Your cart is currently empty!
Category: Time and Tense in English
Understand the relationship between time and tense in English with clear explanations, examples, and grammar rules. Explore all 12 tenses and how they represent actions in the past, present, and future. Ideal for learners aiming to master English verb tenses.
-

Simple Past Tense in English: Grammar Rules, Usage & Examples
Simple Past Tense in English: Learn How to Use It with Easy Examples and Grammar Rules
Are you confused about how to talk about things that happened yesterday, last week, or a few minutes ago? Learning the Simple Past Tense in English is one of the most important steps in becoming confident with your English speaking, writing, and understanding. Whether you’re just starting out or polishing your skills, this guide will help you use the simple past tense correctly—with lots of examples, grammar rules, and easy tips you can use right away.
The simple past tense is used every day in real conversations, writing, and storytelling. You hear it in songs, movies, and even short greetings like “How was your day?” or “I saw that movie too!” Understanding this tense will help you express actions, experiences, and events that happened in the past with ease.
In this full guide, we’ll explain:
- What the simple past tense is
- How to use it in everyday sentences
- Common grammar rules and mistakes
- Easy verb conjugation tips
- Exercises and answers to check your learning
By the end of this blog post, you’ll feel more confident using the simple past tense in conversations, writing, and exams. Let’s get started!
What Is the Simple Past Tense? Explanation and Overview
The simple past tense is a verb tense used to describe actions, events, or situations that happened in the past and are now finished. These actions could have happened a few seconds ago, yesterday, last year, or even many years ago. If the action started and ended in the past, we use the simple past tense.
Think of the simple past tense as your go-to tense for telling stories, describing past experiences, or reporting something that already happened.
🔹 Basic Formula:
Subject + Past Form of Verb + Object
- I watched a movie.
- She visited her grandma.
- They played football after school.
In these sentences, the verbs “watched,” “visited,” and “played” are in the simple past tense. They show that the actions are completed.
🔹 Why Is It Important?
- It helps you talk about your life: “I studied in Japan for two years.”
- It lets you describe past experiences: “We went to the beach last summer.”
- It helps with storytelling: “He opened the door and walked inside.”
Whether you’re speaking English in daily life, writing an essay, or answering questions in an exam, knowing how to use the simple past tense correctly and confidently will make your communication stronger.
🔹 Time Expressions Often Used with Simple Past:
Here are some common words and phrases that go hand-in-hand with the simple past:
- Yesterday
- Last night/week/year/month
- An hour ago / a minute ago
- In 2010 / in June
- When I was a child
- A few days ago
- Once / Once upon a time
🧠 Tip:
If you’re talking about a specific time in the past, it’s a good sign that you need the simple past tense.
Everyday Sentences Using the Simple Past Tense: 10 Common Examples
The best way to understand the simple past tense is to see it in action. We use this tense all the time in daily conversations, messages, and stories. Below are 10 common and natural-sounding sentences using the simple past tense. These examples show how this tense fits into real life.
Each sentence includes a clear subject, a verb in the past form, and a time clue that tells us when the action happened.
🔟 Common Simple Past Tense Sentences
- I watched a funny movie last night.
- She cooked dinner for her family yesterday.
- They visited the zoo on Sunday.
- He lost his phone two days ago.
- We played basketball after school.
- You cleaned your room this morning.
- My mom bought fresh vegetables from the market.
- The kids laughed at the clown’s jokes.
- I finished my homework before dinner.
- He traveled to London last summer.
🔍 What Do These Sentences Show?
- The action is completed.
- The verb is in the past form.
- A time marker tells us when it happened (e.g., last night, yesterday, two days ago).
Using the simple past like this helps make your speaking and writing clear, natural, and easy to understand.
When to Use the Simple Past Tense: All the Key Situations
The simple past tense is used in many everyday situations. It’s your go-to tense when talking about anything that happened in the past and is finished. Knowing when to use it will help you communicate clearly and avoid confusion.
Here are all the key situations where you should use the simple past tense:
✅ 1. Completed Actions in the Past
Use it to talk about something that started and ended in the past.
- I read that book last week.
- She called you an hour ago.
✅ 2. A Series of Past Actions
Use it when you want to describe a list of actions that happened one after another.
- He opened the door, walked in, and sat down.
- They packed their bags, left the hotel, and caught a taxi.
✅ 3. Repeated Actions in the Past
It’s used for actions that happened again and again in the past.
- We went to the park every Saturday when we were kids.
- She always brought cookies to school.
✅ 4. Actions Happening Over a Period in the Past
Use it to show how long something continued in the past.
- I lived in Spain for three years.
- He studied French from 2018 to 2021.
✅ 5. Actions at a Specific Time in the Past
Use it when the action is tied to a specific moment in time.
- They arrived at 6 p.m.
- I started my new job in July.
✅ 6. Past Facts or General Truths (Now Changed)
Use it to talk about something that used to be true but is no longer true.
- Dinosaurs lived millions of years ago.
- He believed in ghosts when he was younger.
✅ 7. Questions About the Past
Use it to ask about something that already happened.
- Did you see that movie?
- Did she come to school yesterday?
✅ 8. Negative Sentences About the Past
Use it to say something did not happen.
- I did not (didn’t) eat breakfast today.
- They didn’t go to the meeting.
🔍 Summary:
Use the simple past tense whenever the action:
Is not connected to the present
Is finished
Happened at a known time
How to Conjugate Verbs in the Simple Past Tense: Conjugation Rules
To use the simple past tense correctly, you need to know how to change verbs into their past forms. This is called verb conjugation. There are two main types of verbs in English: regular verbs and irregular verbs. Each type follows different rules when forming the past tense.
🔹 1. Regular Verbs
Regular verbs form the simple past tense by adding -ed to the base form of the verb.
✅ Examples:
- walk → walked
- play → played
- jump → jumped
- cook → cooked
🔄 Spelling Rules for Regular Verbs:
✅ If the verb ends in “e”, just add “d”
- like → liked
- dance → danced
✅ If the verb ends in a consonant + “y”, change “y” to “i” and add “ed”
- carry → carried
- study → studied
✅ If the verb is one syllable and ends in consonant–vowel–consonant, double the last consonant and add “ed”
- stop → stopped
- plan → planned
⚠️ Do not double the final consonant if the word ends in “w”, “x”, or “y”
e.g., play → played, mix → mixed
🔹 2. Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs don’t follow a set rule. Their past forms change in different ways, and you need to memorize them.
✅ Examples of Irregular Verbs:
Base Verb Simple Past go went have had eat ate take took buy bought see saw make made There’s no shortcut—just practice and learn them through examples and use.
🔹 3. Negative and Question Forms
In negative and question sentences, we use “did” (the past of “do”) + base verb (not the past form).
✅ Examples:
- Did you eat lunch?
- I did not (didn’t) go to school.
- Did they see the movie?
- She didn’t play tennis yesterday.
Note: The main verb stays in base form in questions and negatives.
Simple Past Tense Grammar Rules You Need to Know
Using the simple past tense correctly means understanding a few key grammar rules. These rules help you form positive sentences, negatives, and questions easily and clearly. The more you practice them, the more naturally they’ll come to you when speaking or writing.
✅ 1. Positive Sentences (Affirmative Form)
Structure:
Subject + past tense verb + object🔹 Examples:
- I played the guitar.
- She watched a movie.
- They visited their grandparents.
➡️ Use the past form of the verb (regular or irregular).
✅ 2. Negative Sentences
Structure:
Subject + did not (didn’t) + base form of verb🔹 Examples:
- I did not eat pizza.
- He didn’t finish his homework.
- We didn’t go to school yesterday.
➡️ Even though the action is in the past, the main verb stays in the base form (not past).
✅ 3. Yes/No Questions
Structure:
Did + subject + base form of verb + object?🔹 Examples:
- Did you watch the game?
- Did she call you?
- Did they come to the party?
➡️ Use “did” + base form of the verb to ask questions.
✅ 4. WH- Questions (What, Where, When, Why, Who, How)
Structure:
WH-word + did + subject + base form of verb?🔹 Examples:
- What did you eat for dinner?
- Where did she go?
- When did they leave?
- Why did he cry?
- How did you learn Spanish?
✅ 5. Time Expressions That Go with Simple Past
Use the simple past tense with clear time markers that show the action is complete.
⏱️ Common Time Expressions:
- Yesterday
- Last night / last week / last year
- An hour ago / two days ago
- In 2005 / in April
- When I was a child
- This morning (if the morning is already over)
❗Grammar Tip:
Never use “did” and a past form together.
Wrong: ❌ She did went to school.
Correct: ✅ She went to school.
Or: ✅ She did go to school.
Important Tips for Using the Simple Past Tense Correctly
The simple past tense may seem easy at first, but there are small details that can trip you up. These practical tips will help you use this tense correctly in speaking and writing—every time.
Whether you’re a beginner or reviewing the basics, these rules and reminders will sharpen your grammar.
✅ 1. Always Use a Clear Time Reference (When Needed)
Mentioning when something happened helps your sentence sound complete and clear.
🔹 Example:
- I visited my grandma. ❓ (When?)
- ✅ I visited my grandma last weekend.
Time expressions like “yesterday,” “last week,” “an hour ago,” or “in 2010” give context and complete the meaning.
✅ 2. Don’t Use the Past Form with “Did” in Negatives or Questions
This is a common mistake. When using “did” or “didn’t,” always keep the main verb in the base form.
❌ Incorrect:
- Did she went to the market?
- I didn’t watched the show.
✅ Correct:
- Did she go to the market?
- I didn’t watch the show.
✅ 3. Learn Irregular Verbs by Groups or Themes
Irregular verbs don’t follow rules. Make it easier by learning them in small groups.
🔹 Group Example (verbs that change to “-ought”):
- Buy → bought
- Bring → brought
- Think → thought
Practice them in context:
- I bought a new phone yesterday.
- She thought it was a good idea.
✅ 4. Use the Correct Verb Form in Compound Sentences
When you join two actions with “and” or “but”, make sure both verbs are in the past tense.
🔹 Example:
- He woke up late and missed the bus.
- I called her, but she didn’t answer.
✅ 5. Use Contractions in Speaking and Informal Writing
Contractions make your speech and writing sound more natural.
🔹 Examples:
- Did not → didn’t
- I didn’t go to school.
- We didn’t enjoy the movie.
✅ 6. Avoid Mixing Tenses
Stay consistent. Don’t switch between tenses in the same sentence unless there’s a clear reason.
❌ Incorrect:
- I woke up, brush my teeth, and went to school.
✅ Correct:
- I woke up, brushed my teeth, and went to school.
✅ 7. Practice with Real-Life Examples
Make your own past-tense sentences based on your day or week. This helps build fluency and confidence.
🔹 Try This:
- What did you do yesterday?
- Write 5 things you did last weekend using the simple past tense.
✅ 8. Use Simple Past for Clear, Complete Actions
If the action is done and not related to the present, use the simple past—not present perfect.
✅ Example:
- I watched that movie. (It’s done.)
Not: ❌ I have watched that movie. (This connects to now.)
Common Mistakes with the Simple Past Tense and How to Fix Them
Even confident learners make mistakes with the simple past tense. Most of these errors are easy to fix once you know what to look for. This section highlights the most common problems and shows you exactly how to correct them.
Let’s break it down in a simple and clear way so you can avoid these issues in your writing and speaking.
❌ 1. Using the Past Form After “Did”
This is the most common mistake.
🔻 Incorrect:
- She did went to the mall.
- I didn’t liked the movie.
✅ Correct:
- She did go to the mall.
- I didn’t like the movie.
✅ Tip: After “did” or “didn’t,” always use the base form of the verb.
❌ 2. Mixing Past and Present Tenses in the Same Sentence
Keep your tenses consistent when describing past events.
🔻 Incorrect:
- He watched TV and plays video games.
✅ Correct:
- He watched TV and played video games.
❌ 3. Using the Present Perfect When Simple Past Is Needed
These two tenses are different. If the action is completely finished, and there’s no connection to the present, use the simple past.
🔻 Incorrect:
- I have seen that movie yesterday.
✅ Correct:
- I saw that movie yesterday.
✅ Tip: Don’t use words like yesterday, last week, in 2005, etc., with the present perfect.
❌ 4. Forgetting to Add “-ed” to Regular Verbs
Learners often forget to change regular verbs to their past form.
🔻 Incorrect:
- We visit our grandma last weekend.
✅ Correct:
- We visited our grandma last weekend.
❌ 5. Incorrect Spelling of Regular Past Verbs
Be careful with spelling when adding “-ed.”
🔻 Incorrect:
- He tryed to call me.
- They stopp the car.
✅ Correct:
- He tried to call me.
- They stopped the car.
✅ Tip: Remember spelling rules:
- Drop the “y” and add “ied” if the verb ends in a consonant + y (cry → cried).
- Double the final consonant if the verb ends in one vowel + one consonant (stop → stopped).
❌ 6. Using the Base Form Instead of the Past Form of Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs don’t follow a pattern—you have to remember them.
🔻 Incorrect:
- She go to work yesterday.
- I eat too much last night.
✅ Correct:
- She went to work yesterday.
- I ate too much last night.
❌ 7. Using Past Tense for Future Events (Out of Habit)
Sometimes learners wrongly use the past tense when talking about future plans.
🔻 Incorrect:
- I went to the market tomorrow. ❌
✅ Correct:
- I will go to the market tomorrow. ✅
✅ Tip: “Tomorrow” is a future word. Don’t use past tense with it.
❌ 8. Forgetting Time Markers Altogether
Sometimes learners speak in the past tense without giving any time reference, making the sentence unclear.
🔻 Vague:
- I saw her. (When?)
✅ Clear:
- I saw her this morning.
✅ Quick Fix Checklist:
- ✅ Use past tense form (add “-ed” or use irregular past form)
- ✅ Use the base verb after “did/didn’t”
- ✅ Don’t mix present and past tenses
- ✅ Add time expressions (yesterday, last week, etc.)
- ✅ Memorize irregular verb forms
20 Simple Past Tense Example Sentences for Better Understanding
Reading real-life examples is one of the easiest ways to understand how the simple past tense works. These 20 clear, short, and useful sentences will help you recognize correct structure and learn how to use this tense in everyday English.
All of the examples below show actions that started and finished in the past.
🔹 General Daily Life Examples
- I woke up late this morning.
- She cooked pasta for dinner last night.
- They watched a movie on Friday.
- We visited the museum yesterday.
- He played football with his friends.
🔹 School and Work Examples
- I finished my homework on time.
- The teacher gave us a quiz last week.
- My brother forgot his notebook at home.
- We had a meeting at 10 AM.
- She wrote a beautiful poem in class.
🔹 Travel and Fun Examples
- We went to the zoo last Sunday.
- They flew to New York last month.
- He drove his car to the beach.
- I took many pictures during the trip.
- She bought souvenirs from Japan.
🔹 Feelings and Reactions
- I felt very tired after the game.
- He cried during the sad movie.
