remember the past perfect continuous tense is to see it in action. These example sentences will help you clearly see how this tense works in real life. Each sentence shows a situation where the action was happening over time before something else in the past.
Let’s go through them one by one:
🔟 Everyday Past Perfect Continuous Examples
- She had been studying all night before the exam started.
- We had been waiting for the bus when it finally arrived.
- I had been working at that company for five years before I got promoted.
- He had been running for thirty minutes before it started to rain.
- They had been arguing for hours before they finally made up.
- The baby had been crying until her mother picked her up.
- We had been looking for a house for months before we found one.
- She had been feeling sick for days before she went to the doctor.
- I had been thinking about quitting, but then things got better.
- He had been living in New York before he moved to London.
🔟 More Real-Life and Contextual Examples
- They had been playing video games all afternoon before dinner.
- The dog had been barking non-stop before the owner came home.
- I had been saving money for years to buy a new car.
- She had been working on the project before the deadline was changed.
- The kids had been jumping on the bed before it broke.
- He had been watching the same show for hours when I came in.
- We had been painting the walls when we ran out of color.
- The mechanic had been fixing the car before the storm started.
- I had been reading that book for weeks before I finally finished it.
- They had been traveling around Europe before settling in France.
These examples show you how flexible and useful the past perfect continuous tense can be—especially when describing background actions, habits, and longer durations in the past.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Fill in the blanks below with the correct form of the verb in parentheses using the past perfect continuous tense. This exercise will help you practice forming sentences and improve your confidence.
- She __________ (study) for three hours before the test started.
- We __________ (wait) for the bus when it suddenly arrived.
- He __________ (work) late every night before he got sick.
- They __________ (play) football before it began to rain.
- I __________ (read) the book all day before I finished it.
- The children __________ (cry) before their parents came home.
- You __________ (run) for 20 minutes when the coach called you.
- She __________ (cook) dinner when the phone rang.
- We __________ (look) for the keys before we found them in the drawer.
- He __________ (sleep) all afternoon before the guests arrived.
- They __________ (argue) about the plan before they reached an agreement.
- I __________ (practice) the piano when my friend visited.
- The cat __________ (hide) under the bed before it came out.
- She __________ (talk) on the phone for hours before she hung up.
- We __________ (drive) for miles before we stopped to rest.
- He __________ (study) English for years before moving to London.
- They __________ (travel) around Asia before settling in Japan.
- I __________ (wait) for the train before it was canceled.
- She __________ (paint) the walls all morning before the guests arrived.
- We __________ (listen) to music when the power went out.
Check Your Answers for the Past Perfect Continuous Exercise
- She had been studying for three hours before the test started.
- We had been waiting for the bus when it suddenly arrived.
- He had been working late every night before he got sick.
- They had been playing football before it began to rain.
- I had been reading the book all day before I finished it.
- The children had been crying before their parents came home.
- You had been running for 20 minutes when the coach called you.
- She had been cooking dinner when the phone rang.
- We had been looking for the keys before we found them in the drawer.
- He had been sleeping all afternoon before the guests arrived.
- They had been arguing about the plan before they reached an agreement.
- I had been practicing the piano when my friend visited.
- The cat had been hiding under the bed before it came out.
- She had been talking on the phone for hours before she hung up.
- We had been driving for miles before we stopped to rest.
- He had been studying English for years before moving to London.
- They had been traveling around Asia before settling in Japan.
- I had been waiting for the train before it was canceled.
- She had been painting the walls all morning before the guests arrived.
- We had been listening to music when the power went out.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Here are some common questions learners ask about the past perfect continuous tense — along with clear, simple answers to help you master this important grammar point.
1. What is the difference between past perfect continuous and past perfect?
- Past perfect continuous focuses on the duration of an action that was ongoing before another past event.
- Past perfect emphasizes that an action was completed before another past event.
Example:
- Past Perfect Continuous: She had been reading for two hours before dinner. (Focus on the activity’s length)
- Past Perfect: She had read the book before dinner. (Focus on completion)
2. Can we use the past perfect continuous with stative verbs?
No, stative verbs (like know, love, believe) usually do not use continuous forms. Use the past perfect instead.
Example:- Correct: I had known him for years.
- Incorrect: I had been knowing him for years.
3. Is it okay to use ‘for’ and ‘since’ with past perfect continuous?
Yes! Both for (duration) and since (starting point) work perfectly to show how long an action lasted before another past event.
Example:- I had been working for three hours.
- She had been living there since 2010.
4. Can the past perfect continuous be used with short actions?
Generally, no. It’s meant for actions that lasted some time, not short or quick actions. For short actions, use the simple past or past perfect.
Example:- Wrong: He had been opening the door when the phone rang.
- Correct: He had opened the door when the phone rang.
5. How do I form negative sentences in the past perfect continuous?
Use had not been + verb-ing.
Example:- She had not been feeling well before the trip.
- They had not been working on the project long before it was canceled.
6. How do I form questions in the past perfect continuous?
Invert had and the subject, followed by been + verb-ing.
Example:- Had you been waiting long before the train arrived?
- Had they been studying before the test?
7. Can we use the past perfect continuous with ‘until’ and ‘by the time’?
Yes! These words often indicate the ending point of an action in the past perfect continuous.
Example:- I had been working until midnight.
- She had been cooking by the time we arrived.
Key Takeaways: Past Perfect Continuous Tense Summary and Important Points
Let’s quickly review the most important facts about the past perfect continuous tense in simple, easy-to-remember bullet points:
- The past perfect continuous tense shows that an action started in the past and continued up until another past event.
- It is formed using:
had been + verb-ing (present participle). - It emphasizes the duration or ongoing nature of the past action.
- Common time expressions include: for, since, before, by the time, until.
- It is NOT used with stative verbs like know, love, believe. Use past perfect instead.
- Use it to describe background actions or things happening over time before something else.
- Negative form: had not been + verb-ing.
- Question form: Had + subject + been + verb-ing?
- Avoid using it for short or completed actions; use simple past or past perfect instead.
- Remember common mistakes such as mixing it up with present perfect continuous or using wrong verb forms.
- Practice with real-life sentences and exercises to improve your understanding and confidence.
Conclusion: Mastering the Past Perfect Continuous Tense in English
Understanding the past perfect continuous tense is a powerful step in becoming a confident and fluent English speaker. This tense helps you describe actions that were happening over time before something else in the past, making your storytelling more natural, rich, and accurate.
Whether you’re saying you had been working, had been waiting, or had been learning, this tense gives your sentences the depth they need when talking about past routines, long actions, or background events.