- We laughed so much at the joke.
- She enjoyed the concert a lot.
- They loved the food at the restaurant.
💡Notice how each sentence uses the past form of the verb and often includes a time word (like yesterday, last night, last week, etc.). These time clues are a big part of simple past tense usage.
Simple Past Tense Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Now it’s time to practice! Fill in the blanks with the correct simple past tense form of the verbs in parentheses. This exercise will help you check how well you understand the conjugation and use of the simple past tense.
Try to answer without looking back—test yourself!
Fill in the blanks:
- Yesterday, I _______ (visit) my grandparents.
- She _______ (finish) her homework before dinner.
- We _______ (go) to the park last weekend.
- He _______ (buy) a new laptop two days ago.
- They _______ (watch) a football match on TV.
- I _______ (eat) pizza for lunch yesterday.
- The teacher _______ (give) us a surprise test last Friday.
- My parents _______ (travel) to Italy last summer.
- She _______ (write) a letter to her friend.
- We _______ (see) a great movie last night.
- He _______ (take) a photo of the sunset.
- They _______ (play) basketball after school.
- I _______ (feel) very happy on my birthday.
- She _______ (lose) her keys yesterday.
- We _______ (clean) the house before the guests arrived.
- He _______ (drink) coffee in the morning.
- They _______ (sing) a song at the party.
- I _______ (read) three books last month.
- She _______ (meet) her best friend at school.
- We _______ (dance) all night at the wedding.
Check Your Answers for the Simple Past Tense Exercise
- Yesterday, I visited my grandparents.
- She finished her homework before dinner.
- We went to the park last weekend.
- He bought a new laptop two days ago.
- They watched a football match on TV.
- I ate pizza for lunch yesterday.
- The teacher gave us a surprise test last Friday.
- My parents traveled to Italy last summer.
- She wrote a letter to her friend.
- We saw a great movie last night.
- He took a photo of the sunset.
- They played basketball after school.
- I felt very happy on my birthday.
- She lost her keys yesterday.
- We cleaned the house before the guests arrived.
- He drank coffee in the morning.
- They sang a song at the party.
- I read three books last month.
- She met her best friend at school.
- We danced all night at the wedding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Simple Past Tense
Here are some common questions learners ask about the simple past tense, along with clear and easy-to-understand answers. These FAQs will help you clarify any doubts and strengthen your grasp of this important grammar tense.
1. What is the simple past tense used for?
The simple past tense is used to talk about actions or events that happened and finished in the past. For example, “I visited my friend yesterday.”
2. How do I form the simple past tense?
For regular verbs, add -ed to the base verb (e.g., walk → walked). For irregular verbs, use the second form, which you need to memorize (e.g., go → went).
3. Can I use the simple past without a time expression?
Yes, but it’s clearer if you include a time reference like “yesterday” or “last week.” Without a time marker, listeners might get confused about when the action happened.
4. What if the verb ends with ‘-e’?
Just add -d to form the past tense. For example, “love” becomes “loved.”
5. How do I make negative sentences in the simple past?
Use did not (didn’t) + base verb. For example, “I didn’t go to school.”
6. How do I ask questions in the simple past?
Use Did + subject + base verb. For example, “Did you eat breakfast?”
7. What are some common irregular verbs I should know?
Some frequent irregular verbs are: go → went, have → had, see → saw, eat → ate, come → came, and do → did.
8. Is the simple past the same as the present perfect tense?
No. The simple past talks about finished actions in the past. The present perfect connects the past with the present (e.g., “I have eaten” means the action is relevant now).
9. Can I use the simple past for repeated actions in the past?
Yes, for actions that happened regularly in the past but no longer happen now, e.g., “I played soccer every weekend when I was a child.”
10. How do I pronounce the -ed ending?
It depends on the last sound of the verb:
- /t/ as in “watched”
- /d/ as in “played”
- /ɪd/ as in “wanted”
Key Takeaways: Simple Past Tense Summary and Important Points
Let’s quickly review the most important things to remember about the simple past tense. These key points will help you use the tense confidently and correctly in your speaking and writing.
- The simple past tense talks about actions or events that happened and finished in the past.
- For regular verbs, add -ed to the base form (e.g., walk → walked).
- For irregular verbs, use the special past form (e.g., go → went).
- Use did + base verb for negative sentences and questions (e.g., didn’t go, did you see?).
- Always use the base verb after “did” (not the past form).
- Include time expressions like yesterday, last week, or in 2000 to make your sentences clear.
- Avoid mixing present tense and past tense in the same sentence about past actions.
- Pronounce -ed endings carefully (/t/, /d/, or /ɪd/).
- Use the simple past for single completed actions and repeated past habits.
- Do not confuse the simple past with the present perfect tense.
Conclusion: Simple Past Tense
Mastering the simple past tense in English is an essential step toward speaking and writing clearly about past events. Whether you’re sharing stories, describing experiences, or explaining what happened yesterday, using the simple past correctly will make your communication confident and precise.
Remember, the key to mastering this tense is practice—learning regular and irregular verb forms, knowing when to use the simple past, and avoiding common mistakes. With consistent effort, you’ll find yourself naturally using the simple past tense in everyday conversations and writing.
If you found this guide helpful, I’d love to hear from you! Share your thoughts in the comments below or connect with me on social media. For more tips, resources, and inspiration, visit my blog at mylanguageclasses.in. Follow on Instagram and subscribe on YouTube
-
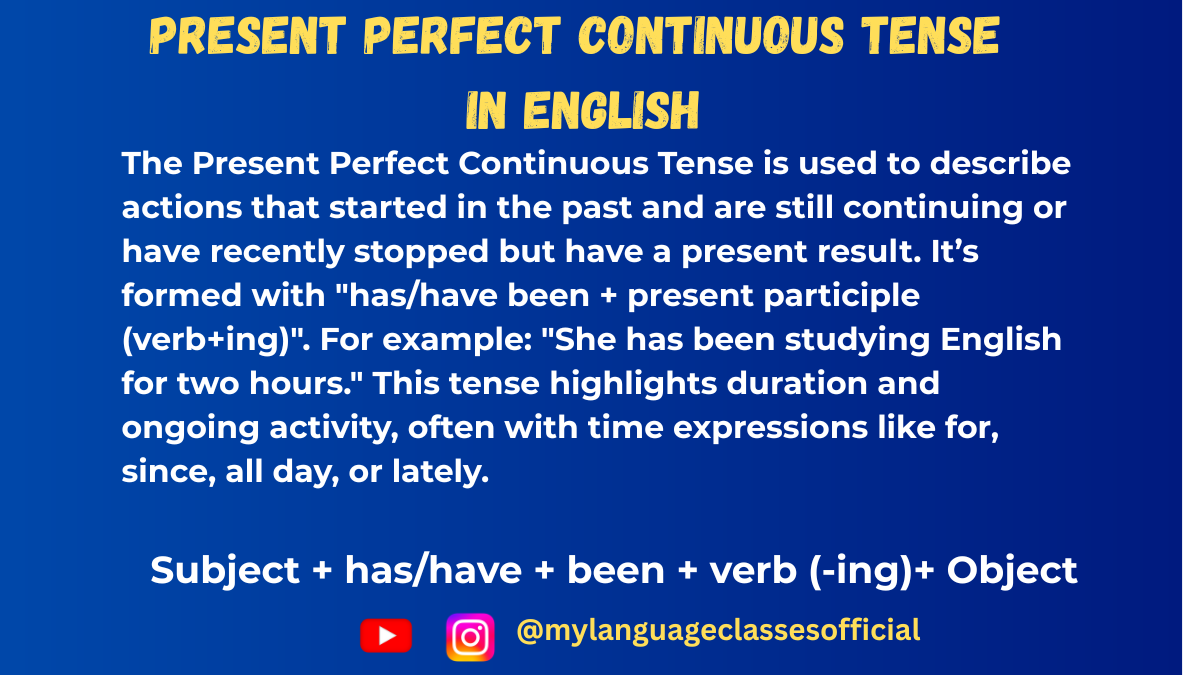
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English: Grammar Rules, Usage & Examples
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English: Easy Explanation with Examples, Grammar Rules, and Everyday Sentences
Have you ever been learning English for a while but still get confused with tenses? You’re not alone! One of the most interesting and useful tenses in English is the Present Perfect Continuous Tense. It’s powerful, easy to use, and helps you sound more natural and fluent in conversations. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced learner, mastering this tense will take your English to the next level.
We often hear and use phrases like “I’ve been studying all day,” “She’s been cooking since morning,” or “They’ve been working on that project for weeks.” All of these are real-life examples of the Present Perfect Continuous tense, a vital part of spoken and written English.
In this complete guide, you’ll learn:
- What the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is
- When and how to use it in real life
- Clear grammar rules and sentence structure
- Common mistakes and how to fix them
- 20 practice examples and exercises
Whether you’re preparing for exams, improving your spoken English, or trying to speak like a native, this guide is for you.
Let’s get started with a simple explanation!
🔍 What Is the Present Perfect Continuous Tense? Explanation and Overview
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense (also known as the Present Perfect Progressive Tense) is used to describe actions that began in the past and are still happening now or were recently completed with a clear result in the present.
This tense helps show the duration of an action, making it easier to talk about how long something has been happening. It’s often used with time expressions like:
- for (a period of time)
- since (a specific point in time)
- lately, recently, all day, for hours, since morning, etc.
🧠 Structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The basic formula is:
Subject + has/have + been + verb (-ing)
Let’s break it down:
- “has” is used with he, she, it, singular nouns
- “have” is used with I, you, we, they, plural nouns
- Then comes “been” (this part never changes)
- Followed by the -ing form of the verb (present participle)
🗣️ Examples:
- I have been studying English for two years.
- She has been working since 8 a.m.
- They have been playing outside all day.
These sentences show that the action started in the past and is still continuing or has just stopped with a visible effect in the present.
💡 Why Is This Tense Important?
The Present Perfect Continuous is essential because:
- It connects the past with the present
- It shows the length or duration of an action
- It adds depth and clarity to your sentences
- It’s used frequently in both spoken and written English
It answers questions like:
- How long have you been learning English?
- What have you been doing all day?
- Has he been feeling okay lately?
By understanding this tense, you’ll be able to express yourself more naturally and clearly—especially when talking about ongoing activities or recent efforts.
🗓️ Everyday Sentences Using the Present Perfect Continuous: 10 Common Examples
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used in everyday conversations all around the world. You’ll often hear native speakers use it to talk about daily routines, ongoing activities, or repeated actions with a clear connection to now.
Here are 10 simple and relatable sentences using the Present Perfect Continuous tense to help you see how it works in real life.
✅ 10 Common Real-Life Examples
- I’ve been studying English every evening.
(The action started in the past and is still happening.) - She’s been cooking dinner since 6 p.m.
(She started cooking at 6, and she’s still in the kitchen.) - They’ve been watching TV for three hours.
(The action continues, and the duration is important.) - We’ve been waiting for the bus for 20 minutes.
(The action hasn’t ended. We are still waiting.) - He’s been playing video games all morning.
(It started in the morning and hasn’t stopped yet.) - I’ve been reading a new book lately.
(The action is recent and ongoing.) - She has been feeling tired this week.
(The feeling started earlier and is still present.) - You’ve been working too hard lately.
(It’s a recent and repeated action.) - The baby has been crying for an hour.
(The action started earlier and continues now.) - We’ve been planning our trip since January.
(The planning started in the past and is still happening.)
🔑 Key Words Often Used with This Tense:
- since (since Monday, since morning, since 10 a.m.)
- for (for two hours, for a long time, for days)
- lately, recently, all day, this week, this month
These expressions show how long the action has been going on. Including them in your sentences helps listeners understand when something started and whether it’s still happening.
⏰ When to Use the Present Perfect Continuous Tense: All the Key Situations
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense helps us explain actions that link the past to the present. But when exactly should you use it? Below are the most common and important situations where this tense is used in English conversations, writing, and real-life communication.
🎯 1. To Talk About Actions That Started in the Past and Are Still Happening
Use this tense to show that something began earlier and is continuing now.
- I’ve been learning Japanese for two years.
- She’s been living in this city since 2021.
- They’ve been building that house for months.
🎯 2. To Show the Duration of an Activity
Use this tense when the amount of time something has happened is important.
- We’ve been waiting for over an hour.
- He has been working nonstop since morning.
- The students have been studying all night.
🎯 3. To Describe Recent Actions That Have a Present Result
Sometimes the action is finished or nearly finished, but the effect is still visible now.
- She’s tired because she’s been running.
- I’ve been crying—that’s why my eyes are red.
- It’s wet because it’s been raining.
🎯 4. To Emphasize Repeated or Ongoing Behavior
This tense can describe things that happen again and again over a short period of time.
- You’ve been complaining a lot lately.
- He’s been calling me every day this week.
- They’ve been visiting their grandma often these days.
🎯 5. To Show Temporary Activities
Use this tense for things that are not permanent and are happening for a limited time.
- I’ve been working from home this month.
- She’s been staying with her parents for a while.
- He’s been taking extra classes this semester.
🎯 6. With Time Expressions Like:
- For (a period): for 10 minutes, for three years, for a long time
- Since (a point in time): since morning, since 2019, since last night
- Lately / Recently: These show something started not long ago and is ongoing
💬 Examples:
- I’ve been reading a lot lately.
- She has been talking about that recently.
Understanding when to use the Present Perfect Continuous will help you speak more clearly and sound more natural in English. It’s all about connecting the past, the present, and the effect.
🔄 How to Conjugate Verbs in the Present Perfect Continuous: Conjugation Rules
Learning how to conjugate verbs in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is simple once you understand the basic structure. This tense has a clear and consistent pattern that works across regular and irregular verbs.
Let’s break it down step by step so you can use it confidently.
📚 Basic Structure:
Subject + has/have + been + verb(-ing)
Subject Auxiliary Verb “Been” Main Verb (-ing) I have been working You have been reading He / She / It has been playing We have been writing They have been studying
🛠️ Rules for Verb Conjugation:
All verbs in the Present Perfect Continuous use the -ing form (present participle). Here are the simple rules for forming it:
✅ Rule 1: Just add -ing to most verbs
- work → working
- play → playing
- study → studying
✅ Rule 2: Drop the final -e and add -ing
- make → making
- come → coming
- write → writing
✅ Rule 3: Double the final consonant if the verb ends in consonant-vowel-consonant and is stressed
- run → running
- sit → sitting
- begin → beginning
📝 Note: Don’t double the consonant if it ends in “w,” “x,” or “y”
- fix → fixing (not fixxing)
- snow → snowing
📌 Positive Sentences:
- I have been reading a book.
- She has been cooking since 10 a.m.
- We have been talking for hours.
❌ Negative Sentences:
Subject + has/have + not + been + verb(-ing)
- I haven’t been sleeping well lately.
- He hasn’t been working this week.
- They haven’t been going to the gym recently.
❓ Question Sentences:
Have/Has + subject + been + verb(-ing)?
- Have you been studying for your test?
- Has she been feeling okay?
- Have they been living here long?
🔑 Key Tip:
Always remember: the helping verbs (“has” / “have”) change based on the subject, but the words “been” and the -ing verb always stay the same.
📘 Present Perfect Continuous Grammar Rules You Need to Know
Understanding the key grammar rules of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense helps you use it correctly and confidently in your speaking and writing. These rules are simple, and once you get them, using this tense will feel natural.
Here’s everything you need to know about how this tense works.
🧩 Rule 1: Use “has” or “have” According to the Subject
- Use “has” with he, she, it, or singular nouns
👉 She has been studying.
👉 The cat has been sleeping. - Use “have” with I, you, we, they, or plural nouns
👉 I have been reading.
👉 They have been working.
🧩 Rule 2: Always Use “Been” Before the Verb + ing
The word “been” is fixed in this tense. It doesn’t change, no matter the subject.
- Correct: I have been watching that show.
- ❌ Incorrect: I have watching…
- ❌ Incorrect: I have being watching…
🧩 Rule 3: Use the -ing Form (Present Participle) of the Verb
The main verb must always be in -ing form.
- play → playing
- do → doing
- study → studying
- eat → eating
🧩 Rule 4: Use Time Expressions to Show Duration or Continuity
This tense is used with time expressions that show how long something has been happening.
⏱️ Use:
- for + a period of time
👉 for two hours, for years, for a long time
👉 I’ve been working for three days. - since + a specific point in time
👉 since Monday, since 8 a.m., since 2010
👉 She’s been practicing since morning. - Other expressions: lately, recently, all day, this week
👉 He has been feeling tired lately.
🧩 Rule 5: Use It for Actions Still Happening or Just Finished
This tense links the past and the present—the action either continues now or has just stopped but has a visible result.
- I’m dirty because I have been gardening.
- She has been learning Spanish for years.
🧩 Rule 6: Use It for Temporary or Repeated Behavior
- I have been staying at a friend’s house. (temporary)
- You have been eating a lot of junk food lately. (repeated)
⚠️ Rule 7: Don’t Use This Tense with Non-Action (Stative) Verbs
Some verbs describe states, not actions, and usually don’t appear in the continuous form.
Common stative verbs:
- know, like, love, believe, understand, need, prefer, own
❌ Incorrect: I have been knowing her for years.
✅ Correct: I have known her for years. (Use present perfect instead)
✨ Summary Table: Present Perfect Continuous Rules
Rule Description Example 1 Use has/have based on subject She has / I have 2 Always include “been” have been reading 3 Use verb+ing studying, cooking, working 4 Use time expressions for 2 hours, since Monday 5 Action started earlier, continues or just ended I’ve been learning English 6 Use for temporary or repeated action He’s been staying with friends 7 Avoid stative verbs in continuous form ❌ have been knowing → ✅ have known
💡 Important Tips for Using the Present Perfect Continuous Correctly
Using the Present Perfect Continuous Tense becomes much easier when you know a few key tips and tricks. These tips will help you avoid confusion and use the tense more naturally in your daily conversations, emails, essays, and more.
Whether you’re just starting or want to fine-tune your grammar, these points are here to support you.
✅ 1. Focus on Actions That Connect the Past to Now
Always remember—this tense is used when an action started in the past and is still going on, or just finished with a visible result.
🗣️ Example:
- She has been working since 9 a.m. (still working now)
- I’m tired because I have been running. (just stopped running)
✅ 2. Always Use “Have/Has Been” – Don’t Skip It!
This is a three-part tense:
👉 has/have + been + verb-ingIt’s easy to forget one part, but that breaks the rule.
🗣️ Correct:
- He has been watching the news.
- They have been studying all night.
❌ Incorrect:
- He been watching…
- They studying all night…
✅ 3. Use Time Expressions to Sound More Natural
Phrases like for, since, lately, and recently add clarity and help the listener know how long the action has lasted.
🗣️ Examples:
- I’ve been reading since this morning.
- She has been feeling tired lately.
✅ 4. Use It for Temporary Actions, Not Permanent States
This tense is usually for temporary or ongoing situations, not for things that are always true.
🗣️ Examples:
- I’ve been staying with a friend. (temporary)
- He’s been working at a café this summer. (not permanent)
✅ 5. Don’t Use Stative Verbs with This Tense
Verbs like know, believe, understand, and love don’t usually appear in continuous forms.
❌ Incorrect:
- I’ve been knowing her for years.
✅ Correct: - I’ve known her for years.
✅ 6. Use It to Show Frustration or Surprise (Advanced Usage)
Sometimes, this tense is used to express a repeated behavior that’s annoying or surprising, often with “lately” or “recently.”
🗣️ Examples:
- You’ve been interrupting me a lot lately.
- He’s been spending too much money recently.
✅ 7. Make Sure the Action Is Still True or Relevant
Don’t use this tense for actions that are completely finished and have no effect now. Use the simple past or present perfect instead.
🗣️ Incorrect:
- I’ve been eating lunch. (if lunch is already done and no trace remains)
🗣️ Better: - I ate lunch.
- I have eaten lunch.
✅ 8. Use Contractions in Conversation
In spoken English, people often say:
- I’ve been = I have been
- She’s been = She has been
- We’ve been = We have been
Using contractions makes your English more natural and fluent.
🧠 Pro Tip: Ask Yourself Two Questions
- Did the action start in the past?
- Is it still happening or are the results still showing?
If yes to both, use Present Perfect Continuous!
❌ Common Mistakes with the Present Perfect Continuous and How to Fix Them
Even experienced learners can make errors when using the Present Perfect Continuous Tense. But don’t worry—these mistakes are easy to fix once you understand them. Below, you’ll find the most common issues and how to correct them so your English sounds clear, fluent, and natural.
❌ Mistake 1: Using the Wrong Helping Verb
Learners often confuse “has” and “have.”
🧩 Wrong:
- He have been playing football.
- They has been watching a movie.
✅ Right:
- He has been playing football.
- They have been watching a movie.
📝 Tip:
Use has for: he, she, it
Use have for: I, you, we, they
❌ Mistake 2: Forgetting “Been”
This is a very common slip! Students leave out “been”, which is essential in this tense.
🧩 Wrong:
- I have reading a book.
- She has watching TV.
✅ Right:
- I have been reading a book.
- She has been watching TV.
📝 Tip:
Always remember: has/have + been + verb-ing
❌ Mistake 3: Using the Wrong Verb Form
The Present Perfect Continuous always uses the -ing form of the verb.
🧩 Wrong:
- He has been study English.
- We have been cook all day.
✅ Right:
- He has been studying English.
- We have been cooking all day.
📝 Tip:
No base form—always use the present participle (verb + ing).
❌ Mistake 4: Using Stative Verbs
This tense is not used with verbs that describe states or feelings.
🧩 Wrong:
- I have been knowing her since 2020.
- She has been liking this song for years.
✅ Right:
- I have known her since 2020.
- She has liked this song for years.
📝 Tip:
Use the Present Perfect (not continuous) with stative verbs like:- know, believe, love, own, understand, need
❌ Mistake 5: Using It for Finished Actions with No Present Result
This tense is for actions still going on or with present results.
🧩 Wrong:
- I have been watching the movie. (if the movie ended long ago)
✅ Right: - I watched the movie. (Past simple)
- I have watched the movie. (Present perfect)
📝 Tip:
If the action is 100% over and there’s no sign of it now, don’t use this tense.
❌ Mistake 6: Using “for” and “since” Incorrectly
Learners sometimes mix these up.
🧩 Wrong:
- I have been working since five hours.
- He has been waiting for 10 a.m.
✅ Right:
- I have been working for five hours.
- He has been waiting since 10 a.m.
📝 Tip:
- Use for + duration (e.g., for 3 days)
- Use since + specific point in time (e.g., since Monday)
❌ Mistake 7: Overusing the Tense
Not every past-to-present action needs this tense.
🧩 Wrong:
- I have been eating breakfast at 8 a.m. (if it’s a daily routine)
✅ Right: - I eat breakfast at 8 a.m.
📝 Tip:
Use Present Perfect Continuous only when the action is ongoing or just completed—not for regular habits or general truths.
✅ Quick Review: Fixing Common Errors
Mistake Wrong Right Helping verb He have been… He has been… Missing “been” I have reading I have been reading Wrong verb form cooking → cook cooking Stative verbs have been knowing have known Time expressions since 2 hours for 2 hours Finished actions have been eating ate or have eaten Habitual actions have been eating at 8 eat at 8
✨ 20 Present Perfect Continuous Example Sentences for Better Understanding
Seeing grammar rules in action makes everything clearer. Below are 20 easy and natural example sentences using the Present Perfect Continuous Tense. These cover different situations—daily life, school, work, emotions, and more—so you can understand how this tense is used in real life.
These examples are written in simple, everyday English for learners at all levels. Read them aloud if you like—it helps with fluency and confidence!
✅ Daily Life and Routine
- I have been studying English every evening after dinner.
- She has been cooking since 5 o’clock.
- They have been cleaning the house all morning.
- He has been listening to music for two hours.
- We have been watching this TV series for a week now.
✅ School and Work
- The students have been reading the new science chapter.
- My brother has been working from home lately.
- I have been writing my homework since 7 p.m.
- She has been learning Japanese with online classes.
- They have been attending the English workshop all week.
✅ Feelings and Health
- I have been feeling really tired these days.
- He has been coughing a lot since yesterday.
- We have been worrying about the test results.
- She has been feeling better since taking the medicine.
- My parents have been hoping for good news.
✅ Fun and Hobbies
- I have been drawing in my sketchbook all day.
- They have been playing football since morning.
- She has been dancing at the studio recently.
- We have been planning our weekend trip together.
- He has been practicing guitar for the school performance.
These examples show how the Present Perfect Continuous connects past actions to the present moment. Some are still happening, while others just finished but have effects that can be seen or felt now.
📝 Present Perfect Continuous Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Try to complete the following 20 sentences by filling in the blanks with the correct form of the Present Perfect Continuous tense. Use the verbs given in parentheses.
- I __________ (work) on this project for three hours.
- She __________ (study) English since last year.
- They __________ (play) football all afternoon.
- He __________ (read) that book for a week now.
- We __________ (wait) for the bus since 7 a.m.
- You __________ (talk) on the phone for too long!
- The children __________ (watch) cartoons since morning.
- My parents __________ (prepare) dinner for the guests.
- I __________ (practice) piano every day this month.
- She __________ (run) in the park for the past hour.
- They __________ (build) a new house since January.
- He __________ (paint) the walls all day.
- We __________ (learn) Spanish for six months now.
- The dog __________ (bark) at strangers lately.
- I __________ (try) to fix the computer for an hour.
- She __________ (sleep) very badly these days.
- The students __________ (discuss) the topic since class started.
- He __________ (drive) the same route every day recently.
- We __________ (plan) the party for weeks.
- You __________ (use) your phone a lot today.
Try to fill these in without looking back, then check your answers below!
✔️ Check Your Answers for the Present Perfect Continuous Exercise
Below are the correct sentences with the Present Perfect Continuous tense filled in. The answer part is bolded for clarity.
- I have been working on this project for three hours.
- She has been studying English since last year.
- They have been playing football all afternoon.
- He has been reading that book for a week now.
- We have been waiting for the bus since 7 a.m.
- You have been talking on the phone for too long!
- The children have been watching cartoons since morning.
- My parents have been preparing dinner for the guests.
- I have been practicing piano every day this month.
- She has been running in the park for the past hour.
- They have been building a new house since January.
- He has been painting the walls all day.
- We have been learning Spanish for six months now.
- The dog has been barking at strangers lately.
- I have been trying to fix the computer for an hour.
- She has been sleeping very badly these days.
- The students have been discussing the topic since class started.
- He has been driving the same route every day recently.
- We have been planning the party for weeks.
- You have been using your phone a lot today.
Great job if you got them right! This exercise will help you feel more confident using the Present Perfect Continuous tense in your own sentences.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Present Perfect Continuous
1. What is the Present Perfect Continuous tense used for?
The Present Perfect Continuous tense shows actions that started in the past and are still happening now or have recently finished but affect the present. It often emphasizes the duration or continuous nature of the action.
2. How do I form the Present Perfect Continuous tense?
Use this structure:
have/has + been + verb-ing
For example:- I have been working.
- She has been studying.
3. Can I use the Present Perfect Continuous with all verbs?
No. It’s mainly used with action verbs. It’s usually not used with stative verbs (verbs that describe a state or feeling) like know, believe, love, own, want.
4. What is the difference between Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous?
- Present Perfect: Focuses on completion or result (e.g., I have finished my homework).
- Present Perfect Continuous: Focuses on the process or duration of the action (e.g., I have been doing my homework for two hours).
5. When do I use “for” and “since” with this tense?
- Use for to talk about a period of time (e.g., for two hours, for a week).
- Use since to talk about a specific starting point (e.g., since Monday, since 2010).
6. Can I use the Present Perfect Continuous to talk about repeated actions?
Yes, especially if the actions are temporary or happening more often than usual and you want to express surprise or annoyance.
Example:- You have been calling me every day lately!
7. Is it correct to say “I have been knowing her for years”?
No. Use the Present Perfect for stative verbs:
- Correct: I have known her for years.
8. Can I use contractions in the Present Perfect Continuous?
Absolutely! Contractions like I’ve been, she’s been, they’ve been are common in spoken and informal English.
9. What’s the difference between Present Perfect Continuous and Past Perfect Continuous?
- Present Perfect Continuous is about an action continuing up to now.
- Past Perfect Continuous talks about an action that was happening before another action in the past.
10. Can I use the Present Perfect Continuous with future time?
No, it refers to the past and present only. For future actions, other tenses like the future continuous are used.
If you have more questions, feel free to ask in comments below!
📌 Key Takeaways: Present Perfect Continuous Summary and Important Points
- The Present Perfect Continuous tense shows actions that started in the past and are still continuing or have recently stopped with effects now.
- It is formed with: have/has + been + verb-ing (present participle).
- Use has with he, she, it, and have with I, you, we, they.
- Common time expressions include for (duration) and since (starting point).
- It’s mostly used with action verbs, not stative verbs like know, believe, love.
- The tense emphasizes how long or how often something has been happening.
- It’s different from Present Perfect, which focuses on completion rather than duration.
- Avoid common mistakes such as forgetting “been,” mixing up helping verbs, or using this tense with finished actions.
- Examples:
- I have been studying English for two hours.
- She has been working here since 2019.
- Use contractions like I’ve been, she’s been for natural speech.
- The Present Perfect Continuous helps make your English more precise and fluent.
🔚 Conclusion: Mastering the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English
The Present Perfect Continuous tense is an essential part of English grammar that helps you express ongoing actions and their connection to the present moment. Whether you’re talking about something you started a long time ago or an activity that just finished, this tense makes your communication clearer and more natural.