Why This Tense Matters:
- It shows how long something was happening.
- It connects one past action with another.
- It makes your English sound more fluent and native-like.
Now that you’ve learned how to:
- Recognize when to use it,
- Conjugate verbs correctly,
- Avoid common mistakes,
- And use it in your own sentences,
…it’s time to take your learning further.
✅ What You Should Do Next:
📘 Explore more grammar lessons and practice quizzes on our blog:
👉 mylanguageclassesblog.wordpress.com📸 Follow us on Instagram for fun daily English tips:
👉 @mylanguageclassesofficial▶️ Subscribe to our YouTube channel for free video lessons on grammar, vocabulary, and conversation skills:
👉 My Language Classes
Keep learning, keep practicing, and keep growing. You’re doing an amazing job—and every new grammar skill you master brings you one step closer to fluency. 💪🌍
See you in the next lesson!
Keep learning, keep growing — you’ve got this!👇
A Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future)
Mastering the Simple Present Tense: A Complete Guide
The Present Perfect Tense in English
Present Continuous Tense In English: A Complete Guide
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English
Articles in English: A, An, and The
Understanding Material Nouns in English: Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Definite Article in English: The
-

Past Continuous Tense in English: Definition, Usage, Rules, and Examples for Everyday Conversations
Have you ever tried to describe what you were doing at a specific moment in the past? Maybe you were watching a movie when the phone rang or studying while your friends were playing outside. That’s where the past continuous tense comes in. It’s a powerful tool in English that helps us talk about ongoing actions in the past, and it’s one of the most natural ways to express real-life situations in English.
Whether you’re a beginner learning English grammar or an intermediate student improving your fluency, mastering the past continuous tense is essential for sounding natural and confident. This tense is used all the time in spoken English, storytelling, and even in interviews and everyday conversations.
In this guide, we’ll explore:
- What the past continuous tense is
- When and how to use it correctly
- Common grammar rules and tricky points
- Real-life examples and fun practice exercises
Let’s dive into the world of past actions, continuous timelines, and English made simple!
📘 What Is the Past Continuous Tense? Explanation and Overview
The past continuous tense—also known as the past progressive tense—is a verb tense used to describe actions that were happening at a specific moment in the past. It’s like pressing pause on a movie that was already playing. You’re focusing on something that was in progress, not just something that happened.
This tense combines the past tense of the verb “to be” (was/were) with the present participle (verb + -ing) to show that the action was ongoing in the past.
🔍 Structure of the Past Continuous Tense
- Subject + was/were + verb(-ing)
Here’s how the structure looks:
Subject Past “to be” Verb + ing Example Sentence I was watching I was watching a movie last night. You were playing You were playing football at 4 PM. He/She was cooking She was cooking dinner when I came. We were studying We were studying all evening. They were laughing They were laughing at the joke.
🧠 Why Use the Past Continuous Tense?
Here’s what makes the past continuous tense super useful:
- It paints a picture of what was happening at a certain time in the past.
- It helps set the scene in stories or conversations.
- It allows us to show two actions happening at once in the past.
- It shows that one action was interrupted by another.
🎯 Keywords and Phrases Often Used with Past Continuous:
These phrases give strong clues that the past continuous is needed:
- While
- When
- As
- At that moment
- All day/night/morning
- At 5 PM (or any time)
- Just then
📝 Example:
- I was sleeping when the alarm rang.
- While he was driving, it started raining.
The past continuous is more than just grammar—it’s a way to bring your stories to life. Ready to see it in action? Let’s look at some real, everyday examples you can relate to.
🗣 Everyday Sentences Using the Past Continuous Tense: 10 Common Examples
The past continuous tense is used all the time in day-to-day conversations. Whether you’re talking about what you were doing yesterday, a funny moment, or something unexpected that happened, this tense helps you describe actions that were in progress at a particular time in the past.
Here are 10 real-life, everyday examples that show how we naturally use the past continuous in spoken English.
✅ 10 Common Past Continuous Sentences
- I was brushing my teeth when the lights went out.
- She was studying for her math test all afternoon.
- We were watching TV when the doorbell rang.
- They were playing outside while it started to rain.
- He was reading a book at midnight.
- You were talking too loudly during the movie.
- The baby was crying all night.
- My parents were working in the garden yesterday.
- It was snowing heavily when we left the house.
- The kids were laughing and running around the park.
💡 Notice These Patterns
- Actions were in progress: “was brushing,” “were playing”
- Often paired with another interrupting action: “when the lights went out”
- Used with time markers like “when,” “while,” and specific times: “at midnight,” “all night”
These examples show that the past continuous is a natural part of conversation. It’s how we talk about the flow of events, especially when something happens in the middle of something else.
🕒 When to Use the Past Continuous Tense: All the Key Situations
The past continuous tense isn’t just for one type of sentence—it helps us express many different ideas from the past. It’s perfect for showing that something was happening over time, got interrupted, or was part of a background scene.
Here are all the main situations where the past continuous tense is used in English, with clear examples for each.
✅ 1. To Talk About an Action in Progress at a Specific Time in the Past
Use the past continuous to show that something was happening exactly at a certain time in the past.
📝 Examples:
- At 7 PM, I was eating dinner.
- At this time last year, we were traveling in Europe.
✅ 2. To Describe Two Actions Happening at the Same Time in the Past
You can show that two actions were happening simultaneously in the past.
📝 Examples:
- I was reading while she was cooking.
- They were studying as the rain was falling.
✅ 3. To Show an Ongoing Action Interrupted by Another Action
This is one of the most common uses. The past continuous sets the background for the main action in the simple past.
📝 Examples:
- I was sleeping when the phone rang.
- He was walking home when it started to snow.
✅ 4. To Set the Scene or Background in a Story
Writers and speakers often use the past continuous to describe what was going on around the main events of a story.
📝 Examples:
- The birds were singing, and the sun was shining.
- People were talking, music was playing, and everyone was smiling.
✅ 5. To Show a Temporary Action in the Past
Use the past continuous for actions that didn’t last long or were not permanent.
📝 Examples:
- She was staying with us for a few days.
- I was using my brother’s laptop until mine got fixed.
✅ 6. To Talk About Repeated or Annoying Actions (Usually with “Always” or “Constantly”)
This use often shows irritation or frustration.
📝 Examples:
- He was always leaving his dirty socks on the floor!
- They were constantly interrupting the meeting.
✅ 7. To Show a Change in a Situation or Atmosphere
This helps describe how a situation was evolving.
📝 Examples:
- The sky was getting darker, and the wind was blowing harder.
- People were becoming more and more excited.
🔑 Summary of Usage Situations:
- Action happening at a specific time in the past
- Two actions happening at the same time
- An interrupted action in the past
- Setting the scene in storytelling
- Temporary or limited-time past actions
- Repeated or annoying actions in the past
- Describing a changing situation
The past continuous tense adds detail, emotion, and context to your stories and sentences. Now, let’s see how to build these sentences correctly by learning the conjugation rules!
🔧 How to Conjugate Verbs in the Past Continuous Tense: Conjugation Rules
The good news? Conjugating verbs in the past continuous tense is super easy! You only need two parts:
👉 The past tense of “to be” (wasorwere)
👉 The present participle (base verb + -ing)Let’s break this down clearly so you can form correct and confident past continuous sentences every time.
✅ The Formula
Subject + was/were + verb + -ing
✅ Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Choose the right form of “to be”:
- Use was with I, he, she, it
- Use were with you, we, they
- Add the main verb in -ing form (present participle):
- walk → walking
- read → reading
- cook → cooking
📝 Examples:
- I was reading a book.
- They were cooking dinner.
- She was running in the park.
🔤 Subject-Verb Table
Subject Past “Be” Verb Example Sentence I was I was studying for the exam. You were You were talking too loudly. He/She/It was He was playing video games. We were We were watching a movie. They were They were laughing together.
📌 Spelling Rules for the -ING Form
Some verbs need slight changes before adding “-ing”. Here’s what to remember:
1. Drop the final “e” and add -ing
(If the verb ends in “e”, drop the “e” before adding “-ing”)
- make → making
- dance → dancing
2. Double the last consonant (for CVC verbs)
(Consonant–Vowel–Consonant pattern, one syllable)
- run → running
- sit → sitting
3. Keep the “ie”, change it to “y”
- die → dying
- lie → lying
4. Just add -ing (for most verbs)
- eat → eating
- jump → jumping
🔄 Negative Form
To make a negative sentence, simply add “not” after “was” or “were”:
📝 Examples:
- I was not (wasn’t) working yesterday.
- They were not (weren’t) listening to the teacher.
❓Question Form
To ask questions in the past continuous, switch the subject and the form of “to be”:
Was/Were + Subject + Verb-ing?
📝 Examples:
- Was she sleeping?
- Were you watching the match?
Now that you know how to conjugate verbs in the past continuous tense, you’re ready to learn the important grammar rules that help make your English more accurate and natural.
📚 Past Continuous Tense Grammar Rules You Need to Know
To use the past continuous tense like a pro, it’s important to know some simple but powerful grammar rules. These rules will help you write and speak more clearly, avoid confusion, and sound more natural in English.
Let’s dive into the most essential grammar rules for the past continuous tense.
✅ 1. Use “Was” or “Were” Based on the Subject
This is the foundation of the past continuous.
- Was → I, he, she, it
- Were → you, we, they
📝 Examples:
- I was writing a story.
- They were having lunch together.
✅ 2. Always Add “-ing” to the Main Verb
The main action verb in the past continuous must be in its -ing form (present participle).
📝 Examples:
- He was playing, not “was play”.
- We were watching, not “were watch”.
✅ 3. Use Specific Past Time References (Optional but Helpful)
The past continuous often includes a clear time reference to show when the action was happening.
📝 Examples:
- At 5 p.m., she was waiting for the bus.
- Yesterday evening, we were cooking dinner.
✅ 4. Combine with Simple Past to Show Interruption
Use the past continuous to show an action in progress, and the simple past to show the action that interrupted it.
📝 Examples:
- I was watching TV when the power went out.
- They were walking home when it started raining.
✅ 5. Use “While” for Two Parallel Actions
Use while to connect two actions that were happening at the same time.
📝 Examples:
- While I was studying, my brother was playing games.
- She was singing while he was driving.
Tip: You can also use as in a similar way:
“As I was cleaning, she was organizing the books.”
✅ 6. Don’t Use Stative Verbs in the Past Continuous
Some verbs describe states or feelings, not actions, and usually don’t go in continuous forms.
Common stative verbs:
know, believe, love, hate, own, need, understand, want🛑 Incorrect: She was knowing the answer.
✅ Correct: She knew the answer.
✅ 7. Use for Repeated or Annoying Past Actions (with “Always” or “Constantly”)
This is a special use that shows emotion, often annoyance or frustration.
📝 Examples:
- He was always forgetting his homework!
- They were constantly making noise during the lecture.
✅ 8. Combine with Other Past Tenses for Richer Storytelling
Mix the past continuous with other past tenses (like simple past or past perfect) to tell more vivid stories.
📝 Example:
- I was reading when I realized I had left my phone at work.
🧠 Quick Recap of Grammar Rules
- Match the subject with “was” or “were”
- Use verb + ing for the main action
- Add time markers like at 5 PM, yesterday, or last night
- Combine with simple past to show interruptions
- Use “while” or “as” for parallel actions
- Avoid stative verbs in continuous form
- Add emotion with “always” or “constantly” for repeated actions
These grammar rules form the backbone of the past continuous tense. Up next, let’s look at some important tips that will help you avoid mistakes and use the past continuous like a native speaker.
💡 Important Tips for Using the Past Continuous Tense Correctly
Mastering the past continuous tense doesn’t have to be hard. With a few smart tips, you can avoid common mistakes and speak or write more fluently and confidently. Here are some helpful and easy-to-follow tips to keep in mind when using this tense.
✅ 1. Always Check the Subject-Verb Agreement
Use “was” for singular subjects (I, he, she, it) and “were” for plural ones (you, we, they).
📝 Example:
- She was walking, not “were walking.”
- They were laughing, not “was laughing.”
✅ 2. Use Time Markers to Make Sentences Clearer
Adding past time expressions like “yesterday,” “last night,” “at 8 PM,” or “when” helps your reader or listener understand exactly when something happened.
📝 Example:
- I was doing my homework at 7 PM.
✅ 3. Focus on the Ongoing Nature of the Action
Use the past continuous to describe something that was happening over a period of time, not something that was completed quickly.
📝 Example:
- He was watching a movie (not just clicked play and stopped—he was in the middle of it).
✅ 4. Combine with Simple Past for Better Storytelling
This is one of the most natural ways to use the past continuous. Show what was going on when something else happened.
📝 Example:
- I was reading a book when the phone rang.
✅ 5. Use “While” or “As” for Two Actions at the Same Time
This makes your English sound more fluent and descriptive.
📝 Examples:
- While we were studying, it was raining.
- As he was talking, she was nodding.
✅ 6. Avoid Using Stative Verbs
Words like know, believe, understand, like, need don’t usually work with continuous tenses.