By understanding how to form, use, and avoid common mistakes with the Present Perfect Continuous, you will boost your English skills and sound more confident in speaking and writing. Remember, practice is key — use the examples, exercises, and tips from this guide to strengthen your knowledge every day.
If you found this guide helpful, I’d love to hear from you! Share your thoughts in the comments below or connect with me on social media. For more tips, resources, and inspiration, visit my blog at mylanguageclasses.in. Follow on Instagram and subscribe on YouTube
📚 Continue Learning English
-

Present Continuous Tense in English: Grammar Rules, Usage & Examples
Present Continuous Tense in English: How to Use It Correctly with Examples and Exercises
Are you wondering what is the Present Continuous Tense and how to use it in real life? Whether you’re saying “I am eating,” “She is studying,” or “They are playing,” you’re already using the Present Continuous Tense! This powerful part of English grammar helps us talk about actions that are happening right now, around now, or in the near future. In this blog, you’ll learn everything you need to know to master this tense — explained in a super simple way, with real-life examples, common mistakes, and fun practice exercises.
The Present Continuous Tense is also known as the Present Progressive Tense, and it’s one of the most common and useful tenses in English. Native speakers use it all the time in daily conversation, storytelling, and even in songs! It helps you express what someone is doing right now, what’s happening these days, or even what’s going to happen soon. Sounds useful, right?
Whether you’re a complete beginner or brushing up your skills, this guide will help you understand:
- What the Present Continuous Tense is
- When and how to use it
- How to form correct sentences using this tense
- Common mistakes and how to fix them
- And lots of examples and exercises for practice
So, let’s jump in and unlock the secret to sounding more natural and confident in English conversations with the Present Continuous Tense!
What Is the Present Continuous Tense? Explanation and Overview
The Present Continuous Tense (also called the Present Progressive Tense) is a verb tense used to describe actions that are happening right now or around the current time. It can also describe future actions that are already planned or arranged. This tense is very useful in both spoken and written English.
🔹 How is the Present Continuous Formed?
We form the Present Continuous by using two parts:
- The present tense of the verb “to be” — am / is / are
- The base verb + -ing
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ingExamples:
- I am reading a book.
- She is cooking dinner.
- They are playing football.
🔹 When Do We Use the Present Continuous?
The Present Continuous is used to talk about:
- Actions happening right now
- Actions happening around now, but not necessarily at the exact moment of speaking
- Temporary actions or situations
- Planned future events
- Changing situations
- Repeated actions that happen too often (often with the word “always” for emphasis)
We’ll explore all these situations in detail in the next section!
🔹 Why Is the Present Continuous Important?
This tense helps you sound more fluent and natural in conversations. It allows you to describe what’s happening at the moment, talk about your current plans, and even express emotions or habits.
Here’s why English learners need to master it:
- It’s used all the time in everyday conversation.
- It helps you describe real-life actions more clearly.
- It builds a strong foundation for understanding other verb tenses.
Once you understand how and when to use it, the Present Continuous Tense becomes easy and fun!
Everyday Sentences Using the Present Continuous Tense: 10 Common Examples
To really understand how the Present Continuous Tense works, it helps to see it in action. These real-life sentences show how people use this tense to talk about what’s happening now, plans for the near future, and even changing situations.
All of these sentences follow the same basic structure:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ingHere are 10 everyday examples of the Present Continuous Tense:
- I am studying for my English test right now.
- She is talking on the phone with her best friend.
- We are having lunch at a new restaurant today.
- He is watching his favorite TV show.
- They are playing outside because the weather is nice.
- You are learning English very quickly!
- My mom is baking a chocolate cake for my birthday.
- It is raining heavily, so don’t forget your umbrella.
- I am meeting my cousin at the mall this evening.
- The baby is sleeping, so please be quiet.
🔹 What Do These Examples Show?
These examples help you see that:
- You can use this tense for right now (“She is talking on the phone”)
- Or for plans in the near future (“I am meeting my cousin”)
- Or even to describe changing situations (“You are learning English very quickly”)
Learning through examples is one of the best ways to improve your grammar naturally. Try making a few similar sentences about yourself after reading these!
When to Use the Present Continuous Tense: All the Key Situations
The Present Continuous Tense is used in many everyday situations. It helps us describe actions, plans, and changes happening right now or soon. Below are the most important times when you should use this tense. These are the key rules that English speakers follow without even thinking!
🔹 1. Actions Happening Right Now
Use the Present Continuous to talk about something that is happening at the exact moment you are speaking.
Examples:
- She is brushing her hair.
- I am writing an email.
- They are waiting for the bus.
🔹 2. Actions Happening Around Now (but Not Exactly Now)
Sometimes the action is happening during this time period, but not exactly at the moment of speaking.
Examples:
- I am reading a great book these days.
- He is studying a lot this week.
- We are working on a group project at school.
🔹 3. Temporary Situations
Use this tense to describe actions or situations that are not permanent. They are happening for a short time only.
Examples:
- She is staying with her aunt for a few days.
- I am living in Paris this month.
- We are using my dad’s car today.
🔹 4. Planned Future Events
We also use the Present Continuous to talk about future plans that are already arranged or decided.
Examples:
- I am visiting my grandma tomorrow.
- They are flying to London next week.
- We are going to the movies tonight.
🔹 5. Changing or Developing Situations
This tense helps describe actions or things that are gradually changing or developing over time.
Examples:
- The weather is getting colder.
- My little brother is growing fast.
- Your English is improving every day!
🔹 6. Annoying Repeated Actions (with “Always”)
Sometimes we use the Present Continuous with the word “always” to show that something happens too often — often in an annoying or funny way.
Examples:
- He is always forgetting his homework!
- She is always talking in class.
- You are always losing your phone!
These are the main situations where the Present Continuous Tense is used. Each one helps you express time and action more clearly, so your English sounds natural and fluent.
How to Conjugate Verbs in the Present Continuous Tense: Conjugation Rules
To use the Present Continuous Tense correctly, you need to know how to conjugate verbs properly. Don’t worry—it’s simple once you understand the steps!
Here’s a quick guide to conjugating verbs in the Present Continuous:
🔹 Step 1: Use the Correct Form of the Verb “To Be” (am / is / are)
Choose the correct form based on the subject of the sentence:
Subject Form of “To Be” I am He / She / It is You / We / They are
🔹 Step 2: Add the Base Verb + –ing
Take the base form of the verb and add –ing to the end.
Examples:
- read → reading
- play → playing
- write → writing
✅ Putting It All Together
Formula:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ingExamples:
- I am eating lunch.
- She is dancing on the stage.
- They are studying for exams.
🔹 Spelling Rules for –ing Verbs
Here are some simple spelling rules to remember when adding –ing:
1. Just add –ing (for most verbs)
- walk → walking
- clean → cleaning
- jump → jumping
2. Drop the final ‘e’ and add –ing
- make → making
- write → writing
- drive → driving
3. Double the final consonant (if the verb has one vowel + one consonant)
- run → running
- sit → sitting
- swim → swimming
⚠️ But don’t double the final letter if the word ends in w, x, or y:
- fix → fixing
- snow → snowing
- play → playing
🔹 Negative Sentences in the Present Continuous
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + not + verb-ingExamples:
- I am not watching TV.
- She is not sleeping now.
- They are not working today.
🔹 Questions in the Present Continuous
Structure:
Am/Is/Are + subject + verb-ing?Examples:
- Are you coming with us?
- Is he doing his homework?
- Am I talking too fast?
Now that you’ve got the conjugation rules down, you’re ready to build strong Present Continuous sentences with confidence!
Present Continuous Grammar Rules You Need to Know
Understanding grammar rules helps you use the Present Continuous Tense correctly and confidently. These simple yet important rules will guide you through building both written and spoken sentences that sound natural and accurate.
Let’s look at the core grammar rules for this tense:
🔹 1. Basic Sentence Structure
The Present Continuous follows a simple formula:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
Examples:
- I am cooking dinner.
- She is watching a movie.
- They are playing football.
🔹 2. Forming Negative Sentences
To make a sentence negative, just add “not” after am, is, or are.
Subject + am/is/are + not + verb-ing
Examples:
- I am not going to school today.
- He is not feeling well.
- We are not working right now.
🔹 3. Forming Yes/No Questions
Move the form of “to be” to the beginning of the sentence.
Am/Is/Are + subject + verb-ing?
Examples:
- Are you doing your homework?
- Is she wearing a new dress?
- Am I talking too fast?
🔹 4. Short Answers for Questions
Use short answers with am, is, or are to sound polite and clear.
Examples:
- Are you coming? → Yes, I am. / No, I’m not.
- Is he studying? → Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
- Are they eating? → Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
🔹 5. Use Only Action Verbs
Use the Present Continuous only with action verbs—verbs that show something happening.
Correct:
- I am writing a letter.
- She is running in the park.
Incorrect:
- I am knowing the answer. ❌
- He is liking this movie. ❌
(These use stative verbs, which are not used in this tense—more on that below.)
🔹 6. Avoid Using Stative Verbs in Present Continuous
Stative verbs describe states, emotions, or thoughts, not actions. These verbs are usually NOT used in the Present Continuous.
Common stative verbs include:
- Know, like, love, hate, believe, understand, want, need, remember, own, seem
Examples:
- I know the answer. ✅
- I am knowing the answer. ❌
🔹 7. Time Expressions Often Used
Use time expressions to make your sentence clearer.
Common ones include:
- now
- right now
- at the moment
- today
- this week
- currently
- tonight
- these days
Examples:
- He is studying at the moment.
- We are working late tonight.
These grammar rules are your foundation for mastering the Present Continuous Tense. Use them regularly to form correct and meaningful sentences every time you speak or write in English.
Important Tips for Using the Present Continuous Tense Correctly
Using the Present Continuous Tense is easy once you get the hang of it. But even fluent speakers can make small mistakes. These simple and smart tips will help you speak and write with clarity and confidence.
Whether you’re a beginner or brushing up your skills, these tips are perfect for learning the correct use of the Present Continuous.
✅ 1. Focus on Actions Happening Right Now
Use this tense to talk about actions that are happening at the moment of speaking.
Correct:
- I am listening to music right now.
- She is cooking dinner now.
Tip: Use words like now, at the moment, and right now to show the action is happening currently.
✅ 2. Use It for Temporary Actions
Use the Present Continuous for things happening temporarily, even if not at this exact second.
Examples:
- I am living in Spain this summer.
- They are taking swimming lessons this month.
Tip: If it’s not permanent, you can often use this tense.
✅ 3. Describe Changing or Developing Situations
Use this tense when something is slowly changing or growing.
Examples:
- The weather is getting colder.
- Your English is improving day by day!
Tip: Verbs like grow, change, improve, get, and develop are often used in this way.
✅ 4. Avoid Using Stative Verbs
Stative verbs describe feelings, thoughts, emotions, or states, and they don’t usually appear in the Present Continuous.
Examples of Stative Verbs:
- know
- believe
- like
- love
- understand
- need
Incorrect:
- I am knowing the answer. ❌
Correct:
- I know the answer. ✅
Tip: If the verb describes a state, use the simple present instead.
✅ 5. Don’t Forget the Verb “To Be”
Many learners skip the am/is/are part by mistake. This is a common error!
Incorrect:
- She reading a book. ❌
Correct:
- She is reading a book. ✅
Tip: Always check that you’re using the correct helping verb before the action verb.
✅ 6. Watch the Spelling of –ing Verbs
Always check spelling rules when adding –ing:
- Drop the e: make → making
- Double the consonant: run → running
- Don’t change if the word ends in w, x, or y: fix → fixing
Tip: A spelling mistake can change the meaning of the word or make it incorrect.
✅ 7. Use Clear Time Expressions
Time phrases help listeners or readers understand your message better.
Examples:
- at the moment
- this week
- right now
- today
- currently
Tip: These phrases help to clearly show that you are talking about ongoing or temporary actions.
✅ 8. Practice Makes Perfect
The more you use the Present Continuous, the easier it becomes. Try:
- Talking about your current day or week.
- Writing diary entries using “I am…”
- Practicing with a friend or tutor.
Tip: Practice out loud for better fluency!
Keep these tips in mind as you move forward. You’ll find yourself using the Present Continuous naturally and correctly in no time!
Common Mistakes with the Present Continuous and How to Fix Them
Even experienced English learners sometimes make mistakes when using the Present Continuous Tense. But don’t worry—these errors are easy to fix once you know what to watch for. Here are the most common Present Continuous mistakes and simple ways to correct them.
❌ 1. Forgetting the “to be” verb (am/is/are)
Wrong:
She eating breakfast.
They going to school.Right:
She is eating breakfast.
They are going to school.Why it happens: Learners sometimes forget the helping verb.
Fix it: Always use am, is, or are before the verb + ing.
❌ 2. Using stative verbs in the continuous form
Wrong:
I am knowing the answer.
She is loving this movie.Right:
I know the answer.
She loves this movie.Why it happens: Some verbs describe feelings, thoughts, or states. These are not used in continuous form.
Fix it: Use the simple present tense with stative verbs.
❌ 3. Wrong verb spelling when adding “-ing”
Wrong:
He is runing.
They are makeing a mess.Right:
He is running.
They are making a mess.Why it happens: Learners forget spelling rules.
Fix it:- Drop the e: make → making
- Double the last letter if one vowel + one consonant: run → running
- Just add –ing if it ends in w, x, or y: fix → fixing
❌ 4. Using the Present Continuous for regular actions
Wrong:
I am waking up at 6 a.m. every day.Right:
I wake up at 6 a.m. every day.Why it happens: Learners confuse daily routines with current actions.
Fix it: Use the simple present tense for habits and routines.
❌ 5. Mixing up “is” and “are”
Wrong:
They is playing soccer.
He are eating now.Right:
They are playing soccer.
He is eating now.Why it happens: Confusion about subject-verb agreement.
Fix it:- Use am with “I”
- Use is with he, she, it
- Use are with you, we, they
❌ 6. Using it for completed actions
Wrong:
I am finished my homework.Right:
I have finished my homework.
Or: I am finishing my homework. (if still doing it)Why it happens: Learners confuse present perfect with present continuous.
Fix it: Use present perfect for completed actions and present continuous for actions still in progress.
❌ 7. Overusing the Present Continuous
Wrong:
I am go to the park every day.
She is have a dog.Right:
I go to the park every day.
She has a dog.Why it happens: Learners try to use present continuous for everything.
Fix it: Know when to use the simple present instead—especially for routines or permanent facts.
Quick Review: Common Mistake Fixes
Mistake Fix Forgetting am/is/are Add the correct helping verb Using stative verbs Use simple present Spelling errors Apply –ing spelling rules Using for daily routines Use simple present Wrong verb agreement Match subject with am/is/are For completed actions Use present perfect Using it everywhere Use correct tense for the situation By learning from these mistakes, you’ll be well on your way to speaking and writing with confidence in English.
20 Present Continuous Example Sentences for Better Understanding
To truly master the Present Continuous tense, seeing plenty of clear and relatable examples helps a lot. Below are 20 example sentences that show how the Present Continuous is used in everyday English. Read them carefully, and notice how each sentence describes an ongoing action or temporary situation.