🛑 Incorrect: I was knowing the answer.
✅ Correct: I knew the answer.
✅ 7. Use “Always” and “Constantly” for Repeated or Annoying Actions
This is a great way to add emotion or tone to what you’re saying.
📝 Examples:
- My brother was always borrowing my clothes!
- She was constantly complaining about school.
✅ 8. Be Careful with Negative Sentences
To make a sentence negative, just add “not” after “was” or “were.”
📝 Examples:
- I was not (wasn’t) watching TV.
- They were not (weren’t) playing outside.
✅ 9. Don’t Forget the “-ing” Ending
This is a super common mistake. The main verb must always end in -ing.
🛑 Incorrect: He was talk to me.
✅ Correct: He was talking to me.
✅ 10. Practice With Real-Life Examples
Use your daily routine, favorite shows, or past memories to practice.
📝 Examples:
- Yesterday at this time, I was riding the bus.
- Last night, we were eating pizza and watching a movie.
🚀 Pro Tip: Record Yourself Speaking
One of the best ways to build confidence is to record yourself using the past continuous tense in short stories or conversations. Listen, correct, and try again!
⚠️ Common Mistakes with the Past Continuous Tense and How to Fix Them
Even advanced learners can make small mistakes when using the past continuous tense. The good news? These mistakes are easy to fix once you understand them. Let’s take a look at some of the most common ones, along with simple corrections.
❌ Mistake 1: Using the Wrong Auxiliary Verb (Was/Were)
Many learners mix up “was” and “were” based on the subject.
🛑 Incorrect: They was playing football.
✅ Correct: They were playing football.🛑 Incorrect: I were reading a book.
✅ Correct: I was reading a book.👉 Fix it: Use was for singular (I, he, she, it) and were for plural (you, we, they).
❌ Mistake 2: Forgetting the “-ing” Form
Sometimes learners forget to use the verb in the correct present participle (-ing) form.
🛑 Incorrect: She was cook dinner.
✅ Correct: She was cooking dinner.👉 Fix it: Always use the base verb + -ing after “was” or “were”.
❌ Mistake 3: Using Stative Verbs in Continuous Form
Stative verbs describe states or feelings, and we usually don’t use them in continuous tenses.
🛑 Incorrect: I was knowing the answer.
✅ Correct: I knew the answer.🛑 Incorrect: She was liking the movie.
✅ Correct: She liked the movie.👉 Fix it: Use the simple past tense with stative verbs like know, love, like, want, need, believe, understand.
❌ Mistake 4: Missing the Time Reference
Without a clear time marker, past continuous sentences can sound confusing or unclear.
🛑 Confusing: He was driving.
✅ Clear: He was driving at 9 PM last night.👉 Fix it: Add time expressions like yesterday, when, while, last night, at that moment to give context.
❌ Mistake 5: Overusing the Past Continuous Tense
Some learners try to use it all the time, even when it’s not needed.
🛑 Incorrect: I was going to the store and was buying some milk and was walking home.
✅ Correct: I went to the store, bought some milk, and walked home.👉 Fix it: Use the past continuous only when you want to focus on the ongoing nature of the action. Use the simple past for completed actions.
❌ Mistake 6: Wrong Word Order in Questions
Learners often struggle with how to structure questions in the past continuous tense.
🛑 Incorrect: What she was doing?
✅ Correct: What was she doing?👉 Fix it: Use the correct word order: was/were + subject + verb-ing.
❌ Mistake 7: Using “When” Incorrectly
“When” is used to show an action that interrupts another ongoing action.
🛑 Incorrect: I was sleeping when she was calling.
✅ Correct: I was sleeping when she called.👉 Fix it: Use past simple after “when,” and past continuous for the ongoing action.
❌ Mistake 8: Forgetting to Use “Not” in Negative Sentences
Learners sometimes skip the “not,” which changes the meaning completely.
🛑 Incorrect: She was working on the project. (when you meant to say she wasn’t!)
✅ Correct: She was not (wasn’t) working on the project.👉 Fix it: Always include “not” after was/were to make negative sentences.
❌ Mistake 9: Using Unnatural Examples Without Context
Using sentences that don’t match real-life scenarios can confuse learners.
🛑 Incorrect: He was jumping mountains.
✅ Correct: He was climbing the mountain trail.👉 Fix it: Use examples from everyday life that make sense.
❌ Mistake 10: Not Practicing Enough!
The biggest mistake? Not using it in real conversations or writing practice.
👉 Fix it: Use the past continuous tense in:
- Storytelling
- Daily conversations
- Journaling about past events
- English language games
✅ 20 Past Continuous Tense Example Sentences for Better Understanding
Understanding grammar rules is important, but seeing them in real-life use is what truly makes them stick. Below are 20 clear and easy-to-understand sentences using the past continuous tense. These examples cover various situations, including actions in progress, interrupted actions, and background activities.
Each sentence is simple, natural, and perfect for beginners as well as more advanced learners looking to strengthen their understanding.
📘 Actions Happening at a Specific Time in the Past
- I was reading a book at 9 PM last night.
- She was cooking dinner when I arrived.
- They were watching a movie all evening.
- He was sleeping during the thunderstorm.
- We were studying English at that moment.
🎯 Interrupted Actions (Past Continuous + Simple Past)
- I was brushing my teeth when the phone rang.
- She was walking to school when it started to rain.
- They were playing football when the bell rang.
- We were talking about you when you walked in.
- He was driving to work when he saw the accident.
🧠 Background Activities in Stories
- The sun was setting, and the birds were singing.
- People were dancing, and music was playing in the background.
- She was typing on her laptop while sipping coffee.
- The baby was crying as the mother was preparing milk.
- I was thinking about my future during the long flight.
❌ Negative Sentences (Past Continuous Negative)
- I wasn’t doing anything important when you called.
- She was not studying last night; she was watching TV.
- They weren’t working on the project over the weekend.
- He wasn’t listening to the teacher.
- We were not waiting for the bus because we had a ride.
These examples highlight how the past continuous tense is used naturally in different everyday situations. You can try saying them out loud or even writing your own sentences by replacing the subjects or actions. It’s a great way to build fluency and confidence!
📝 Past Continuous Tense Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Now it’s your turn! Fill in the blanks with the correct past continuous tense form of the verbs in parentheses. This exercise will help you practice and reinforce your understanding of the past continuous tense in everyday sentences.
- I __________ (watch) TV when the power went out.
- They __________ (play) soccer all afternoon yesterday.
- She __________ (not/listen) to music at 7 PM last night.
- We __________ (study) for the test while it was raining.