Examples Showing Actions Happening Right Now
- I am writing this blog post for you.
- She is watching her favorite TV show at the moment.
- They are playing football in the park right now.
- We are having lunch together today.
- He is listening to music in his room.
Examples of Temporary or Ongoing Actions
- I am learning to speak Spanish this year.
- She is working on a big project this week.
- They are staying at their grandparents’ house for the weekend.
- We are trying a new recipe tonight.
- He is studying hard for his exams these days.
Examples of Changing or Developing Situations
- The climate is getting warmer every year.
- Your English skills are improving nicely.
- The kids are growing so fast!
- The company is expanding its business overseas.
- Prices are rising in the market recently.
Negative Sentences in Present Continuous
- I am not feeling well today.
- She is not coming to the party tonight.
- They are not working on the weekend.
- We are not watching that movie now.
- He is not driving his car today.
These examples cover different uses of the Present Continuous tense — from actions happening right now, to temporary activities, ongoing changes, and negatives. Try making your own sentences using this structure, and you’ll feel more confident every day!
Present Continuous Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
- She __________ (read) a very interesting book right now.
- They __________ (play) basketball at the moment.
- I __________ (learn) how to cook Italian food this week.
- We __________ (watch) a new series on Netflix.
- He __________ (write) an email to his friend.
- The children __________ (not/sleep) yet.
- My parents __________ (travel) to Japan this month.
- You __________ (talk) too loudly!
- The sun __________ (shine) brightly today.
- She __________ (take) dance classes these days.
- I __________ (not/feel) very well today.
- They __________ (work) on their homework right now.
- We __________ (wait) for the bus at the stop.
- He __________ (not/watch) TV at the moment.
- The dog __________ (bark) loudly outside.
- You __________ (listen) to music, aren’t you?
- She __________ (wear) a red dress today.
- They __________ (fix) the car this afternoon.
- I __________ (think) about changing my job.
- We __________ (have) dinner together tonight.
Try to complete this exercise on your own! When you’re ready, I will provide the answers.
Check Your Answers for the Present Continuous Exercise
- She is reading a very interesting book right now.
- They are playing basketball at the moment.
- I am learning how to cook Italian food this week.
- We are watching a new series on Netflix.
- He is writing an email to his friend.
- The children are not sleeping yet.
- My parents are traveling to Japan this month.
- You are talking too loudly!
- The sun is shining brightly today.
- She is taking dance classes these days.
- I am not feeling very well today.
- They are working on their homework right now.
- We are waiting for the bus at the stop.
- He is not watching TV at the moment.
- The dog is barking loudly outside.
- You are listening to music, aren’t you?
- She is wearing a red dress today.
- They are fixing the car this afternoon.
- I am thinking about changing my job.
- We are having dinner together tonight.
Great job if you got them right! If you missed any, review the Present Continuous rules and examples from earlier sections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Present Continuous Tense
1. What is the Present Continuous tense used for?
The Present Continuous tense is used to describe actions happening right now, temporary actions, ongoing changes, or future plans.
2. How do I form the Present Continuous tense?
Use the verb “to be” (am/is/are) + the main verb + -ing. For example, I am eating, She is running, They are studying.
3. Can I use the Present Continuous for habits?
No, habits and routines are usually expressed with the Simple Present tense (e.g., I drink coffee every day). The Present Continuous is for temporary or ongoing actions.
4. Are there verbs that cannot be used in the Present Continuous?
Yes, stative verbs that describe feelings, thoughts, or states (like know, love, want, believe) are generally not used in the Present Continuous.
5. How do I make questions in the Present Continuous?
Invert the subject and the verb “to be”. For example, Are you coming? or Is she working?
6. How do I make negatives in the Present Continuous?
Add not after the verb “to be”. For example, I am not going, He is not sleeping, They are not playing.
7. Can I use the Present Continuous to talk about the future?
Yes, it’s often used to talk about planned future events. For example, We are meeting them tomorrow.
8. What are some common mistakes to avoid with the Present Continuous?
- Forgetting the helping verb am/is/are
- Using stative verbs in the continuous form
- Wrong spelling when adding -ing
- Using it for habits instead of simple present
9. How do I spell verbs when adding “-ing”?
- Drop the final e: make → making
- Double the last consonant if the verb ends with one vowel + one consonant: run → running
- Just add -ing for verbs ending in w, x, or y: fix → fixing
10. Can I use the Present Continuous with all subjects?
Yes! Use am with “I”, is with “he, she, it”, and are with “you, we, they”.
Key Takeaways: Present Continuous Summary and Important Points
- The Present Continuous tense describes actions happening right now, temporary actions, ongoing changes, and future plans.
- It is formed using the verb “to be” (am/is/are) + the main verb + -ing.
- Use am with “I”, is with “he, she, it”, and are with “you, we, they”.
- Negative sentences add not after the verb “to be” (e.g., She is not coming).
- Questions are made by inverting the subject and the verb “to be” (e.g., Are you working?).
- Do not use the Present Continuous with stative verbs like know, love, want.
- Spelling rules when adding -ing: drop final e, double consonants when needed, just add -ing for some verbs.
- Use the Present Continuous for planned future events (e.g., We are meeting tomorrow).
- Avoid common mistakes like forgetting the helping verb or using the Present Continuous for habits.
- Practice by making your own sentences and doing exercises to build confidence.
Conclusion: Master the Present Continuous Tense to Speak English Confidently!
The Present Continuous tense is one of the most useful and common tenses in English. Whether you’re describing what’s happening right now, sharing temporary activities, or talking about future plans, this tense helps you communicate clearly and naturally. By understanding its structure, common uses, and tricky points, you can improve your speaking and writing skills with confidence.
Keep practicing with real-life examples and exercises like those we covered here. The more you use the Present Continuous, the easier it becomes!
If you found this guide helpful, I’d love to hear from you! Share your thoughts in the comments below or connect with me on social media. For more tips, resources, and inspiration, visit my blog at mylanguageclasses.in. Follow on Instagram and subscribe on YouTube
📚 Continue Learning English
-

Present Perfect Tense in English: Grammar Rules, Usage & Examples
Learn the Present Perfect Tense in English: Easy Guide with Examples, Rules, and Exercises
Have you ever wondered when to use “have eaten,” “has gone,” or “have seen”? If yes, you’re in the right place! Understanding the present perfect tense in English can help you sound more fluent and natural. It’s one of the most important grammar topics for speaking, writing, and everyday conversations. Whether you’re just starting to learn English or you want to polish your skills, this guide will make it easy for you.
In this article, we will break down the present perfect tense in a way that’s clear, friendly, and simple to follow. We’ll explain what it means, when to use it, and how to form it. You’ll also learn common mistakes to avoid, tips to use it correctly, and get practice exercises with answers. With lots of real-life examples and useful sentences, this guide is your one-stop solution to master the present perfect tense.
So let’s dive in and understand how this powerful grammar point can improve your English today!
What Is the Present Perfect Tense? Explanation and Overview
The present perfect tense is a verb tense in English used to talk about actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past or started in the past and continue into the present. It connects the past with the present, showing that something is still important, true, or ongoing.
We form the present perfect tense using:
👉 has/have + past participle of the verb
Let’s break it down:
- “Have” is used with I, you, we, they
- “Has” is used with he, she, it
- The past participle is usually the third form of the verb (e.g., eat → eaten, go → gone, play → played)
Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited London three times.
- They have lived here for five years.
- We have never seen such a beautiful view.
These sentences don’t say when the action happened. That’s one of the key features of the present perfect—it’s about the experience, result, or connection to now, not the exact time.
The Present Perfect Is Used For:
- Experiences: “I have traveled to Japan.”
- Recent actions: “He has just left the room.”
- Changes over time: “My English has improved a lot.”
- Actions with present results: “She has broken her arm.”
- Ongoing situations: “We have lived here since 2010.”
Think of the present perfect like a bridge. It connects past actions to the present moment. You use it when you want to focus on what matters now, not just what happened before.
Everyday Sentences Using the Present Perfect Tense: 10 Common Examples
Using the present perfect tense in daily conversations can help you sound more natural and fluent in English. Here are 10 common and useful present perfect sentences that people use in everyday life.
These examples show different situations, such as experience, recent events, and life updates.
✅ 10 Common Present Perfect Tense Sentences
- I have eaten lunch already.
(You don’t need to say when, just that it’s done.) - She has just arrived at school.
(“Just” shows that the action happened very recently.) - We have lived in this city for ten years.
(This action started in the past and is still true.) - They have finished their homework.
(The result is important now—they’re free.) - Have you ever seen a shooting star?
(“Ever” is often used to talk about life experiences.) - He has broken his phone.
(The phone is broken now—that’s the result.) - I have never been to Paris.
(“Never” shows a life experience you haven’t had.) - You have grown so much since I last saw you!
(Shows change over time.) - We have just cleaned the kitchen.
(The action happened recently, and the kitchen is clean now.) - My brother has forgotten his keys again.
(The action affects the present—he can’t get in.)
These sentences are short, simple, and used by English speakers around the world every day. Practice them, change the subjects and verbs, and try making your own sentences to get more confident with the present perfect tense!
When to Use the Present Perfect Tense: All the Key Situations
The present perfect tense is used in many everyday situations. You’ll hear it in casual talks, news reports, and even in formal writing. The key idea is that the action has a connection to now—it either affects the present or continues into the present.
Here are all the main situations where the present perfect tense is used, explained with simple examples.
✅ 1. To Talk About Life Experiences
Use it to talk about things you’ve done at any time in your life until now. The exact time is not important.
- I have visited five countries.
- She has tried sushi before.
- Have you ever ridden a horse?
✅ 2. To Describe Changes Over Time
Use it to show how someone or something has changed from the past to now.
- My English has improved a lot.
- Prices have gone up.
- He has grown taller since last year.
✅ 3. To Show Unfinished Actions or Ongoing Situations
Use it for actions that started in the past and are still happening now.
- We have lived in this house for ten years.
- They have worked at the same company since 2015.
- She has studied English since she was a child.
👉 Tip: Use words like “for” and “since” in these situations.
✅ 4. To Report Recent Events
Use it to talk about something that happened recently, especially when the result matters now.
- I have just finished my homework.
- He has broken his arm.
- We have missed the bus!
👉 Common words: “just,” “already,” “yet,” “recently.”
✅ 5. To Talk About Actions That Have Relevance to Now
Sometimes we don’t care about when it happened—we care about the result or impact now.
- She has lost her wallet. (She doesn’t have it now.)
- They have painted the house. (It looks new now.)
- I have made a cake. (The cake is ready to eat.)
✅ 6. With “Ever,” “Never,” “Always,” “Often,” “Sometimes”
These time words show habits, experiences, or feelings up to now.
- Have you ever eaten dragon fruit?
- I have never failed a test.
- He has always been kind to others.
🧠 Remember:
If the time is finished (like “yesterday,” “last year,” or “in 2005”), do NOT use present perfect. Use the simple past tense instead.
❌ I have seen that movie last week.
✅ I saw that movie last week.
How to Conjugate Verbs in the Present Perfect Tense: Conjugation Rules
The present perfect tense is formed using two parts:
✅ have/has (helping verb) + past participle (main verb in past participle form)
Let’s look at the step-by-step rules for conjugating verbs in the present perfect tense for all subjects.
✅ 1. Use the Correct Helping Verb
Subject Helping Verb I, you, we, they have he, she, it has 🔹 Examples:
- I have eaten breakfast.
- She has gone to the store.
- They have arrived early.
✅ 2. Add the Past Participle of the Main Verb
There are two types of verbs:
- Regular verbs (add -ed to the base form)
- Irregular verbs (change completely)
🔹 Regular Verbs
Just add -ed to the base form.
Base Verb Past Participle play played walk walked call called 🔸 Example:
- We have played soccer today.
- He has walked to school.
🔹 Irregular Verbs
You need to memorize these. They don’t follow a pattern.
Base Verb Past Participle go gone eat eaten do done see seen write written 🔸 Example:
- I have written three emails.
- She has gone to work.
- They have seen that movie.
✅ 3. Negative Sentences
To make the sentence negative, add not after “have/has.”
🔸 Examples:
- I have not finished my homework.
- She has not visited the museum.
- They have not called yet.
👉 Short forms:
- haven’t = have not
- hasn’t = has not
✅ 4. Questions in Present Perfect
To ask a question, switch the order:
Have/Has + subject + past participle?🔸 Examples:
- Have you seen my phone?
- Has she eaten lunch?
- Have they finished the project?
✅ Quick Summary Chart
Sentence Type Structure Example Positive Subject + have/has + past participle She has visited Italy. Negative Subject + have/has + not + past participle We have not seen the movie. Question Have/Has + subject + past participle? Have you done your homework?
Present Perfect Grammar Rules You Need to Know
The present perfect tense can be easy once you understand a few important grammar rules. This section explains how to use this tense correctly, what to avoid, and how to make your English sound more natural and correct.
Let’s break it down in a friendly and simple way.
✅ Rule 1: Use Have/Has + Past Participle
This is the basic formula:
- I/You/We/They ➜ use have
- He/She/It ➜ use has
🔹 Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has called her mom.
- They have played outside.
✅ Rule 2: Use the Past Participle Form of the Verb
- For regular verbs, the past participle is the same as the past tense (add -ed):
➤ walk → walked
➤ clean → cleaned - For irregular verbs, the past participle form is different and must be memorized:
➤ go → gone
➤ see → seen
➤ do → done
🔹 Examples:
- I have gone to the store.
- He has seen that movie.
- We have done the homework.
✅ Rule 3: Time Is Not Specific
The present perfect is used when the time of the action is not exact or not mentioned.
❌ Wrong: I have eaten at 6 p.m.
✅ Right: I have eaten. / I have already eaten.If you know the exact time (yesterday, last week, in 2020), use simple past instead.
✅ Rule 4: Use Time Expressions That Work with Present Perfect
Some time words go well with the present perfect tense. Here are the most common ones:
Time Word Use Example already I have already eaten. yet Have you finished yet? just She has just arrived. ever Have you ever seen a lion? never I have never eaten sushi. since We have lived here since 2010. for He has worked here for five years. recently They have recently moved. lately I haven’t felt well lately.
✅ Rule 5: Do Not Use Present Perfect with Finished Time
If you mention a finished or specific past time, like “last night,” “two days ago,” or “in 2019,” you must use simple past, not present perfect.
❌ I have gone to the zoo yesterday.
✅ I went to the zoo yesterday.
✅ Rule 6: It’s All About the Connection to Now
Even if the action happened in the past, we use the present perfect when the result matters now.
🔹 Examples:
- She has lost her keys. (She can’t get in now.)
- I have finished my project. (It’s ready now.)
- They have broken the window. (The window is still broken.)
✅ Rule 7: Present Perfect Is Not Used with Clear Past Time Phrases
Here are some phrases you should not use with present perfect:
🚫 yesterday
🚫 last week
🚫 in 2010
🚫 when I was a child
🚫 two days agoInstead, use time phrases that refer to a time until now:
✅ ever, never, just, already, yet, for, since, recently, so far
Mastering these rules will help you build strong and correct sentences in English. The more you practice, the more natural this tense will feel to you!
Important Tips for Using the Present Perfect Tense Correctly
The present perfect tense can be tricky because it talks about the past but focuses on the present. These helpful tips will guide you through common situations, avoid mistakes, and make your English sound more natural.
✅ Tip 1: Think About the Result, Not the Time
The present perfect talks about something that happened in the past but is still connected to now.
🔹 Examples:
- I have broken my arm. (It’s still broken now.)
- She has lost her phone. (She can’t find it now.)
- They have finished the game. (It’s over now.)
🟡 Don’t say when it happened—just say that it happened.
✅ Tip 2: Use the Right Helping Verb – “Have” or “Has”
It’s a small word but super important!
Subject Helping Verb I, you, we, they have he, she, it has 🔹 Examples:
- I have cleaned my room.
- She has done her homework.
🔴 Don’t mix them up. Saying “He have” or “I has” is incorrect.
✅ Tip 3: Remember the Past Participle Form
For regular verbs, add -ed:
- walk → walked
- play → played
But irregular verbs are different. Some common ones to remember:
- go → gone
- see → seen
- eat → eaten
- write → written
- do → done
🟢 Practice these! Flashcards or quizzes help a lot.
✅ Tip 4: Use Time Words That Go With Present Perfect
Here are the best time expressions to use with the present perfect:
- Already: I have already eaten.
- Yet: Have you finished yet?
- Just: He has just arrived.
- Ever: Have you ever been to Paris?
- Never: I have never ridden a horse.
- Since: We have lived here since 2015.
- For: She has worked for 3 years.
- Lately / Recently: They have recently moved.
🔴 Don’t say: “I have gone to the zoo yesterday.”
✅ Say: “I went to the zoo yesterday.” (Use simple past for that.)
✅ Tip 5: Ask Good Questions in Present Perfect
To ask a question, start with Have/Has:
- Have you eaten lunch?
- Has she called the doctor?
- Have they seen the show?
🟠 Use “ever” or “yet” in questions to sound more natural:
- Have you ever tried sushi?
- Has he finished his homework yet?
✅ Tip 6: Use Short Forms in Everyday Speaking
In casual conversation, contractions sound more natural:
- I have → I’ve
- You have → You’ve
- He has → He’s
- We have → We’ve
- They have → They’ve
Examples:
- I’ve done my homework.
- She’s gone out.
- We’ve seen that movie.
✅ Tip 7: Practice Makes Perfect
📌 Practice by:
- Writing short sentences using have/has + past participle
- Making your own examples with words like “already,” “just,” “yet,” “never,” etc.
- Listening to native English conversations or watching English shows to hear real-life usage
The more you read, write, and speak using present perfect, the more confident you’ll feel using it correctly!
Common Mistakes with the Present Perfect Tense and How to Fix Them
The present perfect tense can be confusing, even for advanced learners. Here are some common mistakes people make and clear ways to fix them. Let’s learn from these errors so you can avoid them in your own English.
❌ Mistake 1: Mixing Up Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous
🔴 Incorrect: I have worked here since morning. (if you’re still working now)
✅ Correct: I have been working here since morning.🟢 Use present perfect continuous when you want to show the action is still continuing.
💡Use Present Perfect:
- I have lived here for 10 years. (Focus = result)
💡Use Present Perfect Continuous: - I have been living here for 10 years. (Focus = ongoing action)
❌ Mistake 2: Using “Did” in Present Perfect Sentences
🔴 Incorrect: I did not have eaten breakfast.
✅ Correct: I have not eaten breakfast.🚫 Never use did with the present perfect. That’s for the simple past tense only.
❌ Mistake 3: Forgetting to Use “Have” or “Has” at All
🔴 Incorrect: She gone to the market.
✅ Correct: She has gone to the market.🟢 The helping verb have or has is always needed. Without it, the sentence is incomplete and wrong.
❌ Mistake 4: Using the Wrong Verb Form
🔴 Incorrect: I have go to school today.
✅ Correct: I have gone to school today.🟢 Make sure to use the past participle form, not the base or simple past form.
Verb Simple Past Past Participle go went gone eat ate eaten do did done write wrote written
❌ Mistake 5: Using “Have Been” for Simple Actions
🔴 Incorrect: I have been eaten lunch.
✅ Correct: I have eaten lunch.🟢 “Have been” is used in present perfect continuous:
- I have been eating lunch. (means the action was in progress)
For a finished action, just say:
- I have eaten lunch.
❌ Mistake 6: Using “Never” and “Not” Together
🔴 Incorrect: I have not never tried sushi.
✅ Correct: I have never tried sushi.🚫 “Not never” is a double negative and should be avoided.
Use only never when you want to say you haven’t done something at all.
❌ Mistake 7: Overusing “Just” or “Already” in the Same Sentence
🔴 Incorrect: I have just already finished it.
✅ Correct: I have already finished it.
✅ Correct: I have just finished it.🟢 Pick one time word. You don’t need both. Using both sounds unnatural and confusing.
❌ Mistake 8: Using Specific Past Time Words with Present Perfect
🔴 Incorrect: I have visited France last year.
✅ Correct: I visited France last year.
✅ Correct: I have visited France many times. (no exact time)🟢 Remember: If you mention a clear past time, use simple past, not present perfect.
❌ Mistake 9: Forgetting Subject-Verb Agreement
🔴 Incorrect: They has gone home.
✅ Correct: They have gone home.🔴 Incorrect: He have finished his meal.
✅ Correct: He has finished his meal.🟢 Always match the subject with the correct helping verb:
- He/She/It = has
- I/You/We/They = have
❌ Mistake 10: Using Too Many Present Perfect Sentences in One Paragraph
🟠 Present perfect is useful, but don’t overuse it in writing. Mix it with simple past, present continuous, and other tenses to sound more natural.
🔹 Example:
“I have eaten breakfast. I have done my homework. I have taken a shower. I have talked to my friend.”
⬇️
✅ Better:
“I have eaten breakfast and done my homework. Then I took a shower and talked to my friend.”Avoiding these mistakes will make your English stronger, smoother, and more natural. These are small fixes, but they make a big difference!
✅ 20 Present Perfect Tense Example Sentences for Better Understanding
The best way to master the present perfect tense is to see it in action. Below are 20 simple, clear, and real-life examples that show how this tense is used in everyday English. These examples are designed for beginners and intermediate learners to easily understand the structure, usage, and feel of the present perfect tense.
Each sentence follows the basic form:
Subject + has/have + past participle
🔹 Examples with “Have”:
- I have finished my homework.
- We have visited the zoo many times.
- They have never seen snow before.
- You have eaten too much chocolate today!
- I have watched that movie three times.
- We have already booked our tickets.
- They have played soccer this morning.
- I have tried sushi before.
- You have done a great job.
- I have walked five miles today.
🔹 Examples with “Has”:
- She has gone to the market.
- He has written five books.
- It has rained all day.
- My dog has learned a new trick.
- The train has just arrived.
- He has painted his room blue.
- She has lost her phone again.
- My friend has never flown in an airplane.
- The baby has fallen asleep.
- My teacher has given us extra homework.
Fill-in-the-Blank Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Fill in each blank with the correct form of the verb in present perfect.
- She ________ (write) three books already.
- I ________ (never, see) such a beautiful sunset.
- They ________ (eat) all the pizza.
- We ________ (already, finish) our homework.
- He ________ (just, arrive) at the airport.
- I ________ (be) to Paris twice.
- The students ________ (not, complete) their assignment yet.
- They ________ (live) in New York for 10 years.
- My parents ________ (never, travel) to Asia.
- I ________ (see) that movie before.
- She ________ (buy) a new dress.
- We ________ (not, hear) from him yet.
- You ________ (take) your medicine today?
- I ________ (be) sick for a week.
- He ________ (finish) his lunch.
- We ________ (wait) for the bus for 20 minutes.
- My brother ________ (not, do) his homework.
- They ________ (go) to the concert last night.
- I ________ (already, clean) the kitchen.
- She ________ (be) to the doctor this week.
Now that you’ve completed the exercise, let’s check your answers!
Check Your Answers for the Present Perfect Exercise
- She has written three books already.
- I have never seen such a beautiful sunset.
- They have eaten all the pizza.
- We have already finished our homework.
- He has just arrived at the airport.
- I have been to Paris twice.
- The students have not completed their assignment yet.
- They have lived in New York for 10 years.
- My parents have never traveled to Asia.
- I have seen that movie before.
- She has bought a new dress.
- We have not heard from him yet.
- Have you taken your medicine today?
- I have been sick for a week.
- He has finished his lunch.
- We have been waiting for the bus for 20 minutes.
- My brother has not done his homework.
- They went to the concert last night. (This one is simple past because the time is specific: last night)
- I have already cleaned the kitchen.
- She has been to the doctor this week.
🟢 How to Fix Mistakes:
- Make sure to use “have” or “has” correctly.
- Don’t forget to use the past participle form of the verb (e.g., written, eaten, been, etc.).
- Pay attention to whether the action is completed or ongoing, and choose the appropriate verb form.
🎉 Well done! You’ve made it through the exercise!
Now, let’s move on to the next section:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Present Perfect Tense.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Present Perfect Tense
1. What is the present perfect tense used for?
The present perfect tense is used to express:
- Actions or events that have happened at an indefinite time in the past, but are still relevant to the present.
- Example: I have seen that movie. (I saw it at some point in the past, but it’s still important now.)
- Actions that started in the past and continue into the present.
- Example: She has lived here for five years. (She started living here five years ago and still lives here.)
2. Can I use the present perfect with a specific time in the past?
No, the present perfect tense is not used when mentioning specific times in the past. Use the simple past for that.
- Incorrect: I have visited Paris in 2015.
- Correct: I visited Paris in 2015.
3. What is the difference between “I have done” and “I did”?
- “I have done” (present perfect) is used when the action is relevant to the present or has just been completed.
- Example: I have finished my homework. (The action has an impact on now.)
- “I did” (simple past) is used when the action happened at a specific time in the past and is not related to the present.
- Example: I did my homework yesterday.
4. Can I use the present perfect for actions that are still happening?
Yes, the present perfect continuous tense is often used for actions that are still happening, but the present perfect can be used to talk about actions that started in the past and continue to affect the present.
- Example: I have been studying for three hours. (present perfect continuous for the ongoing action)
- Example: I have studied French for five years. (present perfect for the result that affects now)
5. Can I use “for” and “since” with the present perfect?
Yes, both “for” and “since” are used with the present perfect tense to talk about durations:
- For is used for a period of time:
- Example: I have lived here for five years.
- Since is used for a specific point in time:
- Example: She has worked here since 2010.
6. What if I’m talking about something that happened recently?
You can use the present perfect tense when talking about an action that just happened:
- Example: I have just finished my lunch. (The action happened a short time ago, and it’s still relevant.)
7. How do I make negative sentences in the present perfect tense?
To make a negative sentence in the present perfect, just add “not” after have/has.
- Example: I have not seen that movie.
- Example: He has not finished his work yet.
8. Can I ask questions with the present perfect tense?
Yes, you can form questions by moving have/has to the beginning of the sentence.
- Example: Have you finished your homework?
- Example: Has she been to Japan?
🟢 Helpful Tip:
If you’re still unsure about when to use the present perfect tense, remember this simple rule: It connects the past with the present.
Key Takeaways: Present Perfect Tense Summary and Important Points
Here’s a quick recap of all the important information about the present perfect tense:
🔹 What is the Present Perfect Tense?
- The present perfect is used to talk about actions that started in the past and are still relevant to the present.
- It is formed by using “have/has” + past participle.
🔹 When to Use the Present Perfect Tense:
- Actions that have an impact on the present, even though they occurred at some indefinite time in the past.
- Experiences or actions that have happened at some point in time without specifying when.
- Example: I have visited France.
- Actions that started in the past and continue into the present.
- Example: She has worked here for five years.
🔹 Conjugation of Verbs in Present Perfect:
- “Have” is used with I, you, we, they.
- “Has” is used with he, she, it.
- The verb that follows should be in the past participle form (e.g., finished, seen, eaten).
🔹 Key Grammar Rules:
- Present perfect is not used with specific times (like yesterday, in 2015).
- Use for (duration) and since (starting point) with the present perfect.
- The negative form is made with “have/has not”.
🔹 Important Tips to Remember:
- Use “have” or “has” depending on the subject.
- For actions completed recently or with ongoing relevance, use the present perfect.
- Common time expressions: already, never, ever, just, yet, so far, since, for.
🔹 Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Don’t use specific dates or times with the present perfect (e.g., I have gone there in 2020 is incorrect).
- Always check if the verb is in its correct past participle form.
🎯 Conclusion
The present perfect tense is a crucial part of English grammar. It helps link actions from the past with the present, making it one of the most versatile tenses to use. Whether you’re talking about experiences, completed actions, or actions that started in the past and continue today, the present perfect is there to express these ideas effectively.
Now that you’ve learned about the present perfect tense, it’s time to put your knowledge into practice!
If you found this guide helpful, I’d love to hear from you! Share your thoughts in the comments below or connect with me on social media. For more tips, resources, and inspiration, visit my blog at mylanguageclasses.in. Follow on Instagram and subscribe on YouTube
📚 Continue Learning English
-

Simple Present Tense in English: Grammar Rules, Usage & Examples
Mastering the Simple Present Tense in English: A Complete Beginner-to-Expert Guide
The Simple Present Tense is the foundation of everyday English conversations. From saying what you do every day to describing facts and truths, this powerful tense is used all around you—at school, at home, and in the world! If you’ve ever said,“I eat breakfast,” or “The sun rises in the east,” then congratulations—you’ve already used the Simple Present Tense!
In this easy-to-follow guide, you’ll learn what the Simple Present Tense is, how to use it, and how to master it with real-life examples, grammar tips, and fun exercises. Whether you’re just starting your English learning journey or looking to polish your skills, this guide will give you the tools to speak and write English with confidence.
📘 What is the Simple Present Tense?
The Simple Present Tense is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in English. It’s used to talk about things that happen regularly, facts, general truths, and habits.
Here’s a quick and simple definition:
The Simple Present Tense describes actions that happen regularly, always, or sometimes. It also talks about facts and general truths.
Let’s break it down:
- We use the base form of the verb with I, you, we, they (e.g., I play, They eat).
- We add -s or -es to the verb when the subject is he, she, it (e.g., She plays, It rains).
🔍 Real-Life Examples:
- I go to school every day.
- She loves chocolate.
- The Earth orbits the Sun.
- They play soccer on Sundays.
- He works in a bank.
These sentences all describe something that is true now and happens regularly. That’s the Simple Present Tense in action!