- He __________ (drive) to work when he saw the accident.
- You __________ (sleep) when I called you.
- The kids __________ (laugh) loudly during the party.
- I __________ (cook) dinner when the doorbell rang.
- She __________ (write) an email at 8 AM yesterday.
- They __________ (not/watch) the movie because they were tired.
- We __________ (walk) home when it started to rain.
- He __________ (talk) on the phone while driving.
- The students __________ (read) quietly in the library.
- I __________ (not/think) about the problem at that moment.
- She __________ (dance) when the music suddenly stopped.
- They __________ (fix) the car all morning.
- He __________ (not/work) yesterday afternoon.
- We __________ (wait) for the bus when it arrived.
- You __________ (play) video games at 9 PM last night.
- The dog __________ (bark) loudly while I was sleeping.
✅ Check Your Answers for the Past Continuous Tense Exercise
- I was watching TV when the power went out.
- They were playing soccer all afternoon yesterday.
- She was not listening to music at 7 PM last night.
- We were studying for the test while it was raining.
- He was driving to work when he saw the accident.
- You were sleeping when I called you.
- The kids were laughing loudly during the party.
- I was cooking dinner when the doorbell rang.
- She was writing an email at 8 AM yesterday.
- They were not watching the movie because they were tired.
- We were walking home when it started to rain.
- He was talking on the phone while driving.
- The students were reading quietly in the library.
- I was not thinking about the problem at that moment.
- She was dancing when the music suddenly stopped.
- They were fixing the car all morning.
- He was not working yesterday afternoon.
- We were waiting for the bus when it arrived.
- You were playing video games at 9 PM last night.
- The dog was barking loudly while I was sleeping.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Past Continuous Tense
To help you better understand the past continuous tense, here are some common questions learners ask — along with clear and simple answers.
1. What is the past continuous tense used for?
The past continuous tense describes actions that were happening at a specific time in the past. It can show ongoing actions, interrupted actions, or background activities in a story.
2. How do I form the past continuous tense?
You form it with the past tense of the verb “to be” (was/were) + the -ing form of the main verb.
Example: She was reading.
3. When should I use “was” and when should I use “were”?
Use “was” with singular subjects (I, he, she, it).
Use “were” with plural subjects (we, you, they).
Example: I was eating. / They were playing.
4. Can the past continuous tense be used for actions that happened at the same time?
Yes! You can use it to describe two or more actions happening simultaneously in the past.
Example: While I was cooking, he was setting the table.
5. How is the past continuous different from the simple past?
- Past continuous shows an action that was in progress at a specific time.
- Simple past describes completed actions or events.
Example: I was watching TV at 8 PM. (ongoing) vs. I watched TV yesterday. (completed)
6. Can I use the past continuous tense for short actions?
Usually, no. The past continuous is for longer or ongoing actions, not short or instant events. Short actions are better in the simple past.
Example: I was reading (ongoing), but I dropped the book (short action).
7. Is the past continuous tense used in questions?
Yes, you can ask questions using the past continuous by inverting the subject and the past tense of “to be.”
Example: Were you studying last night?
8. How do I make negatives in the past continuous tense?
Add not after “was” or “were.”
Example: She was not (wasn’t) working yesterday.
📌 Key Takeaways: Past Continuous Tense Summary and Important Points
Let’s quickly recap the most important things you need to remember about the past continuous tense. These bullet points make it easy to review and reinforce your learning!
- The past continuous tense describes actions that were happening at a specific time in the past.
- It’s formed by combining was/were + verb + -ing (e.g., She was reading).
- Use was with singular subjects (I, he, she, it) and were with plural subjects (we, you, they).
- It’s used for ongoing or unfinished actions in the past and for background activities in stories.
- The past continuous often shows an action interrupted by another action in the simple past (e.g., I was sleeping when the phone rang).
- Use the past continuous for actions happening at the same time in the past (e.g., They were playing while we were studying).
- Negatives are formed by adding not after “was” or “were” (e.g., He wasn’t listening).
- Questions are made by inverting the subject and was/were (e.g., Were you working?).
- The past continuous is NOT used for short, quick actions; use the simple past for those instead.
- Practice makes perfect—use plenty of example sentences and exercises to become confident!
🔚 Conclusion: Mastering the Past Continuous Tense in English
The past continuous tense is a powerful tool for expressing actions that were happening at a particular moment in the past. Whether you’re telling a story, describing an event, or explaining what was going on around a specific time, this tense adds depth and clarity to your English.
Remember, mastering the past continuous tense helps you sound more natural and confident in both speaking and writing. Keep practicing by using the rules, examples, and exercises shared in this blog.
To keep improving your English skills and explore more grammar topics like this, be sure to visit My Language Classes Blog, follow us on Instagram, and subscribe to our YouTube channel My Language Classes for friendly, clear lessons that make learning fun and effective!
Keep learning, stay curious, and enjoy your English journey!
Keep learning, keep growing — you’ve got this!👇
A Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future)
Mastering the Simple Present Tense: A Complete Guide
The Present Perfect Tense in English
Present Continuous Tense In English: A Complete Guide
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English
Articles in English: A, An, and The
Understanding Material Nouns in English: Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Definite Article in English: The
-

Present Continuous Tense in English: How to Use It Correctly with Examples and Exercises
Are you wondering what is the Present Continuous Tense and how to use it in real life? Whether you’re saying “I am eating,” “She is studying,” or “They are playing,” you’re already using the Present Continuous Tense! This powerful part of English grammar helps us talk about actions that are happening right now, around now, or in the near future. In this blog, you’ll learn everything you need to know to master this tense — explained in a super simple way, with real-life examples, common mistakes, and fun practice exercises.
The Present Continuous Tense is also known as the Present Progressive Tense, and it’s one of the most common and useful tenses in English. Native speakers use it all the time in daily conversation, storytelling, and even in songs! It helps you express what someone is doing right now, what’s happening these days, or even what’s going to happen soon. Sounds useful, right?
Whether you’re a complete beginner or brushing up your skills, this guide will help you understand:
- What the Present Continuous Tense is
- When and how to use it
- How to form correct sentences using this tense
- Common mistakes and how to fix them
- And lots of examples and exercises for practice
So, let’s jump in and unlock the secret to sounding more natural and confident in English conversations with the Present Continuous Tense!
What Is the Present Continuous Tense? Explanation and Overview
The Present Continuous Tense (also called the Present Progressive Tense) is a verb tense used to describe actions that are happening right now or around the current time. It can also describe future actions that are already planned or arranged. This tense is very useful in both spoken and written English.
🔹 How is the Present Continuous Formed?