✅ How to Form Sentences in the Simple Present Tense
In the Simple Present Tense, the basic sentence structure follows this simple pattern:
Subject + Verb (Base Form) + Object
This structure is used for affirmative statements. Let’s break it down:
- Subject: The person or thing performing the action (e.g., I, you, he, she, they).
- Verb: The action or state (in its base form, e.g., eat, play, study).
- Object: The person or thing that receives the action (e.g., book, ball, food).
Examples:
- I read books.
- She plays football.
- They eat pizza.
- We study English.
Tip:
For third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), add -s or -es to the verb:
- She reads.
- He goes.
With this simple structure, you can start creating clear and direct sentences in the Simple Present Tense!
🗣️ Common Expressions Using the Simple Present Tense (With Real-Life Examples)
The Simple Present Tense is everywhere—in daily conversations, schedules, facts, and even instructions. Learning real-life sentences helps you understand how native speakers use it naturally and confidently.
Below are 10 real-life examples of the Simple Present Tense that you can start using right away. These sentences cover everyday routines, habits, facts, and instructions that are useful for students, professionals, and travelers alike.
✅ 10 Real-Life Sentences Using the Simple Present Tense:
- I wake up at 7 a.m. every morning.
👉 (Daily habit) - She drinks a glass of milk before school.
👉 (Routine action) - The train arrives at 6 o’clock sharp.
👉 (Fixed schedule) - We study English at My Language Classes.
👉 (Ongoing learning activity) - They speak Spanish at home.
👉 (Habitual behavior) - My brother plays the guitar very well.
👉 (Hobby or skill) - The sun sets in the west.
👉 (Universal fact) - Dogs bark when they see strangers.
👉 (General truth) - You need a passport to travel abroad.
👉 (Fact and necessity) - Teachers help students learn new things.
👉 (Regular action)
Each of these sentences is short, clear, and meaningful—just the way you should practice speaking and writing in English. Use them as models for your own conversations.
🔤 Conjugation Rules of the Simple Present Tense (With Easy Examples)
Understanding how to conjugate verbs in the Simple Present Tense is essential for forming correct sentences. Luckily, the rules are easy once you get the hang of them. Let’s break it down in a way that’s super simple and beginner-friendly.
👥 Subjects and Verb Forms
In English, verbs change based on the subject (who or what is doing the action). In the Simple Present Tense, we usually use:
- Base form of the verb for:
👉 I, you, we, they
✅ I walk, You eat, They dance - Add -s or -es to the verb for:
👉 He, she, it
✅ He walks, She eats, It dances
📌 Basic Conjugation Chart
Here’s how to conjugate the verb “to play” in the Simple Present Tense:
Subject Verb Form Example I play I play football. You play You play with your dog. We play We play every evening. They play They play video games. He plays He plays the piano. She plays She plays chess. It plays It plays a sound.
📝 Rules for Adding “-s” or “-es”:
Here are the main spelling rules to keep in mind:
- Most verbs → just add -s
➤ play → plays, read → reads, cook → cooks - Verbs ending in -ch, -sh, -s, -x, or -o → add -es
➤ go → goes, watch → watches, wash → washes, fix → fixes - Verbs ending in a consonant + “y” → change y to i + es
➤ study → studies, cry → cries
(BUT: if vowel + y, just add -s: play → plays)
⚠️ Be Careful With These Irregular Verbs
Some verbs have unusual forms in the Simple Present:
- Have → becomes has (He has a book.)
- Do → becomes does (She does her homework.)
- Go → becomes goes (He goes to school.)
Mastering these simple conjugation rules will help you build correct and confident English sentences. Practice these often and you’ll get used to them quickly!
🕒 When Do We Use the Simple Present Tense? (Complete Guide to Usage)
The Simple Present Tense is one of the most flexible and useful tenses in English. You’ll find it in everyday conversations, books, school instructions, and even in signs and advertisements. Knowing when to use it will help you speak clearly and naturally.
Let’s explore the key situations where the Simple Present Tense is used, along with simple examples that make it easy to understand.
🔄 1. Habits and Daily Routines
Use the Simple Present to talk about things you do regularly, like daily or weekly routines.
✅ Examples:
- I brush my teeth twice a day.
- She goes to the gym every morning.
- We eat dinner at 8 p.m.
🌍 2. General Truths and Facts
It is also used to talk about facts or things that are always true.
✅ Examples:
- Water boils at 100°C.
- The moon goes around the Earth.
- Dogs bark.
📅 3. Schedules and Timetables
Use it for planned events and fixed schedules, especially for public transportation or official timings.
✅ Examples:
- The train leaves at 5:00 p.m.
- School starts at 9:00 a.m.
- My flight arrives at 10:15 a.m.
💬 4. Instructions and Directions
It’s used in giving instructions, recipes, or directions.
✅ Examples:
- First, mix the flour and sugar.
- Open your books to page 10.
- Turn left at the traffic light.
🧠 5. Thoughts, Emotions, and States
Use it for mental states, emotions, and conditions that don’t change quickly.
✅ Examples:
- I know the answer.
- She loves reading books.
- He feels tired.
📰 6. Commentaries and Headlines
News headlines and live commentaries often use the Simple Present for quick updates.
✅ Examples:
- Team A wins the match!
- Fire breaks out in the city center.
📣 7. Proverbs and Sayings
Common expressions, quotes, and proverbs also use this tense.
✅ Examples:
- Practice makes perfect.
- Honesty is the best policy.
Now that you know all the main uses of the Simple Present Tense, you can begin recognizing it in real-life situations—on the news, in conversations, and even in songs and movies!
📚 Grammar Rules of the Simple Present Tense (Made Simple for Everyone)
Understanding the grammar rules of the Simple Present Tense is like learning the rules of a fun game—it makes everything easier and more enjoyable. These rules tell you how to use verbs correctly in sentences. Let’s look at them in a way that’s easy to follow and remember.
✅ Rule 1: Use the Base Form of the Verb (for I, You, We, They)
For most subjects (I, you, we, they), just use the verb as it is.
🔹 Examples:
- I walk to school.
- You eat vegetables.
- We like music.
- They play soccer.
✅ Rule 2: Add -s or -es to the Verb (for He, She, It)
When the subject is he, she, or it, you must add -s or -es to the verb.
🔹 Examples:
- He runs fast.
- She watches TV every evening.
- It makes a loud noise.
✅ Rule 3: Use “do/does” to Make Questions
To ask questions in the Simple Present Tense, we use do or does at the beginning.
- Use do with I, you, we, they
- Use does with he, she, it
🔹 Examples:
- Do you like pizza?
- Does she speak English?
- Do they live nearby?
✅ Rule 4: Use “do not” or “does not” to Make Negatives
To make negative sentences, we use do not (don’t) or does not (doesn’t) followed by the base verb.
- Use don’t with I, you, we, they
- Use doesn’t with he, she, it
🔹 Examples:
- I don’t like cold coffee.
- She doesn’t go to the gym.
- They don’t watch TV.
✅ Rule 5: Be Verbs (am, is, are) Are Different
For sentences with am, is, or are, the form depends on the subject.
- I → am
- He, she, it → is
- You, we, they → are
🔹 Examples:
- I am a student.
- He is happy.
- They are ready.
💡 These “be” verbs work like helping hands—they help describe feelings, conditions, and identities.
✅ Rule 6: Verb Agreement Is Key
Always make sure your verb agrees with the subject. This means the verb should match the subject in number and person.
🔹 Wrong: He go to school.
🔹 Correct: He goes to school.
Quick Recap Table:
Subject Verb Type Example I Base I walk to school. You Base You read books. We Base We play music. They Base They cook dinner. He -s/-es He drinks water. She -s/-es She writes well. It -s/-es It makes noise. These grammar rules are your tools for building great English sentences in everyday life. Keep practicing them with real sentences, and soon you’ll use them without even thinking!
⚠️ Things to Keep in Mind While Using the Simple Present Tense
(Tricky Points, Exceptions & Helpful Tips)
Even though the Simple Present Tense is easy to learn, there are a few important things you should always remember. These tricky points can make a big difference in your speaking and writing.
Let’s explore the most common exceptions and helpful tips that learners often miss.
🤔 1. Add -s, -es, or -ies Carefully
When using he, she, it, don’t just add -s blindly! The spelling changes based on the ending of the verb.
🔹 Just add -s:
- She eats apples.
- He walks fast.
🔹 Add -es if the verb ends in: -ch, -sh, -ss, -x, or -o
- She watches cartoons.
- He goes to the park.
- It washes easily.
🔹 Change -y to -ies if there’s a consonant before -y
- She studies hard.
- He tries his best.
⚠️ But if there’s a vowel before the -y, just add -s:
- She plays the guitar.
🙅♂️ 2. Don’t Use the -s Form After “Does” or “Doesn’t”
One common mistake is adding -s to the verb after “does” or “doesn’t.” Don’t do that!
❌ Wrong: She does goes to school.
✅ Correct: She does go to school.
🧠 3. Know When to Use “Be” Verbs Instead of Action Verbs
Use am, is, are (be verbs) for conditions, feelings, and identity—not actions.
🔹 Correct:
- I am tired.
- She is a doctor.
- They are excited.
Don’t say: “I am go to school.” ❌
Say: “I go to school.” ✅
⏰ 4. Don’t Use It for Ongoing Actions
The Simple Present is not used for actions happening right now.
❌ Wrong: I eat dinner now.
✅ Correct: I am eating dinner now. (This is Present Continuous Tense.)
📢 5. Use “Do” and “Does” Only for Questions and Negatives
“Do” and “does” help in forming questions and negatives—but not in positive sentences.
🔹 Question: Does she like chocolate?
🔹 Negative: She doesn’t like chocolate.
🔹 Positive: She likes chocolate.
🧩 6. Third-Person Singular Is a Common Trap
Many learners forget to change the verb for he, she, it. Always double-check!
🔹 Wrong: He play football.
🔹 Correct: He plays football.
✅ Quick Checklist to Keep in Mind:
- ✅ Add -s/-es/-ies with he/she/it.
- ✅ Use do/does for questions and negatives.
- ✅ Never use two verb forms together (e.g., does plays ❌).
- ✅ Use the base verb after do/does/don’t/doesn’t.
- ✅ Use the correct form of be verbs for feelings or states.
- ✅ Don’t use Simple Present for actions happening right now.
Remember: These small points make a huge difference in speaking English correctly and confidently.
❌ Common Mistakes in the Simple Present Tense (And How to Fix Them)
The Simple Present Tense may look easy at first, but many English learners fall into the same traps. Here are the most frequent mistakes and simple tricks to help you speak and write like a pro.
1. ❌ Using the Wrong Verb Form with “I” or “You”
Many learners use the -s form of the verb with “I” or “you,” which is incorrect.
🔹 Wrong: I likes movies.
🔹 Correct: I like movies.🔹 Wrong: You goes to school.
🔹 Correct: You go to school.🧠 Tip: Remember, the -s ending is only for he, she, it—not for “I” or “you.”
2. ❌ Mixing Up Verb Tenses in One Sentence
Sometimes learners start with Simple Present but accidentally shift to another tense.
🔹 Wrong: She goes to the market and bought vegetables.
🔹 Correct: She goes to the market and buys vegetables.🧠 Tip: Keep the tense consistent unless the time changes.
3. ❌ Forgetting to Add Helping Verbs in Negative Sentences
Learners often forget do/does in negatives, creating confusing sentences.
🔹 Wrong: He not like apples.
🔹 Correct: He does not like apples.🧠 Tip: Always use do/does + not to make a proper negative.
4. ❌ Using Present Tense for Future Events Without Time Words
The Simple Present can be used for future events only when paired with time expressions.
🔹 Wrong: My train leaves.
🔹 Correct: My train leaves at 6 PM.🧠 Tip: If talking about future schedules, always include a clear time reference.
5. ❌ Forgetting to Use Articles (a, an, the) Properly
Articles often get skipped, especially by non-native speakers.
🔹 Wrong: She is teacher.
🔹 Correct: She is a teacher.🧠 Tip: Even simple present needs correct grammar structure. Articles matter!
6. ❌ Using Continuous Tense Instead of Simple Present
Some learners mix up continuous tense with simple present for routines.
🔹 Wrong: He is playing football every Sunday.
🔹 Correct: He plays football every Sunday.🧠 Tip: Use Simple Present for regular or repeated actions—not continuous!
7. ❌ Misplacing Time Expressions
Time expressions like “every day,” “always,” or “on Sundays” should be placed clearly in the sentence.
🔹 Confusing: He goes on Sundays to church.
🔹 Better: He goes to church on Sundays.🧠 Tip: Place time words at the beginning or end of the sentence for clarity.
8. ❌ Making Yes/No Questions Without Do/Does
Skipping do/does makes questions sound unnatural.
🔹 Wrong: You like apples?
🔹 Correct: Do you like apples?🧠 Tip: Always begin yes/no questions with do or does.
9. ❌ Using “Don’t” with Third-Person Singular
This one’s very common. Learners say “don’t” instead of “doesn’t” for he/she/it.
🔹 Wrong: She don’t like math.
🔹 Correct: She doesn’t like math.🧠 Tip: “Doesn’t” is only for he, she, it. “Don’t” is for all the rest!
10. ❌ Forgetting Subject-Verb Agreement in Longer Sentences
When the sentence gets longer, people sometimes forget if the subject is singular or plural.
🔹 Wrong: The boy who plays guitar and sings in the choir like pizza.
🔹 Correct: The boy who plays guitar and sings in the choir likes pizza.🧠 Tip: Always match the verb to the main subject, even in long sentences.
These mistakes are easy to fix once you become aware of them. Keep practicing with simple sentences first, and then move on to longer ones.
✅ 20 Clear and Easy Example Sentences Using the Simple Present Tense
The Simple Present Tense is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in English. It talks about habits, daily routines, facts, and regular actions. Here are 20 example sentences that demonstrate how this tense is used naturally in everyday conversation.
These examples cover a variety of sentence structures, subjects, and common topics to give learners a well-rounded understanding.
🧍♂️ With “I” and “You”
- I brush my teeth every morning.
- You always bring your notebook to class.
- I love chocolate ice cream.
- You speak three languages fluently.
- I visit my grandmother on Sundays.
👨👩👧👦 With “He,” “She,” and “It”
- He studies English every day.
- She drinks tea in the morning.
- It rains a lot in April.
- He plays football on the weekends.
- She watches cartoons after school.
👬 With “We” and “They”
- We go to school by bus.
- They work at a big company.
- We play chess during lunch break.
- They enjoy cooking together.
- We celebrate our birthdays at home.
🔁 Habitual Actions and Routines
- The sun rises in the east.
- My dad reads the newspaper every morning.
- Birds sing in the early morning.
- The store opens at 9 a.m.
- Students take a test every Friday.
These sentences show how versatile and useful the Simple Present Tense is in real communication. Whether you’re talking about your daily routine, expressing likes and dislikes, or stating a general fact—this tense keeps your message clear and simple.
📝 20 Fill-in-the-Blank Exercises – Practice the Simple Present Tense
These fill-in-the-blank questions will help you test your understanding of the Simple Present Tense. Each sentence has a blank where the correct form of the verb needs to be used. The subject and context will guide you.
These exercises are great for learners who want to practice verb forms, sentence structure, and subject-verb agreement. Let’s dive in!
✅ Instructions:
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in Simple Present Tense.
- He __________ (like) to play cricket every Sunday.
- I __________ (go) to school by bicycle.
- She __________ (watch) cartoons after dinner.
- They __________ (study) in the library.
- My mother __________ (cook) delicious food.
- The baby __________ (cry) at night.
- You __________ (read) very fast.
- It usually __________ (rain) in July.
- We __________ (walk) to the park every evening.
- The dog __________ (bark) at strangers.
- I __________ (drink) milk every morning.
- He __________ (write) neat handwriting.
- The sun __________ (shine) brightly today.
- She __________ (speak) three languages.
- You __________ (know) the answer, don’t you?
- My friends __________ (play) video games after school.
- The teacher __________ (teach) us math.
- I __________ (love) my pet cat.
- The birds __________ (fly) in the sky.
- He __________ (fix) his bike every weekend.
These examples are carefully chosen to give you a wide range of subjects and action verbs so you can master the use of the Simple Present Tense step by step.
✅ Answers: 20 Fill-in-the-Blank Exercises – Simple Present Tense
Check your answers below. The correct verb forms are highlighted in bold.
- He likes to play cricket every Sunday.
- I go to school by bicycle.
- She watches cartoons after dinner.
- They study in the library.
- My mother cooks delicious food.
- The baby cries at night.
- You read very fast.
- It usually rains in July.
- We walk to the park every evening.
- The dog barks at strangers.
- I drink milk every morning.
- He writes neat handwriting.
- The sun shines brightly today.
- She speaks three languages.
- You know the answer, don’t you?
- My friends play video games after school.
- The teacher teaches us math.
- I love my pet cat.
- The birds fly in the sky.
- He fixes his bike every weekend.
Tips for Reviewing Your Answers:
- Third-person singular (he, she, it): Don’t forget to add -s or -es to the verb.
- Negative and question forms: Always use do/does (and don’t/doesn’t) with the main verb.
- Plural subjects (we, they, I, you): Use the base form of the verb without adding -s.
This practice will help you feel more comfortable with using the Simple Present Tense correctly. Keep practicing to improve your fluency!
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions on Simple Present Tense in English
1. What is the Simple Present Tense?
The Simple Present Tense is used to talk about actions or events that happen regularly, facts, general truths, and things that are always true.2. When do we use the Simple Present Tense?
We use the Simple Present Tense for:- Habits and routines (e.g., I wake up at 7 a.m. every day.)
- General truths (e.g., The sun rises in the east.)
- Facts (e.g., Water boils at 100°C.)
- Scheduled events in the future (e.g., The train leaves at 6:30 p.m.)
3. How do you form the Simple Present Tense?
To form the Simple Present:- For most verbs, use the base form (e.g., I play, they study).
- For third-person singular (he, she, it), add -s or -es to the verb (e.g., She plays, He watches).
4. What is the rule for adding ‘s’ or ‘es’ in the third-person singular?
- Add -s if the verb ends in a consonant (e.g., He works, She plays).
- Add -es if the verb ends in -sh, -ch, -x, -z, -o, or -ss (e.g., She watches, He goes).
5. What are the common mistakes when using the Simple Present?
- Forgetting to add -s or -es for third-person singular subjects (e.g., He play instead of He plays).
- Using the base form for negative sentences and questions with do/does (e.g., I do not plays → I do not play).
6. How do you make a negative sentence in the Simple Present?
To make a negative sentence in the Simple Present, use do not (don’t) or does not (doesn’t):- I don’t like pizza.
- She doesn’t go to the gym.
7. How do you form questions in the Simple Present?
To form questions, use do/does at the beginning of the sentence:- Do you like chocolate?
- Does he speak French?
8. Can the Simple Present Tense be used for future actions?
Yes, we can use the Simple Present to talk about future events that are scheduled or planned, such as transportation or timetables:- The bus leaves at 5:00 p.m.
- My flight departs tomorrow morning.
9. Is there a difference between “I play” and “I am playing”?
Yes! “I play” (Simple Present) refers to a habit or routine, while “I am playing” (Present Continuous) refers to an action happening right now.10. How do I know when to use the Simple Present versus the Present Continuous?
Use the Simple Present for actions that happen regularly, facts, and routines. Use the Present Continuous for actions happening right now or for temporary situations.
✅ Summary: Key Points of the Simple Present Tense
Here’s a quick recap of all the important points you’ve learned about the Simple Present Tense:
- What It Is: The Simple Present Tense is used to talk about habits, routines, general facts, and permanent situations.
- Common Use: It is used to express actions that are regular or habitual (e.g., “I go to school every day”), facts (e.g., “The Earth revolves around the sun”), and truths (e.g., “Water boils at 100°C”).
- Verb Forms:
- Add -s or -es for third-person singular (he, she, it).
- No -s for I, you, we, they.
- Negative Sentences: Use do not (don’t) or does not (doesn’t) for negation (e.g., “He doesn’t like coffee”).
- Questions: Begin questions with do/does (e.g., “Do you like soccer?”).
- Common Mistakes: Avoid forgetting do/does in negatives and questions, using incorrect verb forms with “I” and “you,” and confusing tense usage.
- Time Expressions: Common time expressions with the Simple Present include: always, every day, usually, often, never, etc.
- Examples: “He plays tennis,” “They read books,” “I don’t like pizza.”
✅ Conclusion
The Simple Present Tense is essential for building a solid foundation in English. It’s used to talk about daily routines, habits, general truths, and more. Mastering this tense will significantly improve your speaking and writing skills, helping you express yourself more clearly and naturally in everyday conversations.
Now that you understand how to use the Simple Present Tense correctly, it’s time to practice! Keep working on your sentence structure and verb forms, and you’ll be more confident with your English skills in no time.
If you found this guide helpful, I’d love to hear from you! Share your thoughts in the comments below or connect with me on social media. For more tips, resources, and inspiration, visit my blog at mylanguageclasses.in. Follow on Instagram and subscribe on YouTube
-

A Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future): Grammar Rules, Usage & Examples
Basic Concept of Verb Forms (Present, Past, Future)
Verbs are the heart of every sentence. They show actions, express states, and bring meaning to every idea we communicate. But did you know that verbs come in different forms depending on tense, subject, and usage? Understanding the basic concept of verb forms in English is one of the most important steps in learning the language. Whether you’re a beginner, a language enthusiast, or someone brushing up on grammar, mastering verb forms will help you speak and write more clearly and confidently.
In this easy-to-follow guide, we’ll explore the different verb forms used in English, how they work in real-life communication, and how you can use them correctly. You’ll see plenty of simple examples, useful tips, and short exercises to practice. By the end, you’ll feel more confident about identifying and using the right verb form in any situation.
Let’s start building your foundation in English grammar—one verb form at a time!
What Are Verbs?
A verb is a word that shows an action, a state, or an occurrence. In simple words, verbs tell us what someone is doing, what is happening, or how someone or something is. They are one of the most important parts of a sentence because, without a verb, a sentence can’t be complete.
✅ Types of Verbs (with examples):
Here are the three main roles verbs play:
- Action Verbs – These verbs show what someone or something does.
- Examples:
- She runs every morning.
- They eat lunch at noon.
- Examples:
- State Verbs – These verbs describe a condition or a state of being.
- Examples:
- He feels tired.
- I am happy.
- Examples:
- Occurrence Verbs – These show something happening or coming into being.
- Examples:
- It rains a lot in July.
- A miracle happened.
- Examples:
🧠 Quick Tip:
A good way to spot a verb is to ask, “What is the subject doing or being?” The answer is usually the verb!
Verb Forms and Their Usage
1. Present Verb Forms
Simple Present
Used for general facts, habitual actions, and universal truths.
- Example: She teaches English.
- Example: The sun rises in the east.
Present Continuous (Progressive)
Used for actions happening right now or ongoing actions.
- Example: She is teaching English now.
- Example: They are watching a movie.
Present Perfect
Used for actions that started in the past and continue into the present or have recently been completed.
- Example: I have lived here for five years.
- Example: She has just finished her homework.
Present Perfect Continuous
Used for actions that started in the past and are still ongoing.
- Example: He has been working all day.
- Example: She has been studying for two hours.
2. Past Verb Forms
Simple Past
Used for completed actions in the past.
- Example: She taught English last year.
- Example: They watched a movie yesterday.
Past Continuous (Progressive)
Used for actions that were happening at a specific time in the past.
- Example: She was teaching English when I arrived.
- Example: They were playing football at 5 PM.
Past Perfect
Used for an action that happened before another action in the past.
- Example: She had finished her work before they arrived.
- Example: He had already left when I called.
Past Perfect Continuous
Used for actions that were ongoing in the past before another action.
- Example: She had been teaching for five years before she moved to another city.
- Example: He had been studying before his friend came.
3. Future Verb Forms
Simple Future
Used for actions that will happen in the future.
- Example: She will teach English tomorrow.
- Example: They will watch a movie next week.
Future Continuous (Progressive)
Used for actions that will be happening at a specific time in the future.
- Example: She will be teaching at 10 AM tomorrow.
- Example: They will be playing football in the evening.
Future Perfect
Used for actions that will be completed before a certain time in the future.
- Example: She will have finished her work by 5 PM.
- Example: They will have left before we arrive.
Future Perfect Continuous
Used for actions that will have been ongoing for a period of time in the future.
- Example: She will have been teaching for 10 years by next year.
- Example: He will have been studying for three hours by the time you arrive.
Situations Where Verbs Are Used
- Expressing Actions
- She runs every morning.
- They played football yesterday.
- Describing States
- He feels happy.
- She is tired.
- Giving Instructions
- Open the door.
- Write your name here.
- Making Predictions
- It will rain tomorrow.
- She will pass the exam.
- Talking About Habits
- I drink coffee every morning.
- She goes to the gym daily.
- Talking About Ongoing Actions
- She is reading a book now.
- They are having dinner.
- Expressing Possibilities or Conditions
- If it rains, we will stay inside.
- If you study, you will pass the exam.
- Describing Past Events
- She had completed her work before the meeting started.
- He was driving when the accident happened.
Other Important Aspects Related to Verbs
1. Articles and Verbs
Articles (a, an, the) usually precede nouns, but their presence affects the verb used in the sentence.
- A boy is playing in the park.
- The teacher explains the lesson.
2. Gender and Verbs
Unlike some other languages, English verbs do not change form based on gender. However, subject pronouns (he, she, they) determine verb agreement.
- He runs every morning.
- She sings beautifully.
- They play football on Sundays.
3. Singular vs. Plural Verb Agreement
Verbs change based on the number of the subject.
- She eats an apple every day. (Singular)
- They eat apples every day. (Plural)
Things to Keep in Mind while using Verbs
Even though learning verb forms can be fun and rewarding, there are a few tricky areas and exceptions you should watch out for. Here are some important things to remember when dealing with verb forms in English:
🔁 1. Not All Verbs Follow Regular Rules
Most verbs form their past tense by adding –ed (like walk → walked), but many common verbs don’t follow this pattern. These are called irregular verbs.
- Example:
- Go → went → gone (not goed)
- Buy → bought → bought
👉 Always check a verb list for irregular forms. You’ll see them often in daily conversations.
🧱 2. The Verb “To Be” Is Special
The verb “to be” has many forms depending on the subject and tense. It’s also irregular.
- Present: am, is, are
- Past: was, were
- Past participle: been
- Present participle: being
📝 Example:
- I am ready.
- He was late.
- They have been helpful.
❗ 3. Third-Person Singular in Present Simple
When using present simple tense with he, she, or it, don’t forget to add –s or –es to the verb.
- Correct: She plays the piano.
- Incorrect: She play the piano.
🧠 Tip: Most learners forget this simple but important rule.
🔤 4. Some Verbs Don’t Take –ing or –ed Easily
These are usually stative verbs like:
- know, believe, understand, love, hate, own, want
❌ Incorrect: I am knowing the answer.
✅ Correct: I know the answer.
⏳ 5. Past Participle ≠ Past Tense
Don’t confuse the past tense and past participle forms of irregular verbs.
- Example:
- Past: She sang well.
- Past participle: She has sung well.
They are used in different tenses and must match the helping verbs correctly.
🔄 6. Verb Forms and Helping Verbs Go Together
In perfect and continuous tenses, verb forms must be paired with the correct helping verbs.
- Example:
- I have eaten (perfect tense)
- They are running (present continuous)
🔁 7. Some Verbs Have the Same Past and Past Participle Forms
Examples:
- Cut → cut → cut
- Put → put → put
- Read → read → read (pronounced differently in past)
❓ 8. Gerunds vs. Infinitives Can Be Confusing
Some verbs are followed by a gerund (–ing), some by an infinitive (to + verb), and some can take both with a change in meaning.
- I enjoy swimming. (correct)
- I want to swim. (correct)
- I stopped smoking. ≠ I stopped to smoke.
These small differences can change the meaning entirely.
Example sentences with verbs
📍 Present Tenses
- I read books every night.
- She plays the piano well.
- He is watching a movie now.
- They are playing football in the park.
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited the zoo many times.
- We have been waiting for the bus.
- He has been studying all morning.
📍 Past Tenses
5. Past Simple
- She cooked dinner last night.
- I watched a movie yesterday.
- I was sleeping when the phone rang.
- They were playing outside when it started to rain.
7. Past Perfect
- She had finished the test before the bell rang.
- I had lost my keys before I got home.
- He had been studying for hours before the exam.
- They had been working all day.
📍 Future Tenses
- I will call you later.
- She will travel next month.
- I will be sleeping at midnight.
- They will be playing by the time we arrive.
11. Future Perfect
- He will have finished the work by tomorrow.
- I will have left by 8 a.m.
- She will have been working here for 5 years next month.
- I will have been studying for 3 hours by noon.
✅ Conclusion: Mastering English Verb Forms Made Simple
Understanding the 12 verb forms in English—present, past, and future with their simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous aspects—is the key to building strong, clear, and correct sentences. Whether you’re writing, speaking, or simply trying to understand conversations better, knowing your verb tenses helps you express time, action, and intention effectively. From “I eat” to “I will have been eating,” every verb form tells a different part of the story.
Learning these verb forms may seem overwhelming at first, but with regular practice and real-life usage, it becomes second nature. Keep using the examples and exercises in this guide to strengthen your foundation.
💡 If you found this guide helpful, I’d love to hear from you! Share your thoughts in the comments below or connect with me on social media. For more tips, resources, and inspiration, visit my blog at mylanguageclasses.in. Follow on Instagram and subscribe on YouTube
📚 Continue Learning English
- Action Verbs – These verbs show what someone or something does.