We form the Present Continuous by using two parts:
- The present tense of the verb “to be” — am / is / are
- The base verb + -ing
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ingExamples:
- I am reading a book.
- She is cooking dinner.
- They are playing football.
🔹 When Do We Use the Present Continuous?
The Present Continuous is used to talk about:
- Actions happening right now
- Actions happening around now, but not necessarily at the exact moment of speaking
- Temporary actions or situations
- Planned future events
- Changing situations
- Repeated actions that happen too often (often with the word “always” for emphasis)
We’ll explore all these situations in detail in the next section!
🔹 Why Is the Present Continuous Important?
This tense helps you sound more fluent and natural in conversations. It allows you to describe what’s happening at the moment, talk about your current plans, and even express emotions or habits.
Here’s why English learners need to master it:
- It’s used all the time in everyday conversation.
- It helps you describe real-life actions more clearly.
- It builds a strong foundation for understanding other verb tenses.
Once you understand how and when to use it, the Present Continuous Tense becomes easy and fun!
Everyday Sentences Using the Present Continuous Tense: 10 Common Examples
To really understand how the Present Continuous Tense works, it helps to see it in action. These real-life sentences show how people use this tense to talk about what’s happening now, plans for the near future, and even changing situations.
All of these sentences follow the same basic structure:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ingHere are 10 everyday examples of the Present Continuous Tense:
- I am studying for my English test right now.
- She is talking on the phone with her best friend.
- We are having lunch at a new restaurant today.
- He is watching his favorite TV show.
- They are playing outside because the weather is nice.
- You are learning English very quickly!
- My mom is baking a chocolate cake for my birthday.
- It is raining heavily, so don’t forget your umbrella.
- I am meeting my cousin at the mall this evening.
- The baby is sleeping, so please be quiet.
🔹 What Do These Examples Show?
These examples help you see that:
- You can use this tense for right now (“She is talking on the phone”)
- Or for plans in the near future (“I am meeting my cousin”)
- Or even to describe changing situations (“You are learning English very quickly”)
Learning through examples is one of the best ways to improve your grammar naturally. Try making a few similar sentences about yourself after reading these!
When to Use the Present Continuous Tense: All the Key Situations
The Present Continuous Tense is used in many everyday situations. It helps us describe actions, plans, and changes happening right now or soon. Below are the most important times when you should use this tense. These are the key rules that English speakers follow without even thinking!
🔹 1. Actions Happening Right Now
Use the Present Continuous to talk about something that is happening at the exact moment you are speaking.
Examples:
- She is brushing her hair.
- I am writing an email.
- They are waiting for the bus.
🔹 2. Actions Happening Around Now (but Not Exactly Now)
Sometimes the action is happening during this time period, but not exactly at the moment of speaking.
Examples:
- I am reading a great book these days.
- He is studying a lot this week.
- We are working on a group project at school.
🔹 3. Temporary Situations
Use this tense to describe actions or situations that are not permanent. They are happening for a short time only.
Examples:
- She is staying with her aunt for a few days.
- I am living in Paris this month.
- We are using my dad’s car today.
🔹 4. Planned Future Events
We also use the Present Continuous to talk about future plans that are already arranged or decided.
Examples:
- I am visiting my grandma tomorrow.
- They are flying to London next week.
- We are going to the movies tonight.
🔹 5. Changing or Developing Situations
This tense helps describe actions or things that are gradually changing or developing over time.
Examples:
- The weather is getting colder.
- My little brother is growing fast.
- Your English is improving every day!
🔹 6. Annoying Repeated Actions (with “Always”)
Sometimes we use the Present Continuous with the word “always” to show that something happens too often — often in an annoying or funny way.
Examples:
- He is always forgetting his homework!
- She is always talking in class.
- You are always losing your phone!
These are the main situations where the Present Continuous Tense is used. Each one helps you express time and action more clearly, so your English sounds natural and fluent.
How to Conjugate Verbs in the Present Continuous Tense: Conjugation Rules
To use the Present Continuous Tense correctly, you need to know how to conjugate verbs properly. Don’t worry—it’s simple once you understand the steps!
Here’s a quick guide to conjugating verbs in the Present Continuous:
🔹 Step 1: Use the Correct Form of the Verb “To Be” (am / is / are)
Choose the correct form based on the subject of the sentence:
Subject Form of “To Be” I am He / She / It is You / We / They are
🔹 Step 2: Add the Base Verb + –ing
Take the base form of the verb and add –ing to the end.
Examples:
- read → reading
- play → playing
- write → writing
✅ Putting It All Together
Formula:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ingExamples:
- I am eating lunch.
- She is dancing on the stage.
- They are studying for exams.
🔹 Spelling Rules for –ing Verbs
Here are some simple spelling rules to remember when adding –ing:
1. Just add –ing (for most verbs)
- walk → walking
- clean → cleaning
- jump → jumping
2. Drop the final ‘e’ and add –ing
- make → making
- write → writing
- drive → driving
3. Double the final consonant (if the verb has one vowel + one consonant)
- run → running
- sit → sitting
- swim → swimming
⚠️ But don’t double the final letter if the word ends in w, x, or y:
- fix → fixing
- snow → snowing
- play → playing
🔹 Negative Sentences in the Present Continuous
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + not + verb-ingExamples:
- I am not watching TV.
- She is not sleeping now.
- They are not working today.
🔹 Questions in the Present Continuous
Structure:
Am/Is/Are + subject + verb-ing?Examples:
- Are you coming with us?
- Is he doing his homework?
- Am I talking too fast?
Now that you’ve got the conjugation rules down, you’re ready to build strong Present Continuous sentences with confidence!
Present Continuous Grammar Rules You Need to Know
Understanding grammar rules helps you use the Present Continuous Tense correctly and confidently. These simple yet important rules will guide you through building both written and spoken sentences that sound natural and accurate.
Let’s look at the core grammar rules for this tense:
🔹 1. Basic Sentence Structure
The Present Continuous follows a simple formula:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
Examples:
- I am cooking dinner.
- She is watching a movie.
- They are playing football.
🔹 2. Forming Negative Sentences
To make a sentence negative, just add “not” after am, is, or are.
Subject + am/is/are + not + verb-ing
Examples:
- I am not going to school today.
- He is not feeling well.
- We are not working right now.
🔹 3. Forming Yes/No Questions
Move the form of “to be” to the beginning of the sentence.
Am/Is/Are + subject + verb-ing?
Examples:
- Are you doing your homework?
- Is she wearing a new dress?
- Am I talking too fast?
🔹 4. Short Answers for Questions
Use short answers with am, is, or are to sound polite and clear.
Examples:
- Are you coming? → Yes, I am. / No, I’m not.
- Is he studying? → Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
- Are they eating? → Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
🔹 5. Use Only Action Verbs
Use the Present Continuous only with action verbs—verbs that show something happening.
Correct:
- I am writing a letter.
- She is running in the park.
Incorrect:
- I am knowing the answer. ❌
- He is liking this movie. ❌
(These use stative verbs, which are not used in this tense—more on that below.)
🔹 6. Avoid Using Stative Verbs in Present Continuous
Stative verbs describe states, emotions, or thoughts, not actions. These verbs are usually NOT used in the Present Continuous.
Common stative verbs include:
- Know, like, love, hate, believe, understand, want, need, remember, own, seem
Examples:
- I know the answer. ✅
- I am knowing the answer. ❌
🔹 7. Time Expressions Often Used
Use time expressions to make your sentence clearer.
Common ones include:
- now
- right now
- at the moment
- today
- this week
- currently
- tonight
- these days
Examples:
- He is studying at the moment.
- We are working late tonight.
These grammar rules are your foundation for mastering the Present Continuous Tense. Use them regularly to form correct and meaningful sentences every time you speak or write in English.
Important Tips for Using the Present Continuous Tense Correctly
Using the Present Continuous Tense is easy once you get the hang of it. But even fluent speakers can make small mistakes. These simple and smart tips will help you speak and write with clarity and confidence.
Whether you’re a beginner or brushing up your skills, these tips are perfect for learning the correct use of the Present Continuous.
✅ 1. Focus on Actions Happening Right Now
Use this tense to talk about actions that are happening at the moment of speaking.
Correct:
- I am listening to music right now.
- She is cooking dinner now.
Tip: Use words like now, at the moment, and right now to show the action is happening currently.
✅ 2. Use It for Temporary Actions
Use the Present Continuous for things happening temporarily, even if not at this exact second.
Examples:
- I am living in Spain this summer.
- They are taking swimming lessons this month.
Tip: If it’s not permanent, you can often use this tense.
✅ 3. Describe Changing or Developing Situations
Use this tense when something is slowly changing or growing.
Examples:
- The weather is getting colder.
- Your English is improving day by day!
Tip: Verbs like grow, change, improve, get, and develop are often used in this way.
✅ 4. Avoid Using Stative Verbs
Stative verbs describe feelings, thoughts, emotions, or states, and they don’t usually appear in the Present Continuous.
Examples of Stative Verbs:
- know
- believe
- like
- love
- understand
- need
Incorrect:
- I am knowing the answer. ❌
Correct:
- I know the answer. ✅
Tip: If the verb describes a state, use the simple present instead.
✅ 5. Don’t Forget the Verb “To Be”
Many learners skip the am/is/are part by mistake. This is a common error!
Incorrect:
- She reading a book. ❌
Correct:
- She is reading a book. ✅
Tip: Always check that you’re using the correct helping verb before the action verb.
✅ 6. Watch the Spelling of –ing Verbs
Always check spelling rules when adding –ing:
- Drop the e: make → making
- Double the consonant: run → running
- Don’t change if the word ends in w, x, or y: fix → fixing
Tip: A spelling mistake can change the meaning of the word or make it incorrect.
✅ 7. Use Clear Time Expressions
Time phrases help listeners or readers understand your message better.
Examples:
- at the moment
- this week
- right now
- today
- currently
Tip: These phrases help to clearly show that you are talking about ongoing or temporary actions.
✅ 8. Practice Makes Perfect
The more you use the Present Continuous, the easier it becomes. Try:
- Talking about your current day or week.
- Writing diary entries using “I am…”
- Practicing with a friend or tutor.
Tip: Practice out loud for better fluency!
Keep these tips in mind as you move forward. You’ll find yourself using the Present Continuous naturally and correctly in no time!
Common Mistakes with the Present Continuous and How to Fix Them
Even experienced English learners sometimes make mistakes when using the Present Continuous Tense. But don’t worry—these errors are easy to fix once you know what to watch for. Here are the most common Present Continuous mistakes and simple ways to correct them.
❌ 1. Forgetting the “to be” verb (am/is/are)
Wrong:
She eating breakfast.
They going to school.Right:
She is eating breakfast.
They are going to school.Why it happens: Learners sometimes forget the helping verb.
Fix it: Always use am, is, or are before the verb + ing.
❌ 2. Using stative verbs in the continuous form
Wrong:
I am knowing the answer.
She is loving this movie.Right:
I know the answer.
She loves this movie.Why it happens: Some verbs describe feelings, thoughts, or states. These are not used in continuous form.
Fix it: Use the simple present tense with stative verbs.
❌ 3. Wrong verb spelling when adding “-ing”
Wrong:
He is runing.
They are makeing a mess.Right:
He is running.
They are making a mess.Why it happens: Learners forget spelling rules.
Fix it:- Drop the e: make → making
- Double the last letter if one vowel + one consonant: run → running
- Just add –ing if it ends in w, x, or y: fix → fixing
❌ 4. Using the Present Continuous for regular actions
Wrong:
I am waking up at 6 a.m. every day.Right:
I wake up at 6 a.m. every day.Why it happens: Learners confuse daily routines with current actions.
Fix it: Use the simple present tense for habits and routines.
❌ 5. Mixing up “is” and “are”
Wrong:
They is playing soccer.
He are eating now.Right:
They are playing soccer.
He is eating now.Why it happens: Confusion about subject-verb agreement.
Fix it:- Use am with “I”
- Use is with he, she, it
- Use are with you, we, they
❌ 6. Using it for completed actions
Wrong:
I am finished my homework.Right:
I have finished my homework.
Or: I am finishing my homework. (if still doing it)Why it happens: Learners confuse present perfect with present continuous.
Fix it: Use present perfect for completed actions and present continuous for actions still in progress.
❌ 7. Overusing the Present Continuous
Wrong:
I am go to the park every day.
She is have a dog.Right:
I go to the park every day.
She has a dog.Why it happens: Learners try to use present continuous for everything.
Fix it: Know when to use the simple present instead—especially for routines or permanent facts.
Quick Review: Common Mistake Fixes
Mistake Fix Forgetting am/is/are Add the correct helping verb Using stative verbs Use simple present Spelling errors Apply –ing spelling rules Using for daily routines Use simple present Wrong verb agreement Match subject with am/is/are For completed actions Use present perfect Using it everywhere Use correct tense for the situation By learning from these mistakes, you’ll be well on your way to speaking and writing with confidence in English.
20 Present Continuous Example Sentences for Better Understanding
To truly master the Present Continuous tense, seeing plenty of clear and relatable examples helps a lot. Below are 20 example sentences that show how the Present Continuous is used in everyday English. Read them carefully, and notice how each sentence describes an ongoing action or temporary situation.
Examples Showing Actions Happening Right Now
- I am writing this blog post for you.
- She is watching her favorite TV show at the moment.
- They are playing football in the park right now.
- We are having lunch together today.
- He is listening to music in his room.
Examples of Temporary or Ongoing Actions
- I am learning to speak Spanish this year.
- She is working on a big project this week.
- They are staying at their grandparents’ house for the weekend.
- We are trying a new recipe tonight.
- He is studying hard for his exams these days.
Examples of Changing or Developing Situations
- The climate is getting warmer every year.
- Your English skills are improving nicely.
- The kids are growing so fast!
- The company is expanding its business overseas.
- Prices are rising in the market recently.
Negative Sentences in Present Continuous
- I am not feeling well today.
- She is not coming to the party tonight.
- They are not working on the weekend.
- We are not watching that movie now.
- He is not driving his car today.
These examples cover different uses of the Present Continuous tense — from actions happening right now, to temporary activities, ongoing changes, and negatives. Try making your own sentences using this structure, and you’ll feel more confident every day!
Present Continuous Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
- She __________ (read) a very interesting book right now.
- They __________ (play) basketball at the moment.
- I __________ (learn) how to cook Italian food this week.
- We __________ (watch) a new series on Netflix.
- He __________ (write) an email to his friend.
- The children __________ (not/sleep) yet.
- My parents __________ (travel) to Japan this month.
- You __________ (talk) too loudly!
- The sun __________ (shine) brightly today.
- She __________ (take) dance classes these days.
- I __________ (not/feel) very well today.
- They __________ (work) on their homework right now.
- We __________ (wait) for the bus at the stop.
- He __________ (not/watch) TV at the moment.
- The dog __________ (bark) loudly outside.
- You __________ (listen) to music, aren’t you?
- She __________ (wear) a red dress today.
- They __________ (fix) the car this afternoon.
- I __________ (think) about changing my job.
- We __________ (have) dinner together tonight.
Try to complete this exercise on your own! When you’re ready, I will provide the answers.
Check Your Answers for the Present Continuous Exercise
- She is reading a very interesting book right now.
- They are playing basketball at the moment.
- I am learning how to cook Italian food this week.
- We are watching a new series on Netflix.
- He is writing an email to his friend.
- The children are not sleeping yet.
- My parents are traveling to Japan this month.
- You are talking too loudly!
- The sun is shining brightly today.
- She is taking dance classes these days.
- I am not feeling very well today.
- They are working on their homework right now.
- We are waiting for the bus at the stop.
- He is not watching TV at the moment.
- The dog is barking loudly outside.
- You are listening to music, aren’t you?
- She is wearing a red dress today.
- They are fixing the car this afternoon.
- I am thinking about changing my job.
- We are having dinner together tonight.
Great job if you got them right! If you missed any, review the Present Continuous rules and examples from earlier sections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Present Continuous Tense
1. What is the Present Continuous tense used for?
The Present Continuous tense is used to describe actions happening right now, temporary actions, ongoing changes, or future plans.
2. How do I form the Present Continuous tense?
Use the verb “to be” (am/is/are) + the main verb + -ing. For example, I am eating, She is running, They are studying.
3. Can I use the Present Continuous for habits?
No, habits and routines are usually expressed with the Simple Present tense (e.g., I drink coffee every day). The Present Continuous is for temporary or ongoing actions.
4. Are there verbs that cannot be used in the Present Continuous?
Yes, stative verbs that describe feelings, thoughts, or states (like know, love, want, believe) are generally not used in the Present Continuous.
5. How do I make questions in the Present Continuous?
Invert the subject and the verb “to be”. For example, Are you coming? or Is she working?
6. How do I make negatives in the Present Continuous?
Add not after the verb “to be”. For example, I am not going, He is not sleeping, They are not playing.
7. Can I use the Present Continuous to talk about the future?
Yes, it’s often used to talk about planned future events. For example, We are meeting them tomorrow.
8. What are some common mistakes to avoid with the Present Continuous?
- Forgetting the helping verb am/is/are
- Using stative verbs in the continuous form
- Wrong spelling when adding -ing
- Using it for habits instead of simple present
9. How do I spell verbs when adding “-ing”?
- Drop the final e: make → making
- Double the last consonant if the verb ends with one vowel + one consonant: run → running
- Just add -ing for verbs ending in w, x, or y: fix → fixing
10. Can I use the Present Continuous with all subjects?
Yes! Use am with “I”, is with “he, she, it”, and are with “you, we, they”.
Key Takeaways: Present Continuous Summary and Important Points
- The Present Continuous tense describes actions happening right now, temporary actions, ongoing changes, and future plans.
- It is formed using the verb “to be” (am/is/are) + the main verb + -ing.
- Use am with “I”, is with “he, she, it”, and are with “you, we, they”.
- Negative sentences add not after the verb “to be” (e.g., She is not coming).
- Questions are made by inverting the subject and the verb “to be” (e.g., Are you working?).
- Do not use the Present Continuous with stative verbs like know, love, want.
- Spelling rules when adding -ing: drop final e, double consonants when needed, just add -ing for some verbs.
- Use the Present Continuous for planned future events (e.g., We are meeting tomorrow).
- Avoid common mistakes like forgetting the helping verb or using the Present Continuous for habits.
- Practice by making your own sentences and doing exercises to build confidence.
Conclusion: Master the Present Continuous Tense to Speak English Confidently!
The Present Continuous tense is one of the most useful and common tenses in English. Whether you’re describing what’s happening right now, sharing temporary activities, or talking about future plans, this tense helps you communicate clearly and naturally. By understanding its structure, common uses, and tricky points, you can improve your speaking and writing skills with confidence.
Keep practicing with real-life examples and exercises like those we covered here. The more you use the Present Continuous, the easier it becomes!
Ready to take your English skills even further?
Visit My Language Classes for more helpful lessons and resources.
Follow us on Instagram for daily tips and fun language learning content.Subscribe to our YouTube channel: My Language Classes for easy-to-follow videos that make learning English, Japanese, and Spanish enjoyable.
Keep learning, keep growing — you’ve got this!👇
A Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future)
Mastering the Simple Present Tense: A Complete Guide
The Present Perfect Tense in English
Present Continuous Tense In English: A Complete Guide
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English
Articles in English: A, An, and The
Understanding Material Nouns in English: Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Definite Article in English: The